INTRODUCTION
METHODS
1. Study Design
2. Participants
3. Outcome Measures and Assessments
4. Statistical Analyses
RESULTS
1. Patient Disposition and Baseline Characteristics
Table 1.
| Characteristics |
Induction study A: biologic-naïve patients |
Induction study B: biologic-experienced patients |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n=6) | Filgotinib 100 mg (n=16) | Filgotinib 200 mg (n=15) | Placebo (n=14) | Filgotinib 100 mg (n=29) | Filgotinib 200 mg (n=29) | |
| Age (yr), mean ± SD | 48 ± 11 | 48 ± 13 | 52 ± 12 | 49 ± 16 | 39 ± 14 | 45 ± 17 |
| Female sex | 0 | 5 (31.3) | 8 (53.3) | 6 (42.9) | 6 (20.7) | 10 (34.5) |
| Body weight (kg), median (Q1–Q3) | 61.7 (60.0–64.4) | 60.3 (57.0–70.7) | 62.2 (52.0–64.2) | 58.0 (47.5–63.5) | 59.2 (56.6–67.5) | 56.7 (51.8–65.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2), median (Q1–Q3) | 20.6 (20.2–21.9) | 21.7 (20.3–23.6) | 21.8 (20.4–23.3) | 21.2 (19.7–23.2) | 20.6 (18.5–23.9) | 21.5 (20.3–22.9) |
| Smoking status | ||||||
| Former | 3 (50.0) | 9 (56.3) | 8 (53.3) | 7 (50.0) | 12 (41.4) | 10 (34.5) |
| Current | 0 | 2 (12.5) | 1 (6.7) | 0 | 4 (13.8) | 1 (3.4) |
| Never | 3 (50.0) | 5 (31.3) | 6 (40.0) | 7 (50.0) | 13 (44.8) | 18 (62.1) |
| Duration of UC (yr), mean ± SD | 11.8 ± 14.0 | 8.2 ± 9.5 | 7.2 ± 6.8 | 9.5 ± 8.3 | 9.4 ± 7.4 | 9.2 ± 7.7 |
| Total Mayo Clinic score, mean ± SD | 8.7 ± 2.1 | 8.0 ± 1.3 | 8.5 ± 1.1 | 8.9 ± 1.4 | 9.2 ± 1.0 | 8.5 ± 1.4 |
| MES of 3 | 5 (83.3) | 9 (56.3) | 10 (66.7) | 13 (92.9) | 23 (79.3) | 25 (86.2) |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L), mean ± SD | 6.2 ± 10.1 | 4.1 ± 6.7 | 4.1 ± 5.1 | 3.4 ± 4.3 | 6.9 ± 10.8 | 7.0 ± 11.4 |
| Fecal calprotectin (μg/g), mean ± SD | 6,670 ± 8,295 | 1,995 ± 1,448 | 3,556 ± 3,348 | 1,685 ± 1,332 | 1,399 ± 1,218 | 2,352 ± 2,484 |
| Concomitant use of systemic corticosteroidsa | 2 (33.3) | 4 (25.0) | 6 (40.0) | 4 (28.6) | 5 (17.2) | 6 (20.7) |
| Concomitant use of immunosuppressantsa,b | 2 (33.3) | 6 (37.5) | 4 (26.7) | 3 (21.4) | 7 (24.1) | 7 (24.1) |
| Concomitant use of systemic corticosteroids and immunosuppressants | 1 (16.7) | 2 (12.5) | 1 (6.7) | 2 (14.3) | 5 (17.2) | 5 (17.2) |
| Prednisone-equivalent dose (mg/day), median (Q1–Q3) | 5.0 (2.5–10.0) | 10.0 (10.0–20.0) | 5.0 (2.5–10.0) | 5.0 (5.0–10.0) | 7.5 (5.0–20.0) | 10.0 (5.0–15.0) |
| Concomitant use of 5-ASA | 5 (83.3) | 13 (81.3) | 12 (80.0) | 11 (78.6) | 26 (89.7) | 24 (82.8) |
| Number of prior biologic agents used | ||||||
| 0 | 6 (100.0) | 16 (100.0) | 15 (100.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 (50.0) | 13 (44.8) | 13 (44.8) |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 (28.6) | 15 (51.7) | 10 (34.5) |
| ≥3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (21.4) | 1 (3.4) | 6 (20.7) |
| Prior use of at least 1 TNF antagonist | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 (92.9) | 28 (96.6) | 29 (100.0) |
| Prior use of vedolizumab | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 (28.6) | 5 (17.2) | 3 (10.3) |
| Prior use of at least 1 TNF antagonist and vedolizumab | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (21.4) | 4 (13.8) | 3 (10.3) |
| Prior failure of at least 1 TNF antagonist | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 (92.9) | 25 (86.2) | 25 (86.2) |
| Prior failure of vedolizumab | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (7.1) | 2 (6.9) | 1 (3.4) |
2. Efficacy
1) Primary Endpoint in SELECTION
Fig. 1.
