Introduction
Materials and Methods
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Search strategy
Study selection
Data extraction
Risk of bias assessment
Data analysis
Conventional meta-analysis
TSA
Quality of the evidence
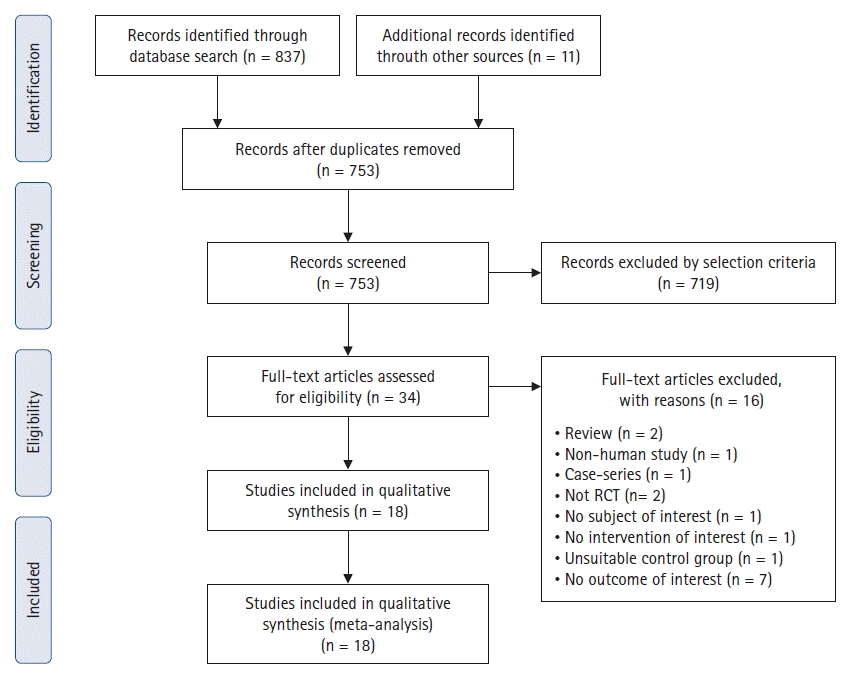
Results
Study selection
Study characteristics
Table 1.
| Author, year | Region | Surgery | Intervention | n | Age, yr* | Sex (M/F) | Temperature measurement site | Time points of temperature measurements included† | Other warming devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen, 1994 [48] | Taiwan | Elective abdominal surgery | Control | 14 | 56.85 ± 4.72 | 8/6 | Nasopharynx | Baseline/15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165, 180 min after induction | None |
| HH | 22 | 50.68 ± 3.33 | 12/10 | ||||||
| Conahan, 1987 [42] | United States | Laparoscopy and ovum harvesting in an ambulatory surgery unit | Control | 9 | 33.8 ± 0.8 | 0/9 | Sublingual | Baseline/15, 30, 45 min after induction/on arrival in the RR | None |
| HH | 10 | 32.1 ± 1.0 | 0/10 | ||||||
| Deriaz, 1992 [45] | France | Gynecological surgery | Control | 25 | NR | NR | Esophagus | Baseline/30, 60, 90 min after induction/end of anesthesia | None |
| HME | 25 | NR | NR | ||||||
| HH | 25 | NR | NR | ||||||
| Goldberg, 1992 [41] | United States | Lower abdominal procedures under general anesthesia anticipated to last 1–4 h | Control | 16 | 41.4 ± 10.1 | NR | Sublingual | Baseline/60, 90 min after induction/on arrival in the PACU | Blood warmed to 36°C |
| HME | 21 | 43.2 ± 14.1 | NR | ||||||
| HH | 14 | 44.7 ± 10.8 | NR | ||||||
| Han, 2013 [36] | South Korea | Elective living donor liver transplantation | HME | 17 | 55 (48,60) | 15/2 | Baseline: tympanic membrane; after induction: pulmonary artery | Baseline/60, 120, 180 min after induction (dissection phase) | Circulating water mattress (Blanketrol II), IV fluid & blood warmed |
| HH | 17 | 54 (49,57) | 12/5 | ||||||
| Jo, 2013 [7] | South Korea | Elective arthroscopic shoulder surgery | Control | 20 | 47.5 ± 16.6 | 14/6 | Esophagus | Baseline/15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120 min after induction | Warm-cotton blanket when core temperature < 35°C |
| HHBC | 20 | 50.4 ± 14.1 | 12/8 | ||||||
| Jung, 2015 [37] | South Korea | Elective spinal surgery with duration of at least 180 min | HHBC | 30 | 49.1 ± 10.4 | 12/18 | Esophagus | Baseline/15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165, 180 min after induction | Forced-air convective warming device (Bair Hugger) when core temperature < 35°C |
| MAK | 30 | 49.3 ± 12.1 | 16/14 | ||||||
| Kim, 2015 [38] | South Korea | Elective craniotomy | Control | 34 | 47.9 ± 14.9 | 16/18 | Esophagus | Baseline/15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165, 180 min after induction/end of surgery | Circulating water mattress, forced-air warmer when core temperature < 35.5°C |
