1. Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 2013; 93:137–88.

2. Cheng G, Huang C, Deng H, Wang H. Diabetes as a risk factor for dementia and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Intern Med J. 2012; 42:484–91.

3. Cherbuin N, Walsh EI. Sugar in mind: untangling a sweet and sour relationship beyond type 2 diabetes. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2019; 54:100769.

4. Kodl CT, Seaquist ER. Cognitive dysfunction and diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev. 2008; 29:494–511.

5. Kawamura T, Umemura T, Hotta N. Cognitive impairment in diabetic patients: can diabetic control prevent cognitive decline? J Diabetes Investig. 2012; 3:413–23.

6. van Harten B, de Leeuw FE, Weinstein HC, Scheltens P, Biessels GJ. Brain imaging in patients with diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:2539–48.
7. Manschot SM, Brands AM, van der Grond J, Kessels RP, Algra A, Kappelle LJ, et al. Brain magnetic resonance imaging correlates of impaired cognition in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006; 55:1106–13.

8. Tiehuis AM, van der Graaf Y, Visseren FL, Vincken KL, Biessels GJ, Appelman AP, et al. Diabetes increases atrophy and vascular lesions on brain MRI in patients with symptomatic arterial disease. Stroke. 2008; 39:1600–3.

9. Manschot SM, Biessels GJ, de Valk H, Algra A, Rutten GE, van der Grond J, et al. Metabolic and vascular determinants of impaired cognitive performance and abnormalities on brain magnetic resonance imaging in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:2388–97.

10. Bruehl H, Sweat V, Tirsi A, Shah B, Convit A. Obese adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus have hippocampal and frontal lobe volume reductions. Neurosci Med. 2011; 2:34–42.

11. Espeland MA, Bryan RN, Goveas JS, Robinson JG, Siddiqui MS, Liu S, et al. Influence of type 2 diabetes on brain volumes and changes in brain volumes: results from the Women’s Health Initiative Magnetic Resonance Imaging studies. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:90–7.
12. de Bresser J, Tiehuis AM, van den Berg E, Reijmer YD, Jongen C, Kappelle LJ, et al. Progression of cerebral atrophy and white matter hyperintensities in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:1309–14.

13. van Elderen SG, de Roos A, de Craen AJ, Westendorp RG, Blauw GJ, Jukema JW, et al. Progression of brain atrophy and cognitive decline in diabetes mellitus: a 3-year follow-up. Neurology. 2010; 75:997–1002.

14. Kooistra M, Geerlings MI, Mali WP, Vincken KL, van der Graaf Y, Biessels GJ, et al. Diabetes mellitus and progression of vascular brain lesions and brain atrophy in patients with symptomatic atherosclerotic disease: the SMART-MR study. J Neurol Sci. 2013; 332:69–74.

15. Debette S, Seshadri S, Beiser A, Au R, Himali JJ, Palumbo C, et al. Midlife vascular risk factor exposure accelerates structural brain aging and cognitive decline. Neurology. 2011; 77:461–8.

16. Fraser MA, Shaw ME, Cherbuin N. A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal hippocampal atrophy in healthy human ageing. Neuroimage. 2015; 112:364–74.

