Abstract
Notes
FUNDING INFORMATION
This study is funded by the National Key Research&Development Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFC2004205).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Xin W. Methodology: Hill AM, Xu D, Xin W, Dou Z. Formal analysis: Xin W, Jacques A, Umbella J. Funding acquisition: Hill AM, Xin W, Dou Z. Project administration: Hill AM, Xu D, Xin W, Dou Z. Visualization: Hill AM, Xu D, Xin W, Dou Z. Writing – original draft: Xin W. Writing – review and editing: Hill AM, Xu D, Dou Z. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table S3.
Supplementary Table S4.
Supplementary Table S5.
Supplementary Table S6.
Supplementary Fig. S2.
Supplementary Fig. S3.
Supplementary Fig. S4.
Supplementary Fig. S5.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1.
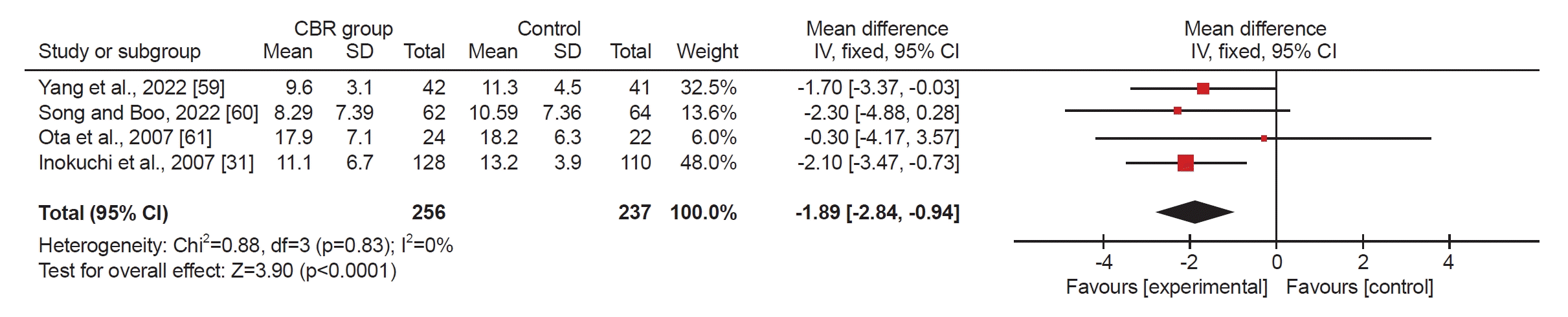
Fig. 2.
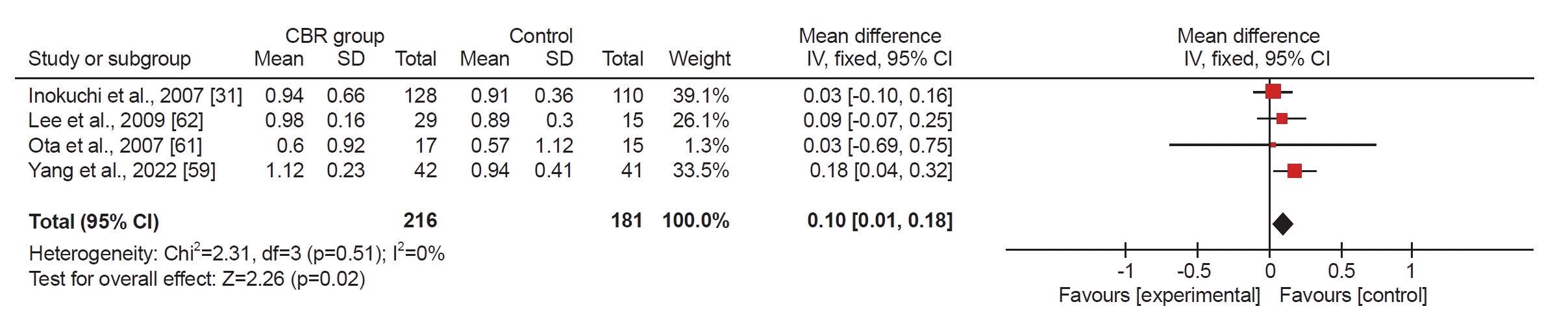
Fig. 3.