| HHBC | 34 | 50.7 ± 11.3 | 17/17 | ||||||
| MAK | 34 | 49.4 ± 12.5 | 20/14 | ||||||
| Kulkarni, 1995 [44] | United Kingdom | Elective unilateral total hip replacement | Control | 10 | 69 (59,83) | 4/6 | Tympanic membrane | Baseline/end of surgery | Blood warmed to 37°C |
| HH | 10 | 70 (58,83) | 5/5 | ||||||
| Kwak, 2013 [40] | South Korea | Escharectomy and skin graft under general anesthesia | HME | 30 | 45.6 ± 13.3 | 24/6 | Esophagus | Baseline/15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165, 180 min after induction | Circulating water mattress (Blanketrol II), IV fluid & blood warmed |
| HHBC | 30 | 45.4 ± 11.6 | 25/5 | ||||||
| Lee, 2011 [8] | South Korea | Posterior lumbar spinal fusion with metal device instrumentation within two spinal levels | Control | 40 | 64.7 ± 8.1 | 22/18 | Tympanic membrane | Baseline/30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180 min after induction | Forced-air warmer, blood warmed to 36°C |
| HH | 40 | 64.2 ± 8.2 | 28/12 | ||||||
| Park, 2009 [39] | South Korea | Elective surgery under general anesthesia | Control | 20 | 48.4 ± 11.3 | 5/15 | Esophagus | Baseline/15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165, 180 min after induction | None |
| HHBC | 20 | 49.9 ± 14.3 | 6/14 | ||||||
| Park HJ, 2017 [6] | South Korea | Elective thyroidectomy | Control | 85 | 47.3 ± 11.9 | 16/69 | Esophagus | Baseline/30, 60, 90 min after induction | None |
| HHBC | 85 | 49.2 ± 11.7 | 22/63 | ||||||
| Park S, 2017 [2] | South Korea | Arthroscopic hip surgery | HME | 28 | 38.4 ± 11.5 | 19/9 | Esophagus | Baseline/120 min after induction | Warming measures (administration of pre-warmed IV fluid, forced air warmer) when core temperature < 35°C |
| HHBC | 28 | 41.6 ± 9.7 | 18/10 | ||||||
| Ralley, 1984 [47] | Canada | Uncomplicated valve replacement or aortocoronary bypass surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass | Control | 15 | 62.3 ± 2.6 | 13/2 | Nasopharynx | Baseline (termination of CPB)/30, 90, 120, 150, 180, 240 min after CPB termination | NR |
| HH | 15 | 58.5 ± 2.4 | 12/3 | ||||||
| Stone, 1981 [43] | United States | Surgical procedures lasting three or more hours | Control | 10 | NR | 10/0 | Nasopharynx | Baseline/15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165, 180, 240 min after induction | Warming blankets applied in some patients |
| HH | 10 | NR | 10/0 | ||||||
| Tølløfsrud, 1984 [46] | Norway | Abdominal aorta surgery (A) | Control | 10 | 64‡ | 16/4 | Esophagus | 60, 120, 180 min after induction | None |
| HH | 10 | ||||||||
| Extra-abdominal vascular surgery (B) | Control | 10 | 70‡ | 16/4 | |||||
| HH | 10 | ||||||||
| Yam, 1990 [3] | United Kingdom | Elective total hip arthroplasty for osteoarthritis | Control | 20 | 73 ± 8 | 6/14 | Aural canal | Baseline/end of surgery | Blood warmed to 37°C |
| HME | 20 | 70 ± 6 | 3/17 | ||||||
| HH | 20 | 68 ± 9 | 8/12 |
Risk of bias assessment
Table 2.
