INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study design
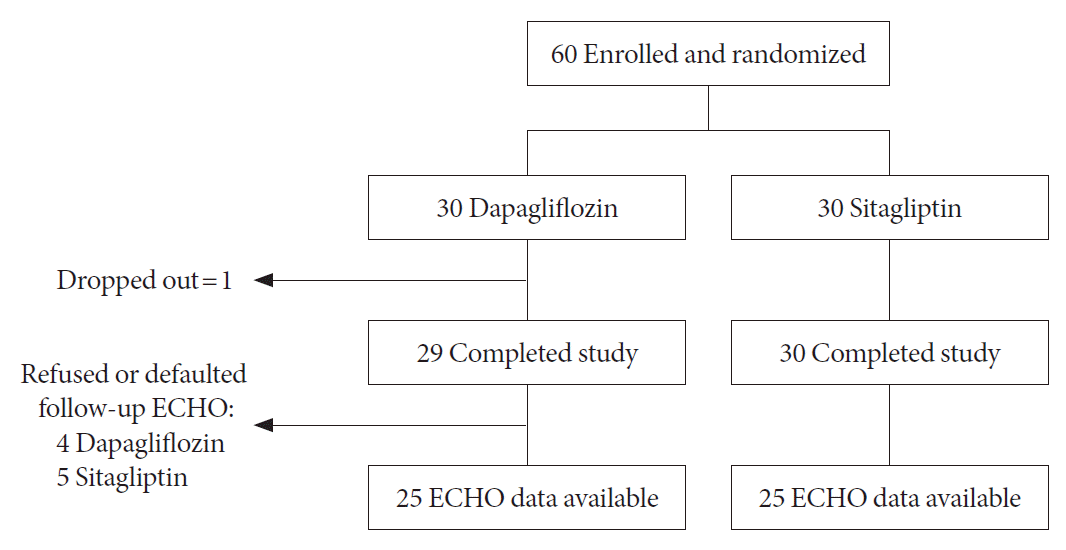
Study participants
Randomization and study intervention
Clinical and biochemical assessments
Measurements of circulating BHB, FFA, and hsCRP levels
HDL-C CEC measurements
Echocardiography assessments
Vibration-controlled transient elastography assessments
Outcomes of interest
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Table 1.
| Baseline variable | Dapagliflozin (n=30) | Sitagliptin (n=30) | P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical parameters | |||||
| Men, % | 53.3 | 66.7 | 0.292 | ||
| Age, yr | 56.9±10.7 | 60.6±7.03 | 0.120 | ||
| Ever smoker, % | 40.0 | 40.0 | 1.000 | ||
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 17.1±9.56 | 19.3±8.50 | 0.357 | ||
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.4±3.87 | 26.9±2.90 | 0.570 | ||
| WC, cm | 92.7±8.28 | 92.9±8.19 | 0.949 | ||
| Men | 94.8±8.96 | 95.0±6.85 | 0.952 | ||
| Women | 90.3±6.98 | 88.6±9.34 | 0.615 | ||
| Central obesity, % | 83.3 | 66.7 | 0.136 | ||
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 132±13.1 | 137±14.5 | 0.143 | ||
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 73.1±7.27 | 75.6±7.99 | 0.207 | ||
| Biochemistry parameters | |||||
| Fasting glucose, mmol/L | 9.35±3.32 | 9.82±2.89 | 0.564 | ||
| HbA1c, % | 8.94±0.60 | 8.79±0.56 | 0.321 | ||
| HbA1c, mmol/mol | 74.20±6.57 | 72.60±6.11 | 0.321 | ||
| C-peptide, nmol/L | 0.29 (0.19–0.39) | 0.28 (0.17–0.46) | 0.444 | ||
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.25±0.34 | 1.24±0.41 | 0.945 | ||
| HDL-CEC, % | 22.2±5.24 | 21.8±6.32 | 0.792 | ||
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 2.08±0.64 | 1.86±0.77 | 0.235 | ||
| Triglyceridesa, mmol/L | 1.15 (0.90–1.63) | 1.35 (0.88–2.18) | 0.328 | ||
| ALTa, U/L | 22 (16–37) | 23 (19–31) | 0.813 | ||
| ASTa, U/L | 20 (18–29) | 22 (17–24) | 0.447 | ||
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 90.4±19.6 | 81.2±16.1 | 0.050 | ||
| ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2, % | 90.0 | 93.3 | 1.000 | ||
| Albuminuria status | 0.865 | ||||
| A1, % | 53.3 | 56.7 | |||
| A2, % | 33.33 | 23.3 | |||
| A3, % | 13.3 | 20.0 | |||
| Fasting FFA, µmol/L | 91.5 (63.2–165) | 110 (86.6–160) | 0.278 | ||
| Fasting BHB, µmol/L | 372 (315–521) | 401 (325–514) | 0.389 | ||
| hsCRPa, mg/L | 0.96 (0.51–2.62) | 0.89 (0.42–2.49) | 0.341 | ||
| VCTE | |||||
| CAP, dB/m | 285±48.2 | 292±56.6 | 0.625 | ||
| Minimal <248 dB/m | 23.3 | 20.0 | |||
| Mild 248–267 dB/m | 16.7 | 23.3 | |||
| Moderate 268–279 dB/m | 0.0 | 3.3 | |||
| Severe >279 dB/m | 60.0 | 63.3 | |||
| LSa, kPa | 5.75 (4.33–8.95) | 6.10 (4.98–8.15) | 0.675 | ||
| F0/1 <5.8 kPa | 50.0 | 46.7 | |||
| F2 5.8–9.5 kPa | 36.7 | 43.3 | |||
| F3 9.6–11.4 kPa | 6.6 | 3.3 | |||
| F4 >11.4 kPa | 6.7 | 6.7 | |||
| Medical diseases, % | |||||
| Hypertension | 80.0 | 83.3 | 0.739 | ||
| Coronary artery disease | 13.3 | 13.3 | 1.000 | ||
| Stroke | 6.7 | 6.7 | 1.000 | ||
| STDR | 6.7 | 10.0 | 1.000 | ||
| Concomitant medications, % | |||||
| Metformin | 100 | 100 | 1.000 | ||
| Pioglitazone | 13.3 | 16.7 | 0.718 | ||
| ACEI | 50.0 | 53.3 | 0.796 | ||
