Introduction
Background
Objectives
Methods
Ethics statement
Study design
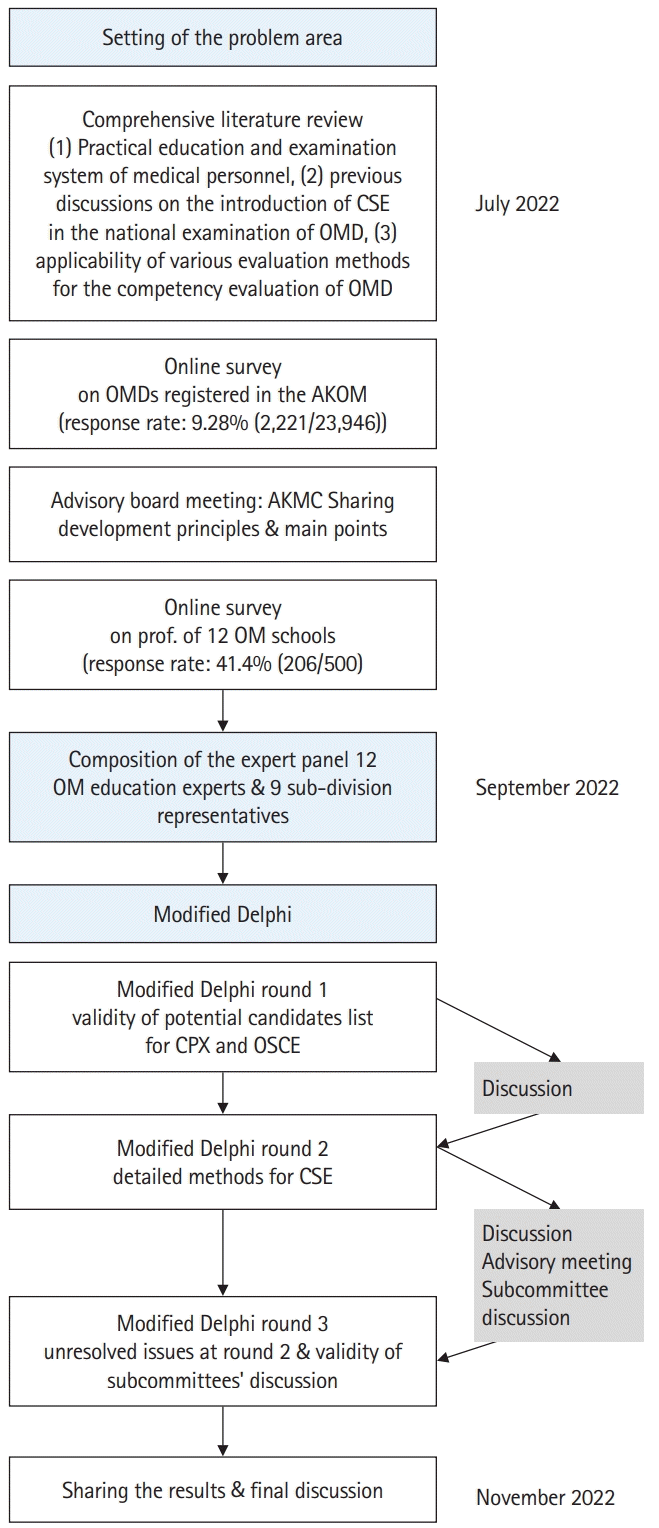
Setting of the problem area
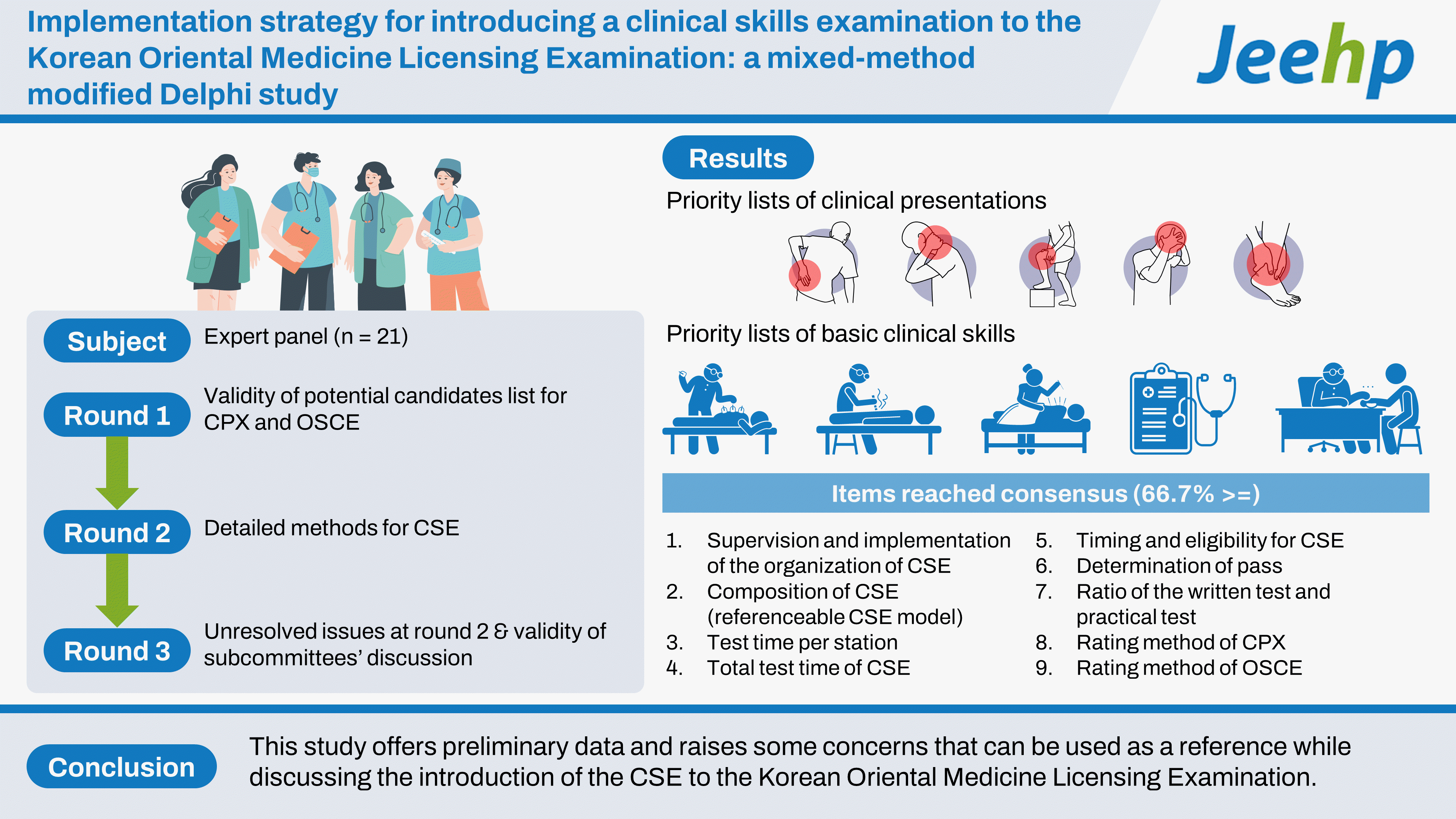
Respondent group
Working group
Instrumentation: 3-round web-based Delphi study
Protocol
Fig. 1.
Data analysis
Results
First round: Questions 1 and 2
Table 1.
Table 2.
Table 3.
Second round: Question 3
Table 4.