| Study | Randomization process | Deviations from the intended interventions | Missing outcome data | Measurement of the outcome | Selection of the reported result | Overall risk of bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen, 1994 [48] | High risk* | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Conahan, 1987 [42] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Deriaz, 1992 [45] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Goldberg, 1992 [41] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Han, 2013 [36] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Jo, 2013 [7] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Jung, 2015 [37] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Kim, 2015 [38] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk |
| Kulkarni, 1995 [44] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Kwak, 2013 [40] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Lee, 2011 [8] | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Park, 2009 [39] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Park, 2017 [6] | High risk† | High risk‡ | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Park, 2017 [2] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Ralley, 1984 [47] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Stone, 1981 [43] | High risk§ | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Tølløfsrud, 1984 [46] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Yam, 1990 [3] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
* Allocation concealment: no information; baseline imbalances: substantial differences in group size.
† Allocation concealment: no information; baseline imbalances: excessive similarity in baseline characteristics owing to the matching process.
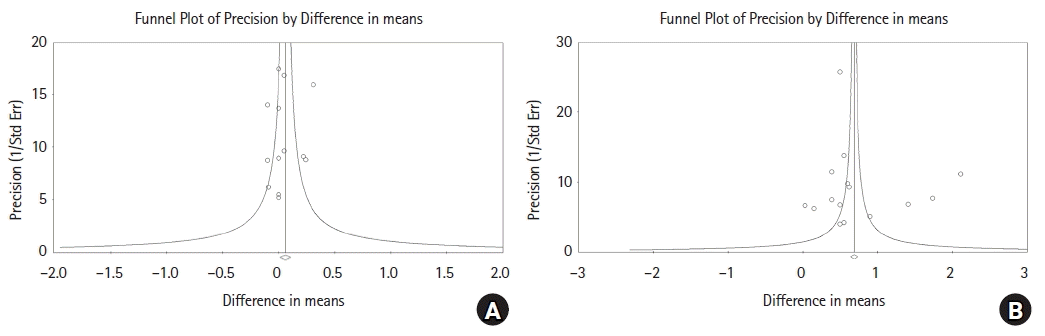
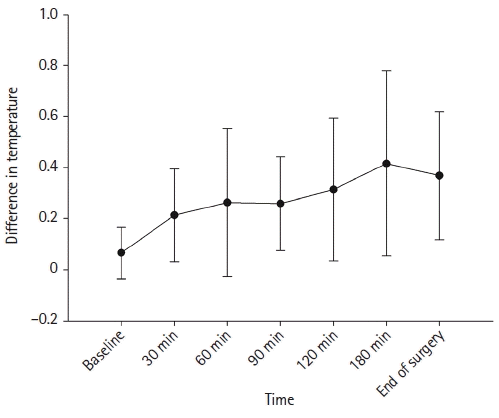
Conventional meta-analysis
HH vs. Control
Fig. 2.