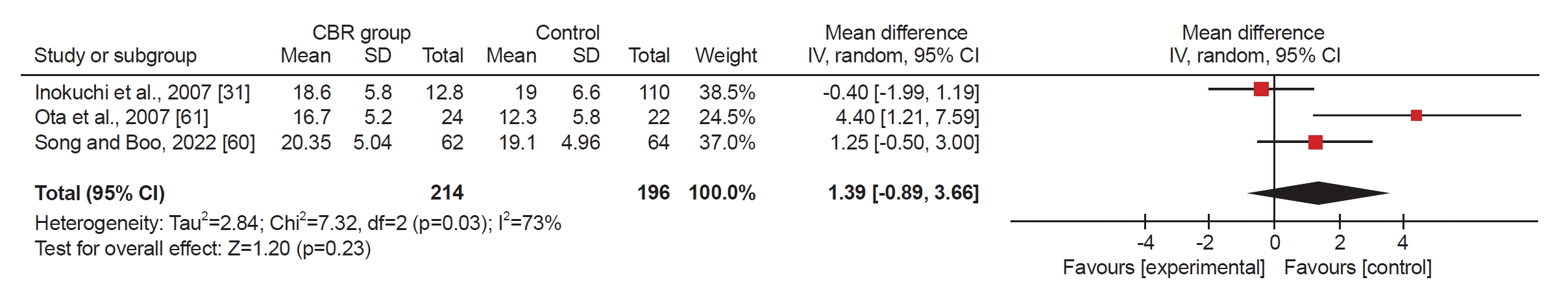
Fig. 4.
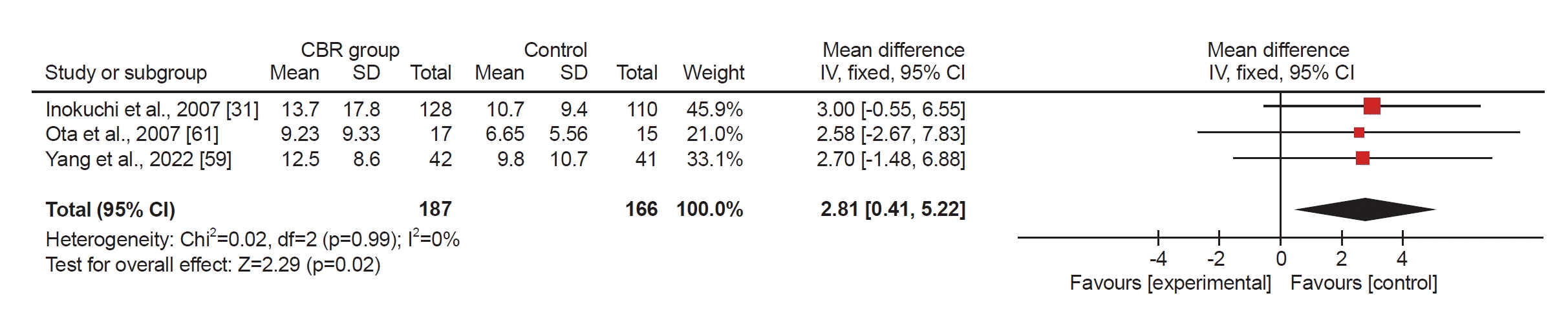
Fig. 5.
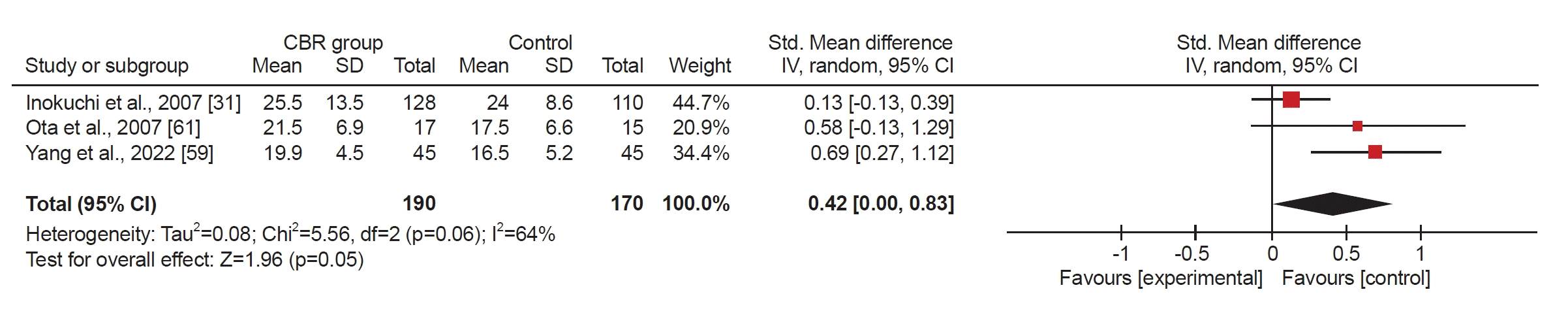
Fig. 6.