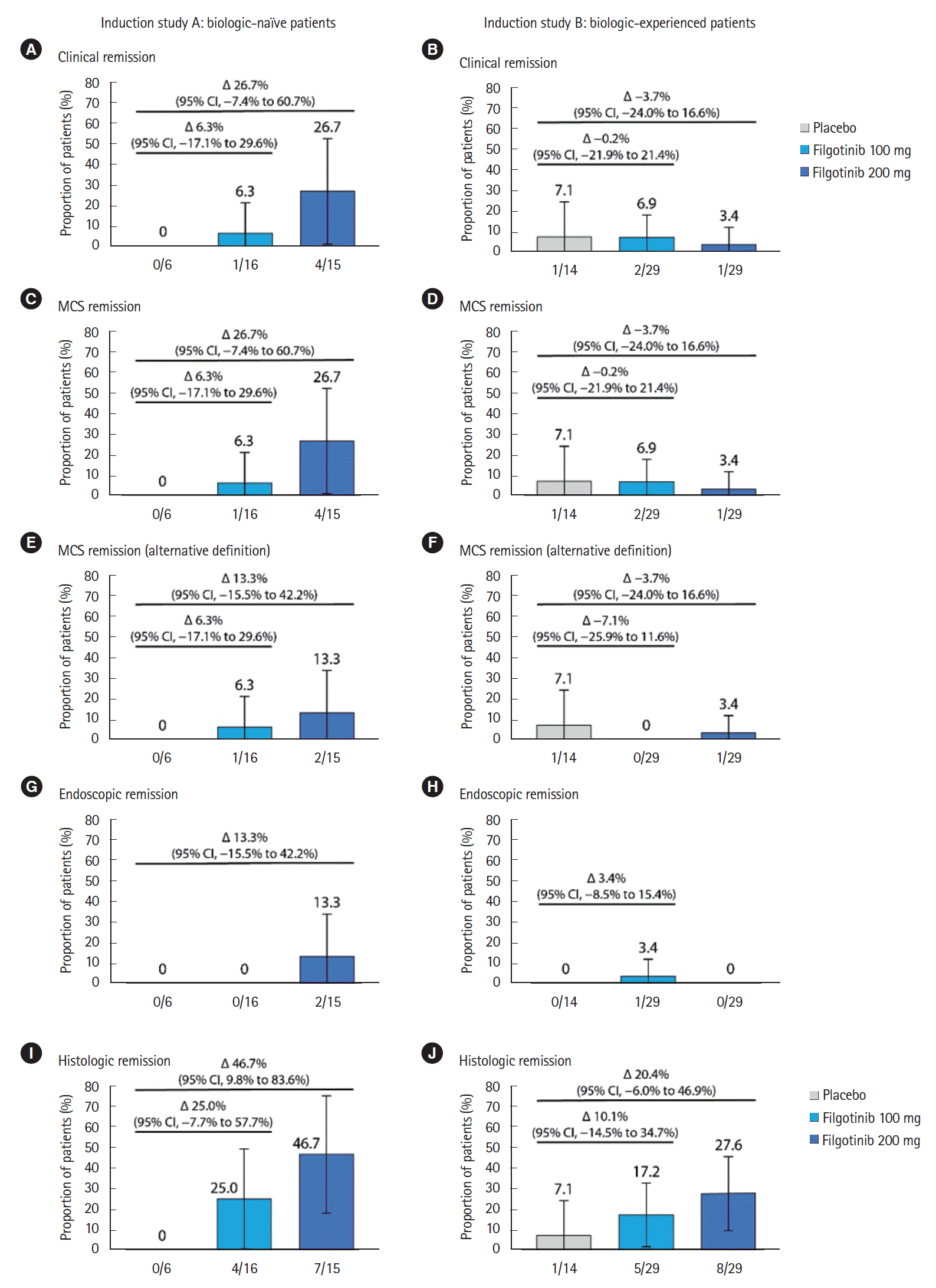
Fig. 2.
