This article has been corrected. See "Erratum: Tables Correction. Development of NQ-E, Nutrition Quotient for Korean elderly: item selection and validation of factor structure" in Volume 51 on page 199.
Abstract
Purpose:
The purpose of this study was to develop a valid instrument for measuring the dietary quality and behaviors of Korean elderly.
Methods:
The development of the Nutrition Quotient for Elderly (NQ-E) was conducted in three steps: item generation, item reduction, and validation. The 41 items of the NQ-E checklist were derived from a systematic literature review, expert in-depth interviews, statistical analyses of the fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data, and national nutrition policies and recommendations. Pearson's correlation was used to determine the level of agreement between the questionnaires and nutrient intake level, and 24 items were selected for a nationwide survey. A total of 1,000 nationwide elderly subjects completed the checklist questionnaire. The construct validity of the NQ-E was assessed using confirmatory factor analysis, LISREL.
Results:
The nineteen checklist items were used as final items for NQ-E. Checklist items were composed of four-factors: food behavior (6 items), balance (4 items), diversity (6 items), and moderation (3 items). The standardized path coefficients were used as the weights of the items. The NQ-E and four-factor scores were calculated according to the obtained weights of the questionnaire items.
References
1. Ministry of Health and Welfare (KR); Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. A study on the living conditions and welfare needs of older Korean persons. Cheongju: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2014.
2. World Health Organization. Global action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs 2013–2020. Geneva: World Health Organization;2013.
3. Oh KW, Nam CM, Park JH, Yoon JY, Shim JS, Lee KH, Suh I. A case-control study on dietary quality and risk for coronary heart disease in Korean men. Korean J Nutr. 2003; 36(6):613–621.
4. Ko KP, Park SK, Yang JJ, Ma SH, Gwack J, Shin A, Kim YJ, Kang D, Chang SH, Shin HR, Yoo KY. Intake of soy products and other foods and gastric cancer risk: a prospective study. J Epidemiol. 2013; 23(5):337–343.

5. Park B, Shin A, Park SK, Ko KP, Ma SH, Lee EH, Gwack J, Jung EJ, Cho LY, Yang JJ, Yoo KY. Ecological study for refrigerator use, salt, vegetable, and fruit intakes, and gastric cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 2011; 22(11):1497–1502.

6. Kim HR. A study on the association of diet quality and risk of mortality and major chronic diseases from nationally representative longitudinal data. Health Soc Welf Rev. 2013; 33(3):5–30.
7. Kang MH, Lee JS, Kim HY, Kwon S, Choi YS, Chung HR, Kwak TK, Cho YH. Selecting items of a food behavior checklist for the development of nutrition quotient (NQ) for children. Korean J Nutr. 2012; 45(4):372–389.

8. Kim HY, Kwon S, Lee JS, Choi YS, Chung HR, Kwak TK, Park J, Kang MH. Development of a nutrition quotient (NQ) equation modeling for children and the evaluation of its construct validity. Korean J Nutr. 2012; 45(4):390–399.

9. Lee JS, Kang MH, Kwak TK, Chung HR, Kwon S, Kim HY, Hwang JY, Choi YS. Development of nutrition quotient for Korean preschoolers (NQ-P): item selection and validation of factor structure. J Nutr Health. 2016; 49(5):378–394.

10. Kim HY, Lee JS, Hwang JY, Kwon S, Chung HR, Kwak TK, Kang MH, Choi YS. Development of NQ-A, nutrition quotient for Korean adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior. J Nutr Health. 2017; 50(2):142–157.

11. Patterson RE, Haines PS, Popkin BM. Diet quality index: capturing a multidimensional behavior. J Am Diet Assoc. 1994; 94(1):57–64.

12. Haines PS, Siega-Riz AM, Popkin BM. The diet quality index revised: a measurement instrument for populations. J Am Diet Assoc. 1999; 99(6):697–704.
13. Kennedy ET, Ohls J, Carlson S, Fleming K. The healthy eating index: design and applications. J Am Diet Assoc. 1995; 95(10):1103–1108.
14. Guenther PM, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM, Reeve BB, Basiotis PP. Development and evaluation of the healthy eating index-2005: technical report. Alexandria (VA): US Department of Agriculture, Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion;2007.
15. McCullough ML, Feskanich D, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci EL, Rimm EB, Hu FB, Spiegelman D, Hunter DJ, Coditz GA, Willett WC. Diet quality and major chronic disease risk in men and women: moving toward improved dietary guidance. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002; 76:1261–1271.

16. US Department of Agriculture, Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion. Healthy Eating Index (HEI) [Internet]. Alexandria (VA): US Department of Agriculture, Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion;2016. [cited 2017 Dec 24]. Available from:. https://www.cnpp.usda.gov/healthyeatingindex.
17. Bailey RL, Miller PE, Mitchell DC, Hartman TJ, Lawrence FR, Sempos CT, Smiciklas-Wright H. Dietary screening tool identifies nutritional risk in older adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009; 90:177–183.