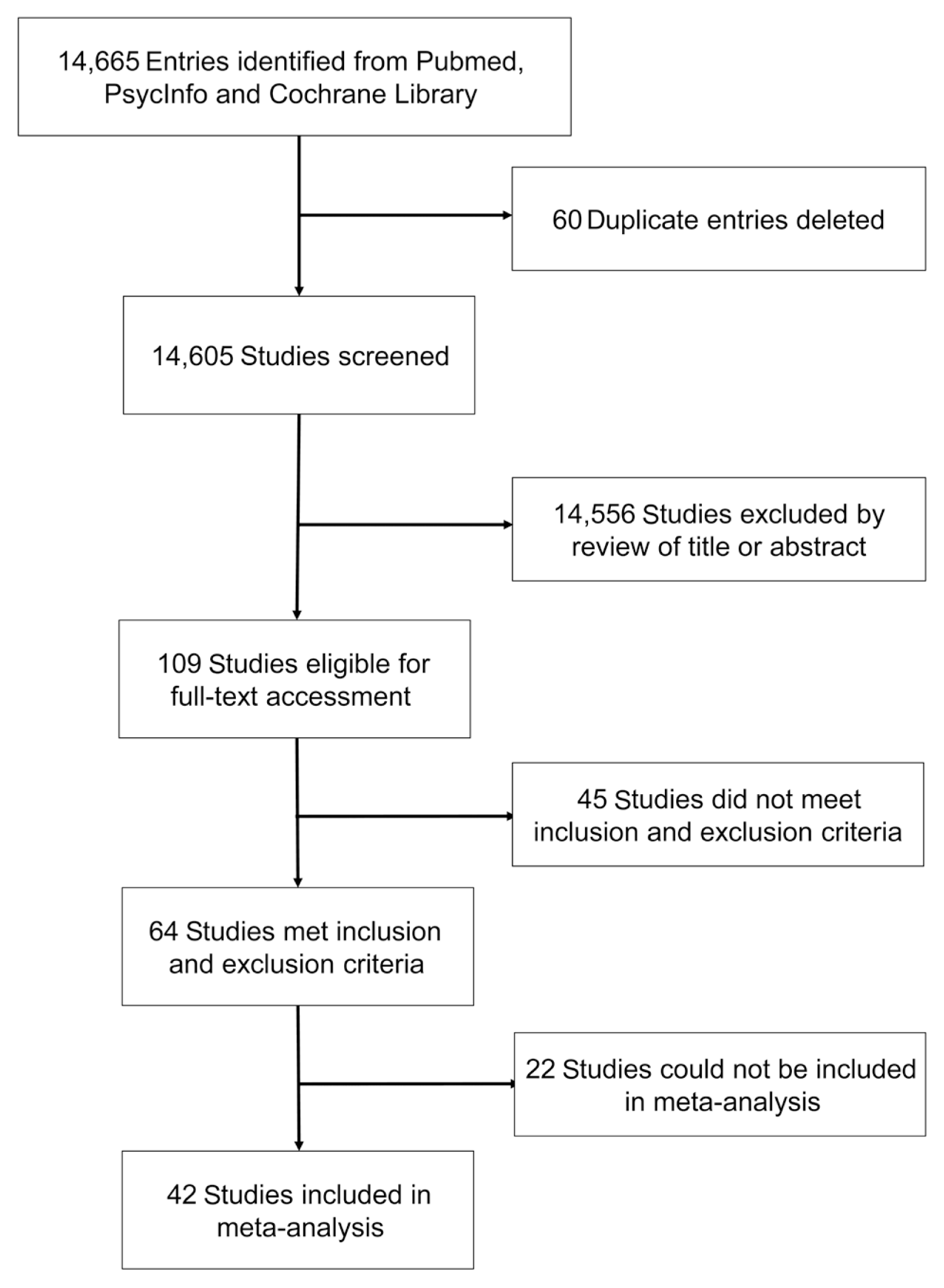
17. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021; 372:n71.
18. R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing;2014.
19. Viechtbauer W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw. 2010; 36:1–48.
20. Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Chichester: Wiley;2011.
21. Samaras K, Lutgers HL, Kochan NA, Crawford JD, Campbell LV, Wen W, et al. The impact of glucose disorders on cognition and brain volumes in the elderly: the Sydney Memory and Ageing Study. Age (Dordr). 2014; 36:977–93.

22. Ajilore O, Narr K, Rosenthal J, Pham D, Hamilton L, Watari K, et al. Regional cortical gray matter thickness differences associated with type 2 diabetes and major depression. Psychiatry Res. 2010; 184:63–70.

