| Korean J Lab Med. 2010 Dec;30(6):647-653. Korean. Published online December 02, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.6.647 | |
| Copyright © 2010 The Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine | |
|
Dong-Jin Park, M.D.,1
Jae-Seok Kim, M.D., | |
|
1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. | |
|
2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. | |
| Received April 30, 2010; Revised July 15, 2010; Accepted October 14, 2010. | |
|
Abstract
| |
|
Background
Norovirus is a common cause of non-bacterial acute gastroenteritis worldwide, and norovirus infection shows symptoms such as vomiting and diarrhea in patients of all age groups. Mass outbreaks of norovirus infection have been recently reported in Korea. Herein, we investigated the epidemiological characteristics of acute norovirus gastroenteritis.
Methods
We analyzed 11,219 fecal specimens of patients with acute gastroenteritis symptoms from the 5 participating hospitals for 3 yr (March 2007-February 2010) to determine positive rates of detection using RIDASCREEN Norovirus ELISA (R-Biopharm AG, Germany) kit by year, prevalence season, sex, age, and region.
Results
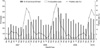
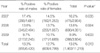
Norovirus infection was prevalent during autumn and winter, and 13.0% specimens were positive for the infection. The positive rates of norovirus detection were 16.2%, 13.8%, and 9.9% in 2007, 2008, and 2009, respectively, and they tended to decrease every year. In 2007 and 2008, the epidemicity of norovirus started from October, reached its peak in November, and lasted until January. However, in 2009, it started from December, reached its peak in January, and lasted until February. Most patients were 0-3 yr old and this patient group had the highest positive rate. There was no significant inter-regional difference among the subjects.
Conclusions
We performed epidemiological analysis of norovirus infection using ELISA assay. Reverse transcription-PCR indicated higher prevalence of norovirus infection as compared with that reported before 2007. Further studies are warranted to examine the changes observed in the epidemic period of 2009. |
|
Keywords: Norovirus; Epidemiology; RIDASCREEN norovirus ELISA |
|
|
Figures
|
|
|
Tables
|
|
|
|
|
References
|
| 1. | Ando T, Noel JS, Fankhauser RL. Genetic classification of "Norwalk-like viruses". J Infect Dis 2000;181 S2:S336–S348. |
| 2. | Tsugawa T, Numata-Kinoshita K, Honma S, Nakata S, Tatsumi M, Sakai Y, et al. Virological, serological, and clinical features of an outbreak of acute gastroenteritis due to recombinant genogroup II norovirus in an infant home. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:177–182. |
| 3. | Vinjé J, Altena SA, Koopmans MP. The incidence and genetic variability of small round-structured viruses in outbreaks of gastroenteritis in The Netherlands. J Infect Dis 1997;176:1374–1378. |
| 4. | Mladenova Z, Korsun N, Geonova T, Di Bartolo I, Fiore L, Ruggeri FM. Prevalence and molecular epidemiology of noroviruses detected in outbreak and sporadic cases of acute gastroenteritis in Bulgaria. J Med Virol 2008;80:2161–2168. |
| 5. | Mounts AW, Ando T, Koopmans M, Bresee JS, Noel J, Glass RI. Cold weather seasonality of gastroenteritis associated with Norwalk-like viruses. J Infect Dis 2000;181 S2:S284–S287. |
| 6. | Lysén M, Thorhagen M, Brytting M, Hjertqvist M, Andersson Y, Hedlund KO. Genetic diversity among food-borne and waterborne norovirus strains causing outbreaks in Sweden. J Clin Microbiol 2009;47:2411–2418. |
| 7. | Hansman GS, Natori K, Shirato-Horikoshi H, Ogawa S, Oka T, Katayama K, et al. Genetic and antigenic diversity among noroviruses. J Gen Virol 2006;87:909–919. |
| 8. | Kageyama T, Shinohara M, Uchida K, Fukushi S, Hoshino FB, Kojima S, et al. Coexistence of multiple genotypes, including newly identified genotypes, in outbreaks of gastroenteritis due to norovirus in Japan. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:2988–2995. |
| 9. | Ambert-Balay K, Bon F, Le Guyader F, Pothier P, Kohli E. Characterization of new recombinant noroviruses. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:5179–5186. |
| 10. | Pang XL, Preiksaitis JK, Lee B. Multiplex real time RT-PCR for the detection and quantitation of norovirus genogroups I and II in patients with acute gastroenteritis. J Clin Virol 2005;33:168–171. |
| 11. | Phan TG, Kuroiwa T, Kaneshi K, Ueda Y, Nakaya S, Nishimura S, et al. Changing distribution of norovirus genotypes and genetic analysis of recombinant GIIb among infants and children with diarrhea in Japan. J Med Virol 2006;78:971–978. |
| 12. | de Bruin E, Duizer E, Vennema H, Koopmans MP. Diagnosis of norovirus outbreaks by commercial ELISA or RT-PCR. J Virol Methods 2006;137:259–264. |
| 13. | Widdowson MA, Sulka A, Bulens SN, Beard RS, Chaves SS, Hammond R, et al. Norovirus and foodborne disease, United States, 1991-2000. Emerg Infect Dis 2005;11:95–102. |
| 14. | Svraka S, Duizer E, Vennema H, de Bruin E, van der Veer B, Dorresteijn B, et al. Etiological role of viruses in outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis in The Netherlands from 1994 through 2005. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:1389–1394. |
