Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Study population
2. Treatment and assessment
3. Statistical analysis
Results
1. Patient characteristics
Table 1.
| Variable | Total (n=246) | Short-term treatment groupa) (n=177) | Long-term treatment groupb) (n=69) | p-valuec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 61 (54-68) | 62 (53-68) | 61 (55-68) | 0.810d) |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 209 (85.0) | 152 (85.9) | 57 (82.6) | 0.520 |
| Female | 37 (15.0) | 25 (14.1) | 12 (17.4) | |
| Etiology of HCC | ||||
| Hepatitis B | 166 (67.5) | 115 (65.0) | 51 (73.9) | 0.130e) |
| Hepatitis C | 18 (7.3) | 17 (9.6) | 1 (1.5) | |
| Alcohol | 31 (12.6) | 22 (12.4) | 9 (13.0) | |
| Others | 31 (12.6) | 23 (13.0) | 8 (11.6) | |
| Cirrhosis | ||||
| Yes | 207 (84.1) | 151 (85.3) | 56 (81.2) | 0.423 |
| No | 39 (15.9) | 26 (14.7) | 13 (18.8) | |
| AFP (ng/mL) | ||||
| < 400 | 150 (61.0) | 103 (58.2) | 47 (68.1) | 0.152 |
| ≥ 400 | 96 (39.0) | 74 (41.8) | 22 (31.9) | |
| ECOG performance status | ||||
| 0 | 102 (41.5) | 58 (32.8) | 44 (63.8) | < 0.001e) |
| 1 | 139 (56.5) | 115 (65.0) | 24 (34.8) | |
| 2 | 5 (2.0) | 4 (2.3) | 1 (1.5) | |
| Portal vein tumor thrombosis | ||||
| No | 144 (58.5) | 95 (53.7) | 49 (71.0) | 0.013 |
| Yes | 102 (41.5) | 82 (46.3) | 20 (29.0) | |
| Extrahepatic spread | ||||
| No | 91 (37.0) | 62 (35.0) | 29 (42.0) | 0.467 |
| Yes | 155 (63.0) | 115 (65.0) | 40 (58.0) | |
| Prior local treatment | ||||
| No | 81 (32.9) | 63 (35.6) | 18 (26.1) | 0.154 |
| Yes | 165 (67.1) | 114 (64.4) | 51 (73.9) | |
| Child-Pugh classification | ||||
| A5 | 128 (52.0) | 82 (46.3) | 46 (66.7) | 0.006e) |
| A6 | 62 (25.2) | 47 (26.6) | 15 (21.7) | |
| B7 | 36 (14.6) | 33 (18.6) | 3 (4.4) | |
| B8-9 | 20 (8.1) | 15 (8.5) | 5 (7.3) | |
| ALBI grade | ||||
| 1 | 126 (51.2) | 79 (44.6) | 47 (68.1) | 0.002e) |
| 2 | 115 (46.7) | 95 (53.7) | 20 (29.0) | |
| 3 | 5 (2.0) | 3 (1.7) | 2 (2.9) | |
| BCLC stage | ||||
| B | 41 (16.7) | 26 (14.7) | 15 (21.7) | 0.183 |
| C | 502 (83.3) | 151 (85.3) | 54 (78.3) | |
| Intrahepatic tumor burden (%) | ||||
| < 25 | 134 (54.5) | 83 (46.9) | 51(73.9) | 0.002e) |
| 25-50 | 57 (23.2) | 47 (26.6) | 10 (14.5) | |
| 50-75 | 43 (17.5) | 36 (20.3) | 7 (10.1) | |
| > 75 | 12 (4.9) | 11 (6.2) | 1 (1.5) | |
| PIVKA-II (mAU/mL) | ||||
| < 200 | 120 (48.8) | 78 (44.1) | 42 (60.9) | 0.018 |
| ≥ 200 | 126 (51.2) | 99 (55.9) | 27 (39.1) | |
| NLR (n=244) | 2.78 (1.81-4.27) | 2.87 (1.98-4.43) | 2.12 (1.47-3.93) | 0.061d) |
| PLR (n=244) | 0.13 (0.09-0.20) | 0.14 (0.10-0.20) | 0.10 (0.08-0.17) | 0.323d) |
| CRP (mg/dL) (n=198) | 0.52 (0.16-1.66) | 0.81 (0.18-2.00) | 0.25 (0.09-0.99) | 0.172d) |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%). AFP, α-fetoprotein; ALBI, albumin-bilirubin grade; BCLC, Barcelona Clinical Liver Cancer stage; CRP, C-reactive protein; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; PIVKA-II, protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II; PLR, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio.