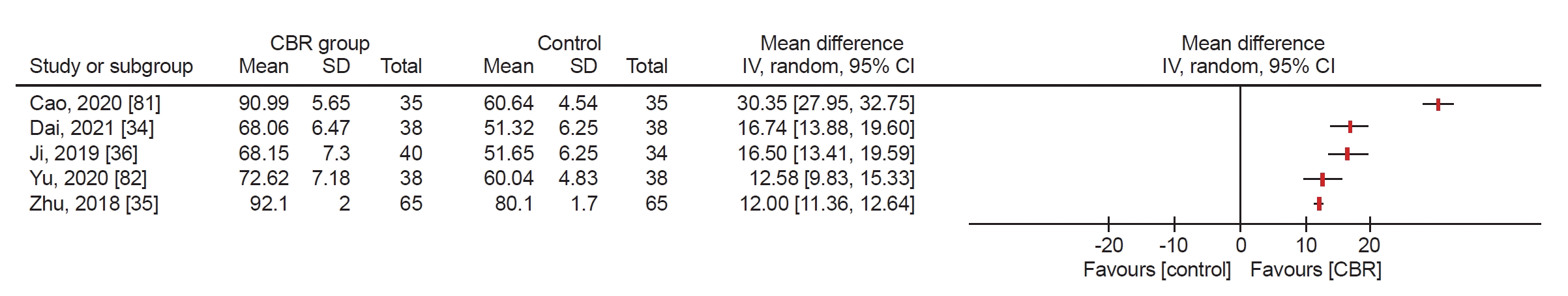
Fig. 7.
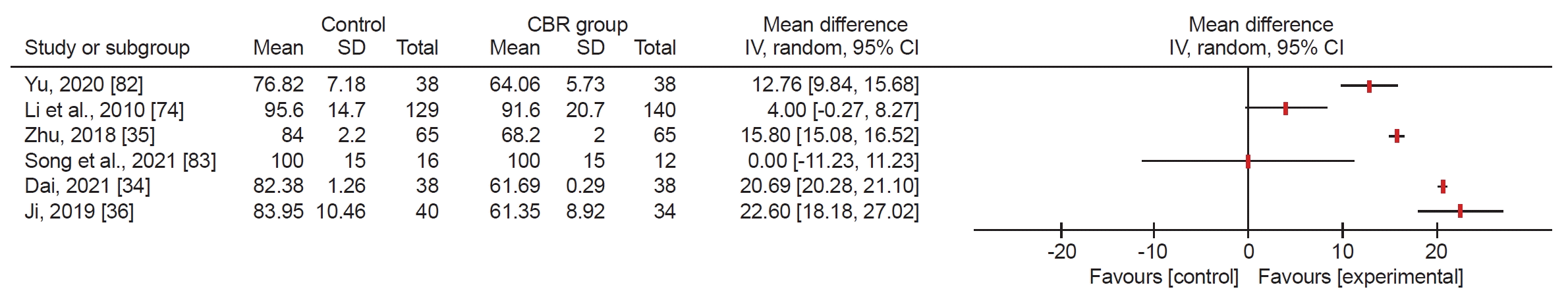
Fig. 8.