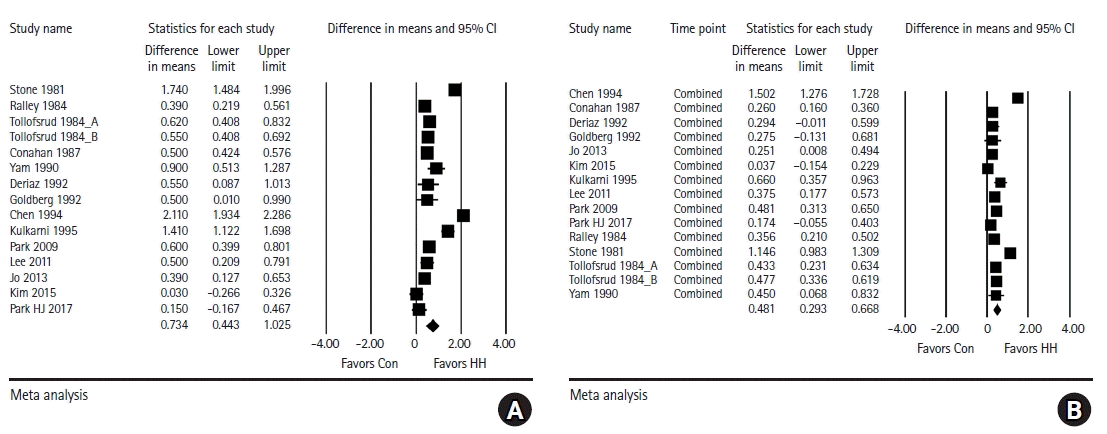
Fig. 3.
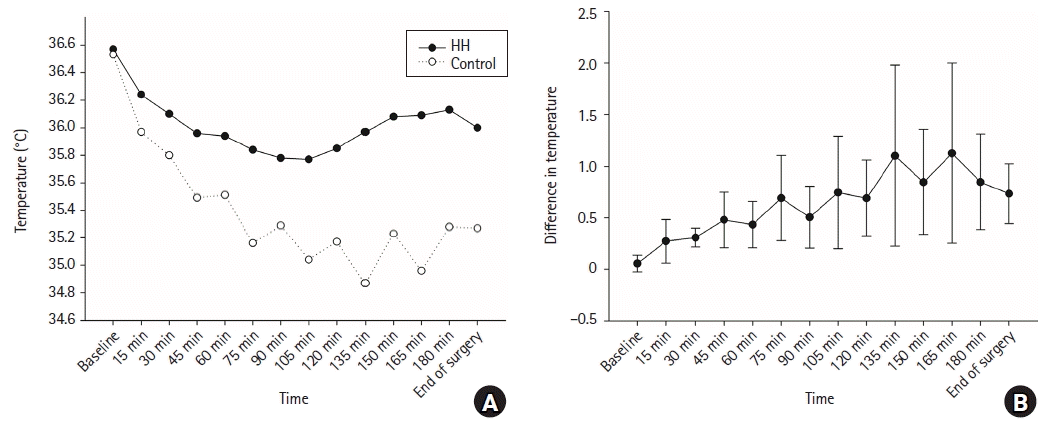
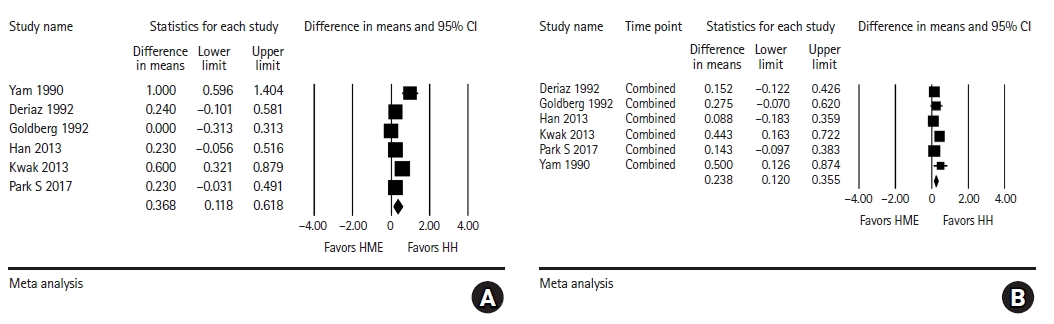
HH vs. HME
Fig. 5.