23. Ajilore O, Lamar M, Medina J, Watari K, Elderkin-Thompson V, Kumar A. Disassociation of verbal learning and hippocampal volume in type 2 diabetes and major depression. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015; 30:393–9.

24. Armstrong NM, An Y, Beason-Held L, Doshi J, Erus G, Ferrucci L, et al. Predictors of neurodegeneration differ between cognitively normal and subsequently impaired older adults. Neurobiol Aging. 2019; 75:178–86.

25. van Bloemendaal L, Ijzerman RG, Ten Kulve JS, Barkhof F, Diamant M, Veltman DJ, et al. Alterations in white matter volume and integrity in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Metab Brain Dis. 2016; 31:621–9.

26. Bruehl H, Wolf OT, Convit A. A blunted cortisol awakening response and hippocampal atrophy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009; 34:815–21.

27. Bruehl H, Wolf OT, Sweat V, Tirsi A, Richardson S, Convit A. Modifiers of cognitive function and brain structure in middle-aged and elderly individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Brain Res. 2009; 1280:186–94.

28. Brundel M, van den Heuvel M, de Bresser J, Kappelle LJ, Biessels GJ; Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy Study Group. Cerebral cortical thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Neurol Sci. 2010; 299:126–30.

29. Brundel M, Reijmer YD, van Veluw SJ, Kuijf HJ, Luijten PR, Kappelle LJ, et al. Cerebral microvascular lesions on high-resolution 7-Tesla MRI in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2014; 63:3523–9.

30. Callisaya ML, Beare R, Moran C, Phan T, Wang W, Srikanth VK. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, brain atrophy and cognitive decline in older people: a longitudinal study. Diabetologia. 2019; 62:448–58.

31. Chen X, Wen W, Anstey KJ, Sachdev PS. Effects of cerebrovascular risk factors on gray matter volume in adults aged 60–64 years: a voxel-based morphometric study. Psychiatry Res. 2006; 147:105–14.

32. Chen Z, Li L, Sun J, Ma L. Mapping the brain in type II diabetes: voxel-based morphometry using DARTEL. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:1870–6.

33. Chen Z, Li J, Sun J, Ma L. Brain expansion in patients with type II diabetes following insulin therapy: a preliminary study with longitudinal voxel-based morphometry. J Neuroimaging. 2014; 24:484–91.

34. Chen J, Zhang J, Liu X, Wang X, Xu X, Li H, et al. Abnormal subcortical nuclei shapes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur Radiol. 2017; 27:4247–56.

35. Climie RE, Srikanth V, Beare R, Keith LJ, Fell J, Davies JE, et al. Aortic reservoir characteristics and brain structure in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus; a cross sectional study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014; 13:143.

36. Cox SR, Lyall DM, Ritchie SJ, Bastin ME, Harris MA, Buchanan CR, et al. Associations between vascular risk factors and brain MRI indices in UK Biobank. Eur Heart J. 2019; 40:2290–300.

37. Cui X, Abduljalil A, Manor BD, Peng CK, Novak V. Multi-scale glycemic variability: a link to gray matter atrophy and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e86284.

38. Cui Y, Liang X, Gu H, Hu Y, Zhao Z, Yang XY, et al. Cerebral perfusion alterations in type 2 diabetes and its relation to insulin resistance and cognitive dysfunction. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017; 11:1248–57.

39. Cui Y, Tang TY, Lu CQ, Cai Y, Lu T, Wang YC, et al. Abnormal cingulum bundle induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus: a diffusion tensor tractography study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020; 12:594198.

40. de Bresser J, Kuijf HJ, Zaanen K, Viergever MA, Hendrikse J, Biessels GJ, et al. White matter hyperintensity shape and location feature analysis on brain MRI; proof of principle study in patients with diabetes. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:1893.

41. den Heijer T, Vermeer SE, van Dijk EJ, Prins ND, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, et al. Type 2 diabetes and atrophy of medial temporal lobe structures on brain MRI. Diabetologia. 2003; 46:1604–10.