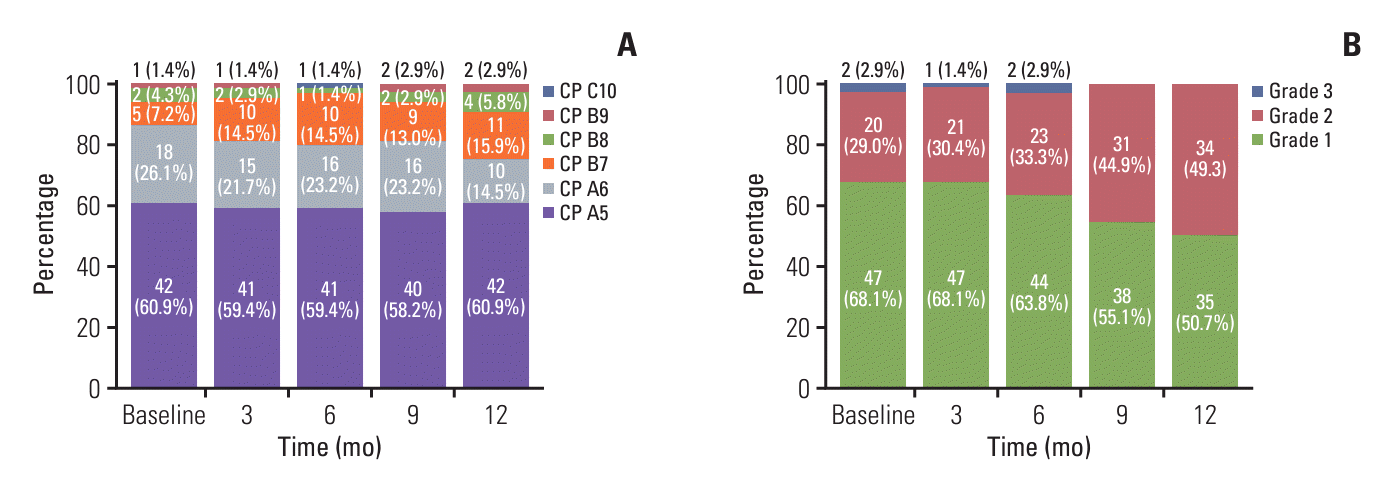
2. Characteristics of the long-term treatment group
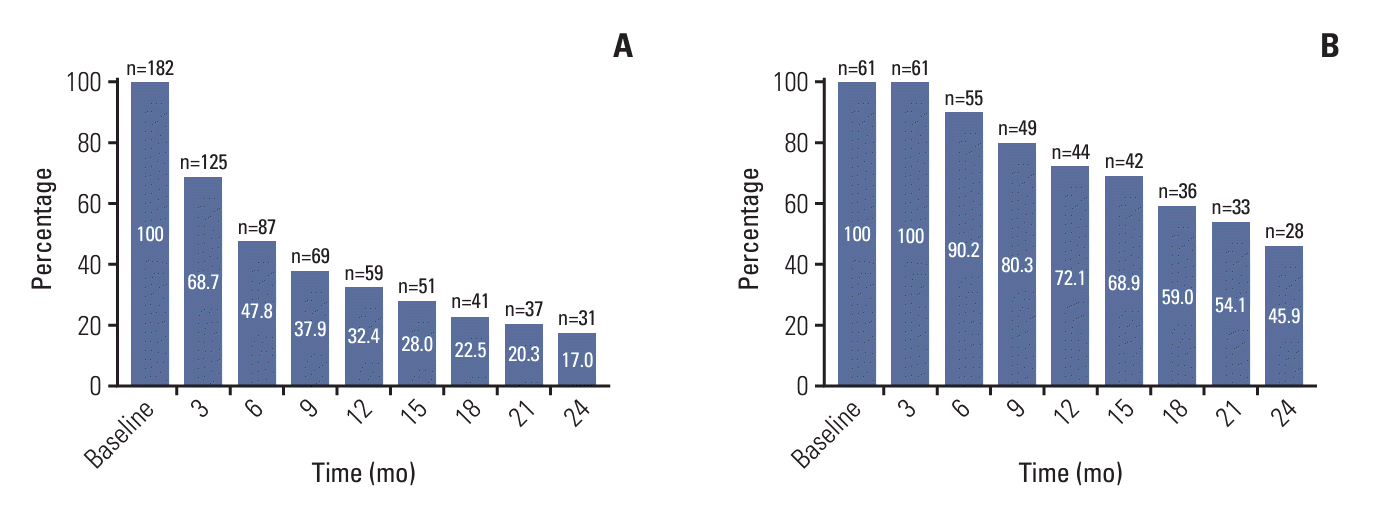
3. Survival outcomes
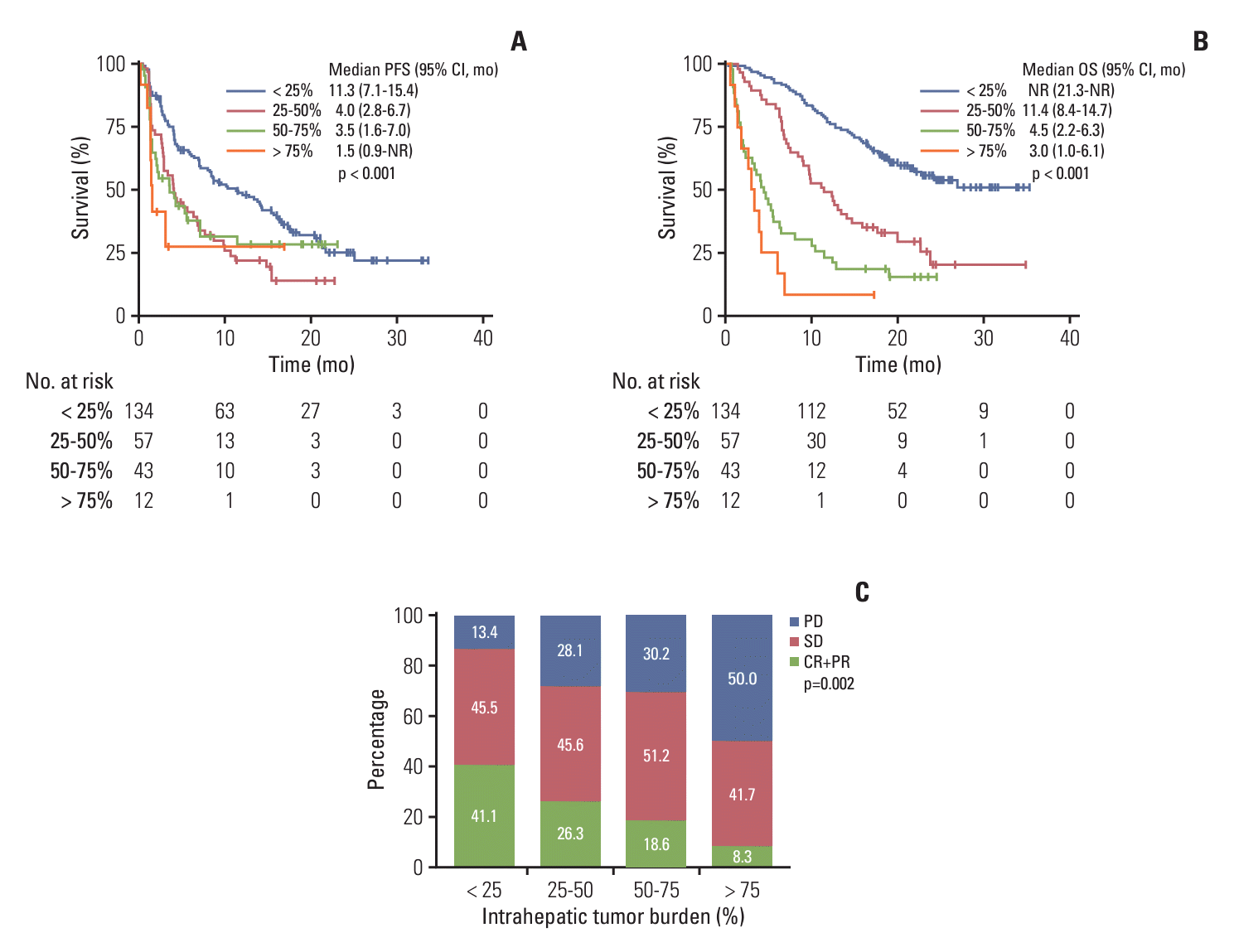
4. Survival outcomes according to the intrahepatic tumor burden
Fig. 1.
5. Safety of long-term treatment with Ate/Bev
Table 2.
| Short-term treatment groupa) (n=177) | Long-term treatment groupb) (n=69) | p-valuec) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atezolizumab-related AEs (any grade) | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 6 (3.4) | 3 (4.3) | 0.713 |
| Adrenal insufficiency | 4 (2.3) | 3 (4.3) | 0.404d) |
