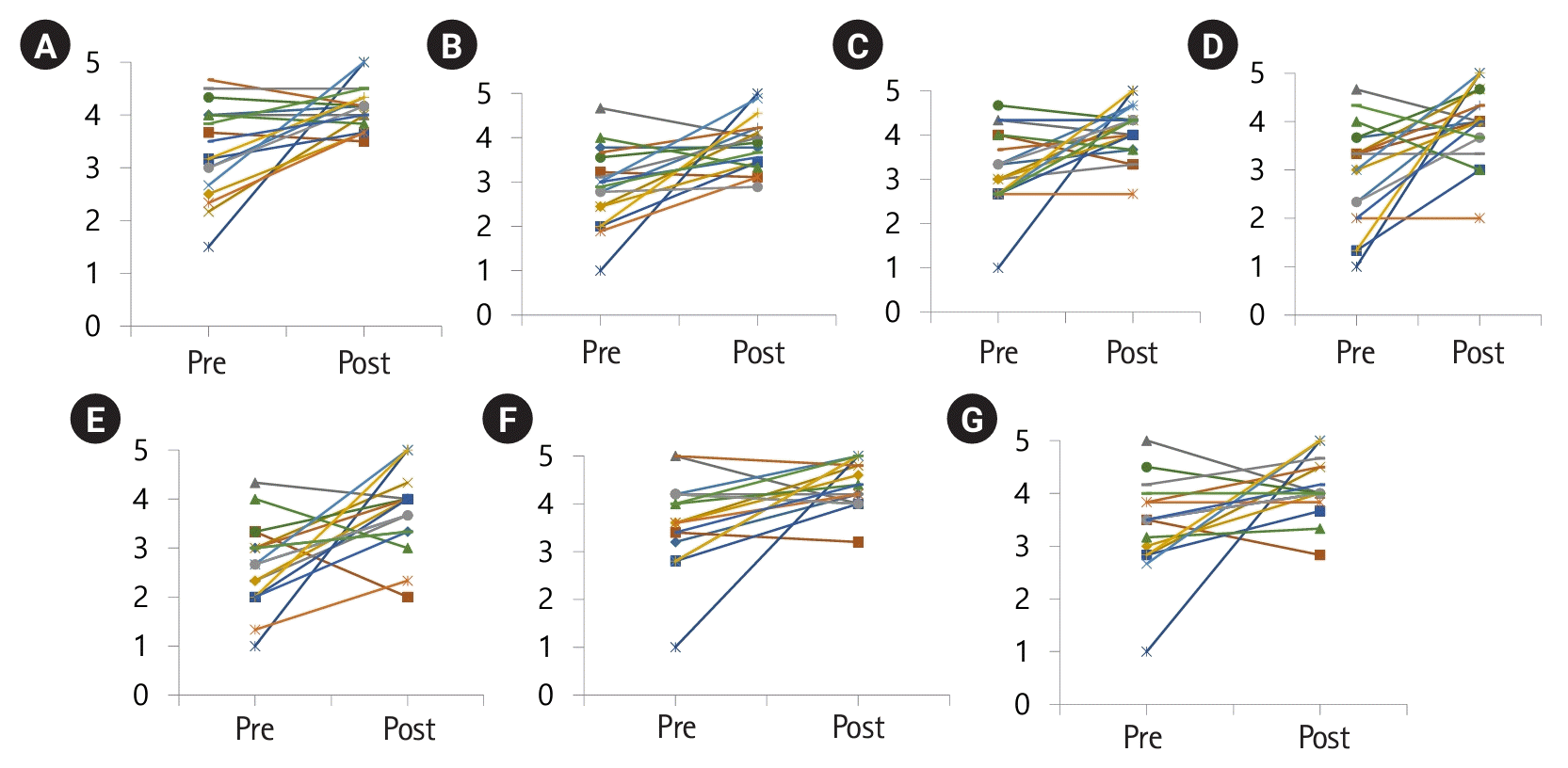
No other study has used the same measurement tool as that in this study for graduate students. The original scale was developed with registered nurses [
7]. Additionally, the curriculum of transcultural nursing in other universities is not the same as that of this study. Therefore, it is impossible to directly compare the results of the present study to any others. However, there have been multiple studies evaluating cultural competency courses. In Japan, international nursing courses increased nursing students’ intercultural sensitivity [
8]. At the Medical University in Tokyo, nursing students participated in the international nursing course. They listened to a lecture in English. They discussed, collaborated, and completed common tasks with students in the United States through online classes. That collaborative work will loosen the tension during the care for foreigners. In Korea, a standardized patient was used for improving cultural competency among undergraduate nursing students. The standardized patient and his mother were set to be from the United Arab Emirates in the simulation. Through this simulation program, nursing students’ cultural competency increased compared to that of the control group [
9]. In Vietnam, when nursing students completed a cultural competence course with a field visit, they reported “obtaining cultural experiences” and “expanding understanding of cultural competence through field experience” compared to students without a field visit [
10]. In various health science fields, including pharmacy, occupational therapy, health science, podiatry, and physical therapy, interventions focusing on cultural competency have proven to improve knowledge, skill execution, attitudes, and student satisfaction [
11]. A study on the effectiveness of virtual simulations and problem-based learning in 61 undergraduate or postgraduate nursing students from 5 Asian countries found that students’ cultural competence increased [
12]. In Iran, the cultural competence and self-efficacy of postgraduate nursing students improved after an online cultural care training program.
The training program was executed online due to coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic [
13]. Four 2-hour sessions of the curriculum consisted of lectures with PowerPoint presentations, questions and answers, case scenarios, case reports, group discussions, and videos. There are other studies on the effect of transcultural nursing curriculum on nursing competency; however, the content of the curricula and measurement tools varied among studies. Although it is difficult to directly compare those studies, the curriculum used in each study should be considered for adoption at other institutions.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download