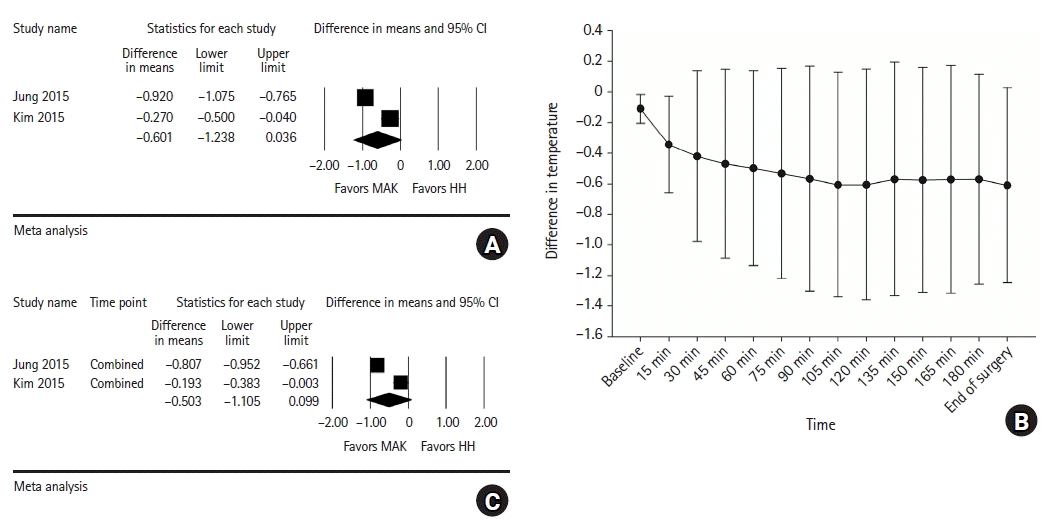
HH vs. MAK
Fig. 7.
Sensitivity analysis
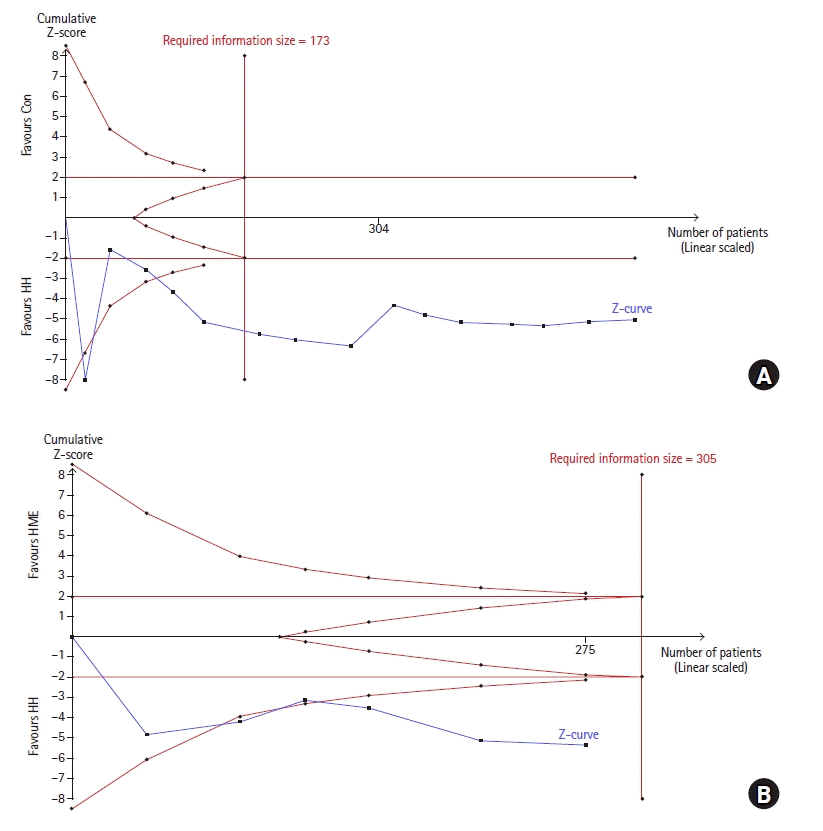
TSA
HH vs. Control
Fig. 8.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download