| Thyroid toxicity | 18 (10.2) | 22 (31.9) | < 0.001 |
| Dermatologic toxicity | 26 (14.7) | 20 (29.0) | 0.010 |
| Colitis | 14 (7.9) | 10 (14.5) | 0.118 |
| Fatigue | 45 (25.4) | 13 (18.8) | 0.275 |
| Liver toxicity | 60 (33.9) | 30 (43.5) | 0.161 |
| Pituitary toxicity | 2 (1.1) | 4 (5.8) | 0.054d) |
| Arthritis | 3 (1.7) | 5 (7.3) | 0.041d) |
| Pneumonitis | 1 (0.6) | 1 (1.5) | 0.483d) |
| Bevacizumab-related AEs (any grade) | |||
| Hypertension | 40 (22.6) | 31 (44.9) | 0.001 |
| Proteinuria | 68 (38.4) | 48 (69.6) | < 0.001 |
| Palmo-plantar erythrodysesthesia | 1 (0.6) | 0 | > 0.99d) |
| Bleeding | 14 (7.9) | 10 (14.5) | 0.118 |
| Thrombosis | 2 (1.1) | 0 | > 0.99d) |
| AEs leading to treatment discontinuation | |||
| Atezolizumab | 0 | 0 | |
| Bevacizumab | 15 (8.5) | 19 (27.5) | < 0.001 |
| Grade 5 Aese) | 7 (4.0) | 1 (1.5) | 0.448d) |
e) Grade 5 adverse events in the short-term group included gastrointestinal hemorrhage (in 3 patients), multi-organ dysfunction syndrome, intracranial hemorrhage, duodenal ulcer perforation, and mesenteric vein thrombosis (in 1 patient each); grade 5 events in the long-term treatment group included gastrointestinal hemorrhage (in 1 patient).




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download