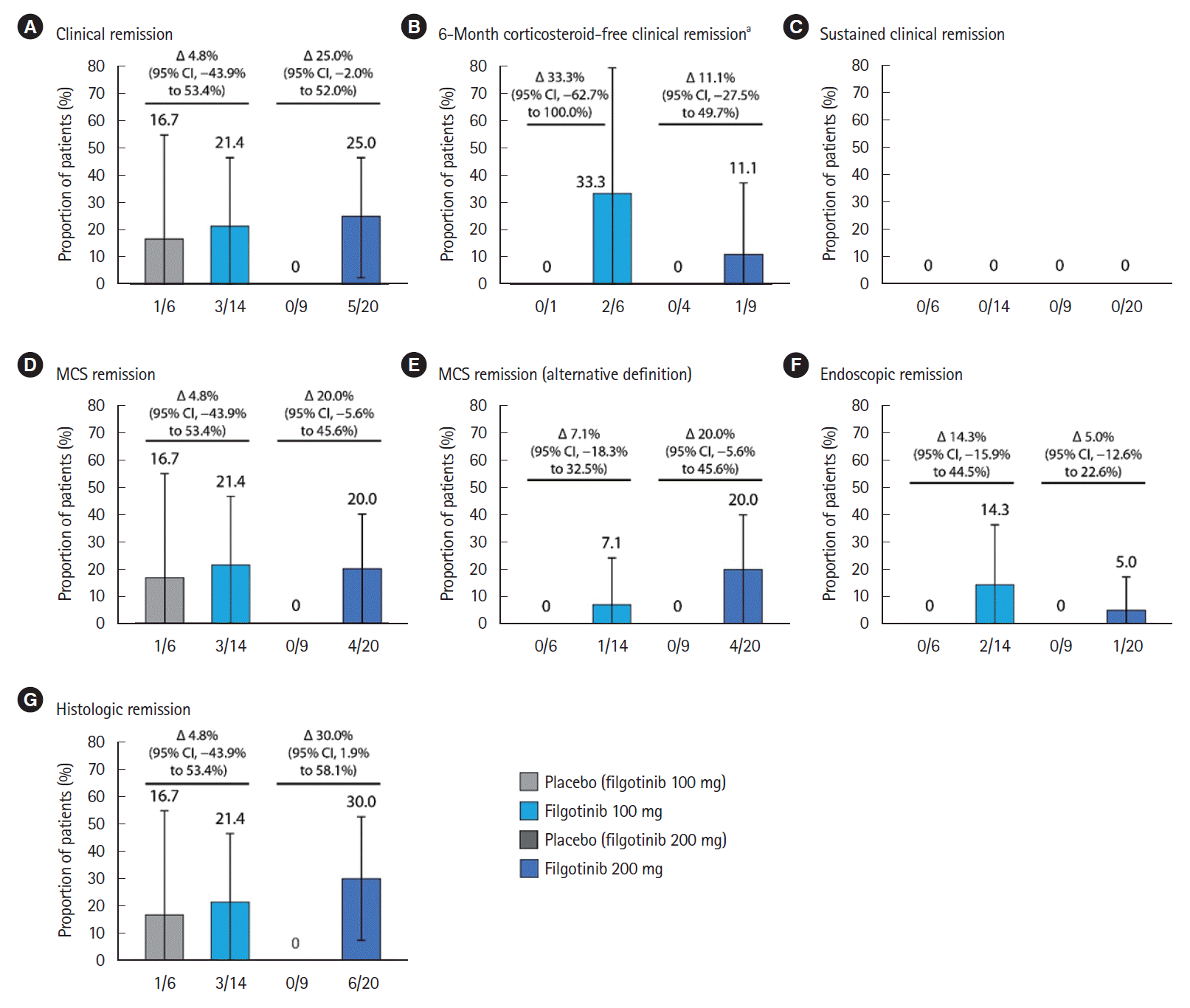
2) Key Secondary Endpoints in SELECTION
3) Exploratory Endpoints in SELECTION
4) Symptomatic Remission
3. Safety
Table 2.