18. Vellas B, Villars H, Abellan G, Soto ME, Rolland Y, Guigoz Y, Morley JE, Chumlea W, Salva A, Rubenstein LZ, Garry P. Overview of the MNA®-its history and challenges. J Nutr Health Aging. 2006; 10(6):456–463.
19. Posner BM, Jette AM, Smith KW, Miller DR. Nutrition and health risks in the elderly: the nutrition screening initiative. Am J Public Health. 1993; 83(7):972–978.

20. Lee HO, Lee JS, Shin JW, Lee GJ. Nutrition assessment of older subjects in a health care center by MNA (Mini Nutritional Assessment). J Korean Diet Assoc. 2010; 16(2):122–132.
21. Park HK, Lim BK, Choi SH, Lee HR, Lee DS. Verification of the appropriateness when a shortened version of the Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) is applied for determining the malnutrition state of elderly patients. J Korean Soc Parenter Enter Nutr. 2009; 2(1):13–18.

22. Son SM, Park JK. The changes of dish consumption frequencies, dietary attitudes and health-nutrition risk for single living female elderly on food-aid program. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2005; 11(3):286–298.
23. Kim HY, Kim MH, Hong SG, Hwang SJ, Park MH. A study on the nutrient intake, health risk factors, blood health status in elderly Korean women living alone. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005; 10(2):216–223.
24. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2012: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-3). Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2013.
25. Ministry of Health and Welfare (KR). Dietary guidelines for Korean elderly. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2010.
26. Kim OS, Ryu HS. The study on blood lipid levels according to the food habits and food intake patterns in Korean elderly. Korean J Food Nutr. 2009; 22(3):421–429.
27. Pala V, Sieri S, Masala G, Palli D, Panico S, Vineis P, Sacerdote C, Mattiello A, Galasso R, Salvini S, Ceroti M, Berrino F, Fusconi E, Tumino R, Frasca G, Riboli E, Trichopoulou A, Baibas N, Krogh V. Associations between dietary pattern and lifestyle, anthropometry and other health indicators in the elderly participants of the EPIC-Italy cohort. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006; 16(3):186–201.

28. Heidemann C, Hoffmann K, Spranger J, Klipstein-Grobusch K, Möhlig M, Pfeiffer AF, Boeing H. A dietary pattern protective against type 2 diabetes in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC)-Potsdam study cohort. Diabetologia. 2005; 48(6):1126–1134.

29. Yang KM. A Study on nutritional intake status and health-related behaviors of the elderly people in Gyeongsan area. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2005; 34(7):1018–1027.
30. Kim JE, Shin S, Lee DW, Park JH, Hong EJ, Joung H. Association between compliance with dietary guidelines and Alzheimer's disease in Korean elderly. J Nutr Health. 2015; 48(3):221–227.

31. Kim MH. Characteristics of nutrient intake according to metabolic syndrome in Korean elderly: using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010. Korean J Food Nutr. 2013; 26(3):515–525.
32. Park YK, Lee YJ, Lee SS. The intake of food and nutrient by the elderly with chronic disease in the Seoul area. Korean J Nutr. 2012; 45(6):531–540.

33. Oh C, No JK, Kim HS. Dietary pattern classifications with nutrient intake and body composition changes in Korean elderly. Nutr Res Pract. 2014; 8(2):192–197.

34. Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM, Miller PE, Liese AD, Kahle LL, Park Y, Subar AF. Higher diet quality is associated with decreased risk of all-cause, cardiovascular disease, and cancer mortality among older adults. J Nutr. 2014; 144:881–889.

35. Amarantos E, Martinez A, Dwyer J. Nutrition and quality of life in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001; 56:Spec No 2:. 54–64.

36. Shatenstein B, Ferland G, Belleville S, Gray-Donald K, Kergoat MJ, Morais J, Gaudreau P, Payette H, Greenwood C. Diet quality and cognition among older adults from the NuAge study. Exp Gerontol. 2012; 47:353–360.

37. McNaughton SA, Ball K, Crawford D, Mishra GD. An index of diet and eating patterns is a valid measure of diet quality in an Australian population. J Nutr. 2008; 138(1):86–93.

38. van Lee L, Geelen A, Kiefte-de Jong JC, Witteman JC, Hofman A, Vonk N, Jankovic N, Hooft van Huysduynen EJ, de Vries JH, van't Veer P, Franco OH, Feskens EJ. Adherence to the Dutch dietary guidelines is inversely associated with 20-year mortality in a large prospective cohort study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2016; 70(2):262–268.

39. Guenther PM, Casavale KO, Reedy J, Kirkpatrick SI, Hiza HA, Kuczynski KJ, Kahle LL, Krebs-Smith SM. Update of the healthy eating index: HEI-2010. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2013; 113(4):569–580.

40. National Cancer Institute (US). Epidemiology and genomics research program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute;2017. [cited 2017 Dec 24]. Available from:. https://epi. grants.cancer.gov.
41. Han KH, Choi MS, Park JS. Nutritional risk and its related factors evaluated by the mini nutritional assessment for the elderly who are meal service participants. Korean J Nutr. 2004; 37(8):675–687.
42. Kim SH, Choi-Kwon S. Nutritional status among elderly Korean women and related factors. J Korean Biol Nurs Sci. 2012; 14(1):16–24.