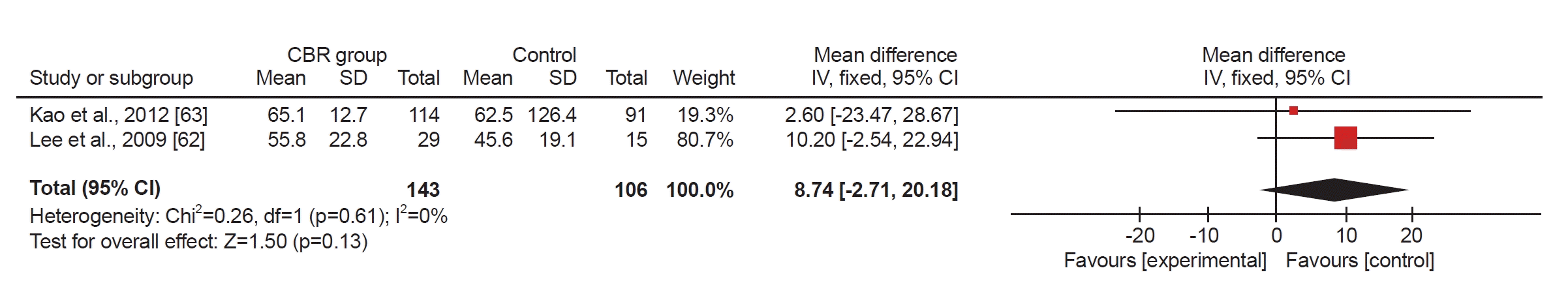
Fig. 9.
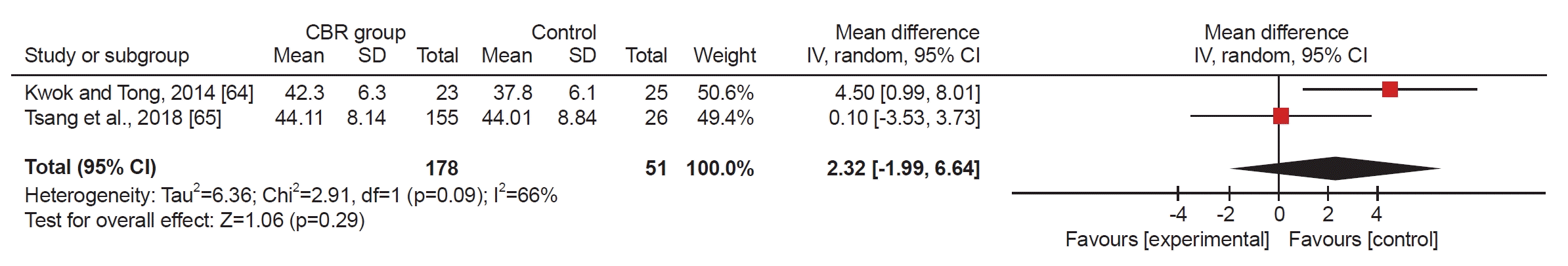
Table 1.
| Reference/country | Design | Participants | Primary/secondary outcomes (how measured) | Intervention group | Control group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cao [81]/China | Quasi-exp | Stroke survivors (n=70, CBR=35, control=35) | Physical fitness (FMA) | Education | Usual care |
| Exercisea) | |||||
| Cui and Zhang [80]/China | RCT | COPD patients (n=150, CBR=75, control=75) | Physical fitness (6MWT) | Education | Usual care |
| Standardized drug therapy | |||||
| Lung rehabilitation training | |||||
| Exercisea) | |||||
| Dai [34]/China | RCT | Stroke survivors (n=76, CBR=38, control=38) | Physical fitness (FMA)/ADL (BI) | Education | Usual care |
| Exercise | |||||
| Counsellinga) | |||||
| Dun et al. [76]/China | RCT | Adults≥65 pre-frailty (n=43, CBR=21, control=22) | Physical fitness (2.4-meter Up and Go, 6 min walk distance) | Exercise: 15 min/3×/wk, once every other day/3 mo (stretching exercise and strength exercise) | Exercise without supervision |
| Gong et al. [68]/China | RCT | Hypertensive patients (n=450, CBR=232, control=218) | Physical fitness (self report physical activity) | Education, counselling, group exercise: 2×wk/45–60 m/6 mo | Usual care |
| Harel-Katz et al. [67]/Israel | RCT | Stroke survivors (n=39, CBR=20, control=19) | Physical fitness (FIM) | Occupational therapy-based group intervention: 2.5 h/once weekly/12 wk | Usual care |
| Hasegawa et al. [66]/Japan | Quasi-exp | High risk elderly individuals with motor function decline (n=193, CBR=68, control=125) | Physical fitness (WOMAC and VAS) | Exercise: 2 h/per week/12 wk (relaxation of general joints and muscles, strength training, and stretching) | Only observation |
| Inokuchi et al. [31]/Japan | Quasi-exp | ≥5 or more risk factors for fall (n=238, CBR=144, control=124) | Physical fitness (TUG, 9FRT), 5MWT, leg standing test (LST) | Exercise: 2 h/per week/17 wk (stretching and strengthening the hip flexors, hip extensors, hip abductors and quadriceps muscles, balance retraining and cool-down) | Usual care |
| Ji [36]/China | RCT | Stroke survivors (n=74, CBR=35, control=35) | Physical fitness (FMA)/ADL (BI) | Education | Usual care |
| Exercisea) | |||||
| Kamada et al. [69]/Japan | RCT | Adults 40 to 79 years old, (n=3,337, CBR=2,518, control=819) | Physical fitness (regular physical activity) | Exercise: for 3 yr | |
| Kao et al. [63]/China | Quasi-exp | Older people who suffered from knee pain, (n=205, CBR=114, control=91) | Physical fitness (WOMAC) | Exercise: 20 m/4 per week (stretching and strengthening) | Usual care |
| Education: 20 m/4 per week | |||||
| Discussion: 40 m/4 per week | |||||
| Kwok and Tong [64]/China | Quasi-exp | Participants with moderate or severe level of impairment (n=50, CBR=2518, HBR=819) | Physical fitness (Elderly Mobility Scale [EMS], Berg Balance Scale [BBS]/quality of life SF-12) | Exercise: 60 m 1–2 sessions/w/6 mo (including flexibility, strength, balance, and aerobic exercise with pain management) | Home-based rehabilitation |
| Lee et al. [62]/Korea | RCT | Older people with osteoarthritis of the knee, (n=44, CBR=29, control=15) | Physical fitness (WOMAC/6MWT)/HRQoL (SF-36) | Exercise: 1 h, 2×/per week/8 wk | Waiting list control |
| (Tai Chi Qigong) | |||||