| Outcomes | Placebo (n = 20) | Filgotinib 100 mg (n = 45) | Filgotinib 200 mg (n = 44) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment-emergent AEs, No. (%) | |||||
| AEs | 11 (55.0) | 23 (51.1) | 24 (54.5) | ||
| Serious AEs | 3 (15.0) | 2 (4.4) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| AEs leading to study drug discontinuation | 3 (15.0) | 1 (2.2) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| Deaths | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| AEs of interest, No. (%) | |||||
| Infections | 3 (15.0) | 7 (15.6) | 8 (18.2) | ||
| Serious infections | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Herpes zoster | 0 | 0 | 1 (2.3)a | ||
| Opportunistic infections | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Malignancies excluding non-melanoma skin cancers | 0 | 1 (2.2)b | 0 | ||
| Non-melanoma skin cancers | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Gastrointestinal perforation | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Venous thrombosis excluding pulmonary embolism | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Pulmonary embolism | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Arterial thrombosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Cerebrovascular events | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities, No. (%) | |||||
| Hematology | |||||
| Decreased hemoglobin | 1 (5.0) | 1 (2.2) | 1 (2.3) | ||
| Decreased WBC | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Decreased neutrophils | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Decreased lymphocytes | 0 | 2 (4.4) | 0 | ||
| Chemistry | |||||
| Increased AST | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Increased ALT | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Increased creatine kinase | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Decreased phosphorus | 0 | 0 | 2 (4.5) | ||
| Fasting HDL/LDL cholesterol value change from baseline at week 10, mean ± SD | |||||
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 10 ± 22 | 12 ± 23 | 18 ± 30 | ||
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 4 ± 17 | 15 ± 15 | 23 ± 18 | ||
| LDL:HDL ratio | 0.1 ± 0.4 | −0.2 ± 0.3 | −0.3 ± 0.4 | ||
Table 3.
| Outcomes | Placebo (n=5)a | Placebo (n=6)b | Filgotinib 100 mg (n=14)c | Placebo (n=9)d | Filgotinib 200 mg (n=20)e | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEs, No. (%) | |||||||
| AEs | 5 (100.0) | 4 (66.7) | 10 (71.4) | 7 (77.8) | 16 (80.0) | ||
| Serious AEs | 0 | 1 (16.7) | 1 (7.1) | 0 | 1 (5.0) | ||
| AEs leading to study drug discontinuation | 0 | 0 | 2 (14.3) | 0 | 0 | ||
| Deaths | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| AEs of interest, No. (%) | |||||||
| Infections | 4 (80.0) | 2 (33.3) | 6 (42.9) | 3 (33.3) | 10 (50.0) | ||
| Serious infections | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Herpes zoster | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (5.0)f | ||
| Opportunistic infections | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Malignancies excluding non-melanoma skin cancers | 0 | 0 | 1 (7.1)g | 0 | 0 | ||
| Non-melanoma skin cancers | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Gastrointestinal perforation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Venous thrombosis excluding pulmonary embolism | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Pulmonary embolism | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Arterial thrombosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Cerebrovascular events | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Grade 3–4 laboratory abnormalities, No. (%) | |||||||
| Hematology | |||||||
| Decreased hemoglobin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Decreased WBC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Decreased neutrophils | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Decreased lymphocytes | 0 | 1 (16.7) | 0 | 0 | 2 (10.0) | ||
| Chemistry | |||||||
| Increased AST | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Increased ALT | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Increased creatine kinase | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Decreased phosphorus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Fasting HDL/LDL cholesterol value change from baseline at week 58, mean ± SD | |||||||
| Number | 2 | 3 | 8 | 1 | 14 | ||
| LDL cholesterol, mg/dL | −12 ± 23 | 1 ± 41 | 16 ± 23 | 18 | 1 ± 31 | ||
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | −19 ± 26 | −11 ± 15 | 4 ± 8 | −14 | −8 ± 19 | ||
| LDL:HDL ratio | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | ||
a Patients who responded with placebo in the induction studies and continued to receive placebo in the maintenance study.
b Patients who responded with filgotinib 100 mg in the induction studies and were randomly assigned to placebo in the maintenance study.
c Patients who responded with filgotinib 100 mg in the induction studies and were randomly assigned to filgotinib 100 mg in the maintenance study.
d Patients who responded with filgotinib 200 mg in the induction studies and were randomly assigned to placebo in the maintenance study.
e Patients who responded with filgotinib 200 mg in the induction studies and were randomly assigned to filgotinib 200 mg in the maintenance study.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download