| ARB | 27.7 | 26.7 | 1.000 | ||
| Statin | 63.3 | 80.0 | 0.152 | ||
| Fibrate | 0.0 | 10.0 | 0.237 | ||
| Aspirin | 26.7 | 26.7 | 1.000 | ||
| Total daily insulin dosage, units | 42.0±15.9 | 45.0±14.1 | 0.447 | ||
Values are presented as percent, mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range). Albuminuria status was assessed with a random urine sample, and categorized according to urine albumin to creatinine ratio (A1: <30 mg/g; A2: ≥30–<300 mg/g; A3 ≥300 mg/g).
BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; BP, blood pressure; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CEC, cholesterol efflux capacity; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; FFA, free fatty acid; BHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; hsCRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; VCTE, vibration-controlled transient elastography; CAP, controlled attenuation parameter; LS, liver stiffness; STDR, sight threatening diabetic retinopathy; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker.
Table 2.
| Baseline variable |
Dapagliflozin (n=30) |
Sitagliptin (n=30) |
Change from baseline |
P value (Δchange) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At baseline | At week 24 | At baseline | At week 24 | Dapagliflozin | Sitagliptin | |||
| Primary outcome | ||||||||
| BHBa, μmol/L | 372 (315 to 521) | 472 (349 to 587)c | 401 (325 to 514) | 403 (326 to 524) | 90.5 (–8.10 to 193) | –11.9 (–123 to 79.3) | 0.045b | |
| Secondary outcomes | ||||||||
| Body weight, kg | 70.3±12.8 | 69.3±12.5c | 71.5±11.6 | 72.2±12.8 | –0.94±1.89 | 0.65±2.46 | 0.006 | |
| WC, cm | 92.7±8.28 | 91.6±8.19 | 92.9±8.19 | 94.0±9.02c | –1.09±4.47 | 1.11±2.90 | 0.028 | |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 132±13.1 | 129±12.9 | 137±14.5 | 136±16.4 | –2.20±13.2 | –1.18±15.8 | 0.787 | |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 73.1±7.27 | 71.7±8.66 | 75.6±7.99 | 74.9±9.26 | –1.40±6.46 | –0.75±6.61 | 0.701 | |
| Total daily insulin dose, units | 42.0±15.9 | 41.4±15.8 | 45.0±14.1 | 45.8±14.9 | –0.60±3.33 | 0.80±2.66 | 0.077 | |
| FG, mmol/L | 9.35±3.32 | 7.21±2.11d | 9.82±2.89 | 6.79±2.02e | –2.14±3.28 | –3.03±3.32 | 0.298 | |
| HbA1c, % | 8.94±0.60 | 7.69±0.86e | 8.79±0.56 | 7.81±0.93e | –1.25±0.78 | –0.98±0.80 | 0.198 | |
| HbA1c, mmol/mol | 74.20±6.57 | 60.60±9.38e | 72.60±6.11 | 61.80±10.10e | –13.60±0.56 | –10.70±8.78 | 0.198 | |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 91.9±18.1 | 90.2±19.8 | 81.2±16.1 | 77.7±15.6c | –0.21±5.97 | –3.43±8.50 | 0.092 | |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.25±0.34 | 1.30±0.37 | 1.24±0.41 | 1.20±0.41 | 0.05±0.15 | –0.04±0.18 | 0.041 | |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 2.08±0.64 | 2.06±0.74 | 1.86± 0.77 | 1.76±0.62 | –0.02±0.47 | –0.11±0.62 | 0.545 | |
| TGa, mmol/L | 1.15 (0.90 to 1.63) | 1.15 (0.80 to 1.53) | 1.35 (0.88 to 2.18) | 1.25 (0.80 to 1.70)c | –0.15 (–0.40 to 0.10) | –0.25 (–0.50 to 0.05) | 0.611 | |
| ALTa, U/L | 21.5 (15.8 to 37.3) | 20.0 (15.8 to 27.5) | 22.5 (19.0 to 30.5) | 27.0 (19.8 to 32.0) | –1.00 (3.00 to –5.50) | 2.00 (–2.00 to 5.25) | 0.284 | |