| Lee et al. [78]/Korea | RCT | Adults≥60, (n=80, CBR=40, control=40) | Physical fitness (angle of ROM) | Resistance program: 2 h, 3×/per week/12 wk (resistance program using an elastic band) | Usual care |
| Li et al. [74]/China | RCT | Olde people reside within 15 walking distance from the hospital (n=269,CBR=129, control=140) | Physical fitness (fried frailty criteria [FFC]/ADL [BI]) | 6-month medication adjustment, exercise instructiona), nutritional support, physical rehabilitation, social worker consultation and specialty referrals | Screening evaluation |
| Liang et al. [77]/China | RCT | Currently receiving Taiwan National Health Insurance services (n=733, CBR=382, control=351) | Physical fitness (frailty score, handgrip strength, gait speed and physical activity) | Exercise: 45 m/12 mo (strength, balance, and flexibility) | Health education lessons |
| Education: 15 m/12 mo | |||||
| Ota et al. [61]/Japan | RCT | Certified for long term care need at the levels of requiring support (n=46,CBR=24, control=22) | Physical fitness (hand grip strength, lower limb strength, one legged standing, functional reach, TUG, timed 10MWT) | Exercise: 2×wk/12 wka) (machine training with light resistance) | Usual care |
| Ru et al. [73]/China | Quasi-exp | Stroke survivors, (n=1,008,CBR=520, control=488) | Physical fitness (FMA)/social functional activities (BI) | Group training: 2×wk/1 h/2 yr (technique treatment) | Usual care |
| Song et al. [83]/China | RCT | (DEMMI score 39–67) and had gait speed of ≤1 m/s (n=28, CBR=16, control=12) | Mobility (DEMMI), ADL (BI), physical function (SPPB) | Physical training: 2.5 h group for 10 wk (balance, stretching, pelvic floor exercises, aerobic exercises) | Placebo treatments |
| Education: 2.5 h for 10 wk | |||||
| Song and Boo [60]/Korea | Quasi-exp | Adults≥65, pre-frail, candidates for home visiting nursing services (n=126, CBR=62, control=64) | Physical fitness (TUG, measure of frailty, hand grip strength) | Exercise, cognitive training, and education for nutrition and disease management | Usual care |
| Exercise: two 40 m/1×wk/12 wk (stretching, resistance exercises with elastic TheraBands, and aerobic movements | |||||
| Sun et al. [72]/China | Quasi-exp | Adults 65 years and over (n=122, CBR=62, control=60) | Physical fitness (total fitness score), frailty (Kihon checklist) | Exercise and music: 1×wk/120 m/12 wk (warm-up, followed by a main body movement, and ended with a relaxation exercise, with a 10-min break between each part) | Usual care |
| Tong et al. [79]/China | RCT | COPD patients (n=252, CBR=127, control=125) | Physical fitness (6 min walk distance) | Education | Standardized drug therapy |
| Standardized drug therapy | |||||
| Exercise training (4×wk/30 m/12 wk) | |||||
| Tsang et al. [65]/China | Retrospective study | Pneumoconiosis patients (n=181, community-based rehabilitation program=155, home-based rehabilitation program=26) | Physical fitness (6 min walk distance)/quality of life SF-12 | Exercisea) | Home-based rehabilitation |
| Health education, teaching energy conservation techniques and panic control skills | |||||
| Wang et al. [71]/China | RCT | KOA (n=189, CBR=103, control=86) | Physical fitness (five time sit to stand test/WOMAC and TUG) | Exercise: 30–40 min/3 days/per week/2 wk | Exercise program guidance without any exercise adherence interventions |