| 15. | Kim SH, Cheon DS, Kim JH, Lee DH, Jheong WH, Heo YJ, et al. Outbreaks of gastroenteritis that occurred during school excursions in Korea were associated with several waterborne strains of norovirus. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:4836–4839. |
| 16. | Division of Epidemic Intelligence Service, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Annual Report on the Epidemiological Investigation of Infectious Diseases. 2006. Epidemic investigation of group diarrhea in the metropolitan area spread by a large meal service provider; pp. 153-159. |
| 17. | Victoria M, Carvalho-Costa FA, Heinemann MB, Leite JP, Miagostovich M. Prevalence and molecular epidemiology of noroviruses in hospitalized children with acute gastroenteritis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2004. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2007;26:602–606. |
| 18. | Chen SY, Chang YC, Lee YS, Chao HC, Tsao KC, Lin TY, et al. Molecular epidemiology and clinical manifestations of viral gastroenteritis in hospitalized pediatric patients in Northern Taiwan. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:2054–2057. |
| 19. | Clark B, McKendrick M. A review of viral gastroenteritis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2004;17:461–469. |
| 20. | Jee YM. Epidemiology of norovirus infection in Korea. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis 2007;14:17–24. |
| 21. | Yi J, Lee JK, Chung EH, Cho DH, Kim EC. An outbreak of astrovirus infection of newborns with hemorrhagic diarrhea in a neonatal unit. Korean J Clin Microbiol 2004;7:55–58. |
| 22. | Ma SH. Acute infectious diarrhea in pediatric patients. Korean J Pediatr 2005;48:235–250. |
| 23. | Thornton AC, Jennings-Conklin KS, McCormick MI. Noroviruses: agents in outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis. Disaster Manag Response 2004;2:4–9. |
| 24. | Chung JY. Acute viral gastroenteritis: recent trends and updates. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2007;10 S1:53–57. |
| 25. | Hwang PJ, Kwak JH, Lee TJ, Jeong SJ. Clinical features of acute noroviral gastroenteritis in children: comparison with rotaviral gastroenteritis. Korean J Pediatr 2009;52:453–457. |
| 26. | Division of Epidemic Intelligence Service, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Annual report of epidemiologic investigation on infectious disease. 2003. Epidemic investigation on Norwalk virus that caused food poisoning in Seoul; pp. 103-113. |
| 27. | Lee JI, Park SH, Park SH, Kim MS, Oh YH, Yu IS, et al. Surveillance of acute gastroenteritis in Seoul, Korea, during May 2004 and June 2007. J Bacteriol Virol 2009;39:363–371. |
| 28. | Chung JY, Han TH, Park SH, Kim SW, Hwang ES. Detection of GII-4/2006b variant and recombinant noroviruses in children with acute gastroenteritis, South Korea. J Med Virol 2010;82:146–152. |
| 29. | Monitoring status of national virus that caused acute diarrhea disease in testing laboratories, 2005-2008. Division of Hepatitis-Poliovirus, Infectious Disease Center, National Institute of Health, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
http://www.cdc.go.kr.
|
| 30. | Division of Hepatitis-Poliovirus, Infectious Disease Center, National Institute of Health, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Public Health Weekly Report, KCDC. 2. 2009. Laboratory prevalence of norovirus infections in Korea and sensitive monitoring system for norovirus related outbreak combined automated diagnostic process and web-based reporting; pp. 229-232. |
| 31. | Monitoring information on pathogens that cause acute infectious symptom, 2009. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
|
| 32. | Okitsu-Negishi S, Okame M, Shimizu Y, Phan TG, Tomaru T, Kamijo S, et al. Detection of norovirus antigens from recombinant virus-like particles and stool samples by a commercial norovirus enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:3784–3786. |
| 33. | Castriciano S, Luinstra K, Petrich A, Smieja M, Lee C, Jang D, et al. Comparison of the RIDASCREEN norovirus enzyme immunoassay to IDEIA NLV GI/GII by testing stools also assayed by RT-PCR and electron microscopy. J Virol Methods 2007;141:216–219. |
| 34. | Subekti D, Lesmana M, Tjaniadi P, Safari N, Frazier E, Simanjuntak C, et al. Incidence of Norwalk-like viruses, rotavirus and adenovirus infection in patients with acute gastroenteritis in Jakarta, Indonesia. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2002;33:27–33. |
| 35. | Colomba C, De Grazia S, Giammanco GM, Saporito L, Scarlata F, Titone L, et al. Viral gastroenteritis in children hospitalised in Sicily, Italy. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2006;25:570–575. |
| 36. | Guo L, Song J, Xu X, Ren L, Li J, Zhou H, et al. Genetic analysis of norovirus in children affected with acute gastroenteritis in Beijing, 2004-2007. J Clin Virol 2009;44:94–98. |
| 37. | Sakai Y, Nakata S, Honma S, Tatsumi M, Numata-Kinoshita K, Chiba S. Clinical severity of Norwalk virus and Sapporo virus gastroenteritis in children in Hokkaido, Japan. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2001;20:849–853. |
| 38. | Nguyen TA, Yagyu F, Okame M, Phan TG, Trinh QD, Yan H, et al. Diversity of viruses associated with acute gastroenteritis in children hospitalized with diarrhea in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. J Med Virol 2007;79:582–590. |




 ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print