43. Moon HK, Kong JE. Reliability of nutritional screening using DETERMINE checklist for elderly in Korean rural areas by season. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009; 14(3):340–353.
44. Lee JW, Kim KE, Kim KN, Hyun TS, Hyun WJ, Park YS. Evaluation of the validity of a simple screening test developed for identifying Korean elderly at risk of undernutrition. Korean J Nutr. 2000; 33(8):864–872.
Fig. 2.
Comparison of percentage of nutrient intake of the elderly from the pilot study to recommended nutrient intake (RNI) or adequate intake (AI) according to NQ-E score four-grade criterion. a, b: Means with different alphabets are significantly different by Duncan's multiple-range test (p < 0.05).
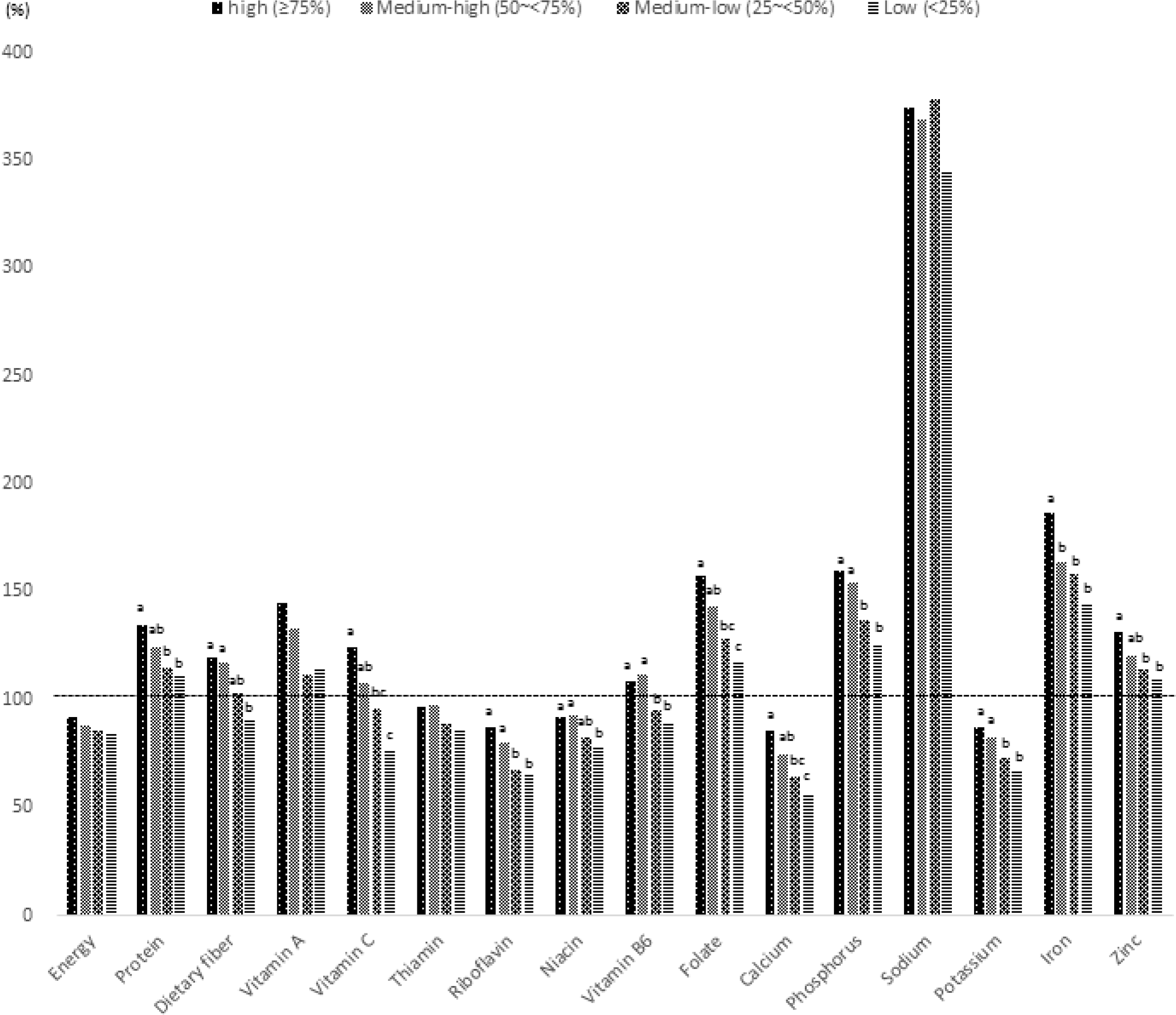
Table 1.
Checklist items selected for the pilot survey
Table 2.
Items selected for a nationwide survey checklist
Table 3.
Results of exploratory factor analysis of the 19 items selected by LISREL analysis (n = 1,000)
Table 4.
Weights and path coefficients of four-factor structure model
Table 5.
NQ-E score and group score calculation using response point of the checklist
Table 6.
6. NQ-E checklist
Table 7.
NQ-E score range by the four-grade criterion




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download