| ASTa, U/L | 20.0 (17.8 to 29.3) | 19.0 (16.8 to 25.0) | 21.5 (16.8–24.0) | 23.0 (20.8 to 27.3)c | 0.00 (–3.50 to 2.00) | 3.00 (–1.00 to 5.25) | 0.160 | |
| CAP, dB/m | 285±48.2 | 268±50.9c | 292±56.6 | 302 ± 58.0 | –17.8±40.6 | 10.0±37.0 | 0.007 | |
| LS, kPa | 5.75 (4.33 to 8.95) | 5.15 (4.58 to 6.75)c | 6.10 (4.98 to 8.15) | 7.00 (5.10 to 8.58) | –0.50 (–1.25 to 0.15) | 0.25 (–0.50 to 1.20) | 0.022 | |
| HDL-CEC, % | 22.2±5.32 | 24.8±7.60c | 21.8± 6.32 | 21.3±6.43 | 2.66±5.14 | –0.50±6.71 | 0.045 | |
| hsCRPa, mg/L | 0.96 (0.51 to 2.62) | 0.63 (0.42 to 2.05) | 0.89 (0.42 to 2.49) | 0.97 (0.42 to 2.22) | –0.19 (–0.95 to 0.002) | –0.10 (–0.60 to 0.63) | 0.177 | |
| FFAa, µmol/L | 91.6 (64.1 to 164) | 119 (69.0 to 164) | 110 (86.6 to 160) | 106 (56.6 to 174) | 9.58 (–41.8 to 45.0) | –6.72 (–43.6 to 26.5) | 0.191b | |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or mean±standard deviation.
BHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; WC, waist circumference; BP, blood pressure; FG, fasting glucose; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CAP, controlled attenuation parameter; LS, liver stiffness; CEC, cholesterol efflux capacity; hsCRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; FFA, free fatty acid.
Table 3.
| Change in clinical and metabolic variable |
Change in BHB levels, μmol/L |
|
|---|---|---|
| Crude r | P value | |
| Body weight, kg | 0.111 | 0.560 |
| Waist circumference, cm | –0.022 | 0.910 |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 0.017 | 0.929 |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 0.239 | 0.204 |
| Total daily insulin dose, units | 0.221 | 0.241 |
| Fasting glucose, mmol/L | 0.068 | 0.723 |
| HbA1c, % | 0.140 | 0.461 |
| Triglyceridea, mmol/L | 0.188 | 0.319 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | –0.344 | 0.063 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | –0.052 | 0.783 |
| HDL-CEC, % | 0.107 | 0.575 |
| ALTa, U/L | 0.088 | 0.644 |
| ASTa, U/L | 0.047 | 0.804 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 0.011 | 0.956 |
| CAP, dB/m | 0.239 | 0.204 |
| LSa, kPa | –0.208 | 0.270 |
| FFAa, µmol/L | 0.433 | 0.017 |
| hsCRPa | –0.206 | 0.274 |
BHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; BP, blood pressure; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; CEC, cholesterol efflux capacity; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; CAP, controlled attenuation parameter; LS, liver stiffness; FFA, free fatty acid; hsCRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Table 4.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation.
IVSd, inter-ventricular septal dimension; LVPWd, left ventricular posterior wall thickness at end-diastole; LV, left ventricular; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; E wave, peak trans-mitral flow velocities in early diastole; A wave, peak trans-mitral flow velocities in late diastole; DT, deceleration time; e’, peak velocities of septal and lateral mitral annulus in early diastole; LAVi, left atrial volume divided by body surface area of the participants.
Paired t-test: aP<0.01, bP<0.05; cP=0.037 for the difference of average E/e’ between dapagliflozin and sitagliptin at 24 weeks.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download