| Yang et al. [59]/China | Quasi-exp | Adults≥65 living in the community (n=90, CBR=45, control=45) | Physical fitness (SPPB, one leg stance, forward reach, TUG, 10MWT) | Exercise: 90 min/2×/wk/3 mo (a stick [length 100–110 cm] or trekking pole for substitution, TheraBand, sandbag and a small ball led by a physical therapist) | Usual care |
| Yoo and Yoo [70]/Korea | Quasi-exp | Stroke survivors (n=28, CBR=14, control=14) | Physical fitness (Wolf Motor Function Test (Korean version), Motor Activity Log (Korean version)/quality of life (stroke short form) | Supervised exercise: 3 day×per week/70 m/24 wk (walking, stretching, muscular relaxation exercises, functional tasks) | Self-monitored exercise |
| Yu [82]/China | Quasi-exp | Stroke survivors (n=76, CBR=38, control=38) | Functional ability (FMA)/quality of life SF-36, ADL (BI) | Education | Usual care |
| Physical exercisea) | |||||
| Zhang et al. [75]/China | RCT | Patients with a recent coronary event defined as acuter myocardial infarction (MI), (n=126, CBR=57, control=69) | Functional ability (6MWT)/quality of life (SF-12) | Exercise: 6 day per week/20–40 m/6 mo (warm-up, aerobic training, cool down) | Usual care |
| Zhu [35]/China | RCT | Stroke survivors (n=130, CBR=65, control=65) | Functional ability (FMA)/ADL (BI) | Education | Usual care |
| Exercisea) |
FMA, Fugl-Meyer Assessment; RCT, Randomised Controlled Trial; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 6MWT, 6-Minute Walk Test; CBR, Community-based Rehabilitation; ADL, Activity of Daily Living; BI, Barthel Index; FIM, Functional Independence Measure; WOMAC, Western Ontario and McMaster; VAS, visual analogue scale; TUG, Timed Up and Go Test; FRT, Functional Reach Test; SF, Short Form; HRQoL, health-related quality of life; ROM, range of movement; DEMMI, de Morton Mobility Index; SPPB, Short Physical Performance Battery; KOA, Knee Osseous Archrophlogosis.
a)No detailed information provided in the study.
Table 2.
GRADE Working Group grades of evidence.
High certainty: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect.
Moderate certainty: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different.
Low certainty: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect.
Very low certainty: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect. GRADE, Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations; CBR, community-based rehabilitation; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval; TUG, Timed Up and Go Test; MD, mean difference; RCT, randomised controlled trial; FRT, Functional Reach Test.
a)A non-provision control is defined as no intervention, usual care, sham exercise (the exercise was intended to be a control or appeared to be of insufficient intensity and progression to have beneficial effects on mobility) or a social visit.
b)Physical fitness, measuring the ability of a person to move. Scales may measure a number of aspects of mobility (e.g., TUG, gait speed, and balance).
c)The basis for the assumed risk (e.g., the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). The absolute relative effect (and its 95% CI) is based on the relative effect between the intervention and control.
d)Downgraded one level for risk of bias (non-RCT).
e)One level for indirection (different duration of intervention), and one level for imprecision (sample size<400).
f)One level for imprecision (sample size<400).




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download