| Item | Options | Most frequent response of professors at the 12 OM schools (N=206) | Agreement rate on the most frequent response of the professors (second round) (N=21) | Agreement rate on the options (third round) (N=21) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Year of introduction of CSE | (1) 2025, (2) 2026, (3) 2027, (4) 2028, (5) 2029, (6) Other | (1) 2025 (37.9%) | (1) 2025 (42.9%) | (1) 2025 (19.0%), (3) 2027 (47.6%), (5) 2029 (33.3%) |
| (b) Supervision and implementation of the organization of CSE | (1) KHPLEI, (2) KHPLEI and University, (3) regional autonomy under the responsibility of KHPLEI, (4) University | (1) KHPLEI (68.9%) | (1) KHPLEI (100%) | Not required, as a consensus was reached in the previous round. |
| (c) Composition of CSE (referenceable CSE model) | (1) 6 CPXs, 6 inter-station tests, and 6 single OSCEs (the CSE model of MDs in South Korea, 2009–2020); (2) 9 CPXs and 1 combined-OSCE of 3 skills (the CSE model of MDs in South Korea, 2021–current); (3) 3 result-assessments and 3 procedure-assessments (the CSE model of dentists in South Korea); (4) case analysis, 4 inter-student demonstrations (similar to OSCE), and 2 oral tests (the CSE model of TCM doctors in China); (5) 12 CPXs and 12 patient notes (the CSE model of MDs in US [i.e., USMLE]); (6) others | (2) 9 CPXs and 1 combined-OSCE of 3 skills (the CSE model of MD in South Korea, 2021–current) (38.3%) | (2) 9 CPXs and 1 combined-OSCE of 3 skills (the CSE model of MD in South Korea, 2021–current) (95.2%) | Not required, as a consensus was reached in the previous round. |
| (d) Test time per stationa) | (1) 10 minutes, (2) 12 minutes, (3) 15 minutes, (4) other | (3) 15 minutes (38.3%) | (3) 15 minutes (85.7%) | (2) 12 minutes (90.5%), (3) 15 minutes (9.5%) |
| (e) Total test time of CSE | (1) 2 hours, (2) 3 hours, (3) 4 hours, (4) 5 hours, (5) 6 hours, (6) other | (2) 3 hours (52.4%) | (2) 3 hours (90.5%) | Not required, as a consensus was reached in the previous round. |
| (f) Timing and eligibility for CSEa) | (1) Before the written test, prospective graduate; (2) after the written test, prospective graduates; (3) after the written test, only prospective graduates who have passed the written test; (4) regardless of the written test and eligibility | (3) After the written test, only prospective graduates who have passed the written test (45.6%) | (3) After the written test, only prospective graduates who have passed the written test (85.7%) | (1) Before the written test, prospective graduates (66.7%); (2) after the written test, prospective graduates (14.3%); (3) after the written test, only prospective graduates who have passed the written test (14.3%) |
| (g) Determination of pass | (1) Passing both the written and clinical skills exams; (2) passing according to the combined score of the written test and clinical skills exams; (3) other | (1) Passing both the written and practical exams, respectively (71.4%) | (1) Passing both the written and practical exams, respectively (95.2%) | Not required, as a consensus was reached in the previous round. |
| (h) Ratio of the written test and practical test (in case of combining the scores of the written test and clinical skills exams) | (1) 8:2, (2) 7:3, (3) 6:4, (4) 5:5, (5) 4:6, (6) 3:7, (7) 2:8 | (1) 8:2 (46.0%) | (1) 8:2 (76.2%) | This consensus was invalidated because the combination of the scores of the written test and clinical skills exams did not reach a consensus. (item [g]) |
| (i) Rating HT, PE, and ED of CPX (PPI is scored by 1 SP who is acting)a) | (1) By 1 university teacher at schools of OM; (2) by 2 university teachers at schools of OM; (3) by 1 SP (acting and scoring); (4) by 2 SPs (1 for acting and the other 1 for scoring); (5) other | (4) By 2 SPs (1 for acting and the other 1 for scoring) (46.8%) | (4) By 2 SPs (1 for acting and the other 1 for scoring) (76.2%) | (1) By 1 university teacher at schools of OM (28.6%); (4) by 2 SPs (1 for acting and the other 1 for scoring) (71.4%) |
| (j) Rating OSCE | (1) By 1 university teacher at schools of OM (scoring); (2) by 2 university teachers at schools of OM; (3) other | (1) By 1 university teacher at schools of OM (66.1%) | (1) By 1 university teacher at schools of OM (90.5%) | Not required, as a consensus was reached in the previous round. |
CSE, clinical skills examination; OMD, Oriental medicine doctor; OM, Oriental medicine; KHPLEI, Korea Health Personnel Licensing Examination Institute; CPX, clinical practice examination; OSCE, objective structured clinical examination; MD, medical doctor; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; USMLE, United States Medical Licensing Examination; HT, history taking; PE, physical examination; ED, education; PPI, patient–physician interaction; SP, standardized patient.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download