42. Fang F, Zhan YF, Zhuo YY, Yin DZ, Li KA, Wang YF. Brain atrophy in middle-aged subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with and without microvascular complications. J Diabetes. 2018; 10:625–32.

43. Fang F, Lai MY, Huang JJ, Kang M, Ma MM, Li KA, et al. Compensatory hippocampal connectivity in young adults with early-stage type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019; 104:3025–38.

44. Ferreira FS, Pereira JM, Reis A, Sanches M, Duarte JV, Gomes L, et al. Early visual cortical structural changes in diabetic patients without diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017; 255:2113–8.

45. Ferreira FS, Pereira JM, Duarte JV, Castelo-Branco M. Extending inferential group analysis in type 2 diabetic patients with multivariate GLM implemented in SPM8. Open Neuroimag J. 2017; 11:32–45.

46. Gold SM, Dziobek I, Sweat V, Tirsi A, Rogers K, Bruehl H, et al. Hippocampal damage and memory impairments as possible early brain complications of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:711–9.

47. Hempel R, Onopa R, Convit A. Type 2 diabetes affects hippocampus volume differentially in men and women. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012; 28:76–83.

48. Hirabayashi N, Hata J, Ohara T, Mukai N, Nagata M, Shibata M, et al. Association between diabetes and hippocampal atrophy in elderly Japanese: the Hisayama Study. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:1543–9.

49. Hoogendam YY, van der Geest JN, van der Lijn F, van der Lugt A, Niessen WJ, Krestin GP, et al. Determinants of cerebellar and cerebral volume in the general elderly population. Neurobiol Aging. 2012; 33:2774–81.

50. Hsu JL, Chen YL, Leu JG, Jaw FS, Lee CH, Tsai YF, et al. Microstructural white matter abnormalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroimage. 2012; 59:1098–105.

51. Jongen C, van der Grond J, Kappelle LJ, Biessels GJ, Viergever MA, Pluim JP, et al. Automated measurement of brain and white matter lesion volume in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:1509–16.

52. Kumar R, Anstey KJ, Cherbuin N, Wen W, Sachdev PS. Association of type 2 diabetes with depression, brain atrophy, and reduced fine motor speed in a 60- to 64-year-old community sample. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2008; 16:989–98.

53. Kumar A, Haroon E, Darwin C, Pham D, Ajilore O, Rodriguez G, et al. Gray matter prefrontal changes in type 2 diabetes detected using MRI. J Magn Reason Imaging. 2008; 27:14–9.

54. Last D, Alsop DC, Abduljalil AM, Marquis RP, de Bazelaire C, Hu K, et al. Global and regional effects of type 2 diabetes on brain tissue volumes and cerebral vasoreactivity. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:1193–9.

55. Launer LJ, Lewis CE, Schreiner PJ, Sidney S, Battapady H, Jacobs DR, et al. Vascular factors and multiple measures of early brain health: CARDIA brain MRI study. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0122138.

56. Lee JH, Yoon S, Renshaw PF, Kim TS, Jung JJ, Choi Y, et al. Morphometric changes in lateral ventricles of patients with recent-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e60515.

57. Li W, Risacher SL, Huang E, Saykin AJ; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with brain atrophy and hypometabolism in the ADNI cohort. Neurology. 2016; 87:595–600.

58. Li C, Li C, Yang Q, Wang B, Yin X, Zuo Z, et al. Cortical thickness contributes to cognitive heterogeneity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e10858.

59. Liu J, Rutten-Jacobs L, Liu M, Markus HS, Traylor M. Causal impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on cerebral small vessel disease: a Mendelian randomization analysis. Stroke. 2018; 49:1325–31.

60. Lucatelli P, Montisci R, Sanfilippo R, Sacconi B, Suri JS, Catalano C, et al. Is there an association between leukoaraiosis volume and diabetes? J Neuroradiol. 2016; 43:273–9.

61. Luchsinger JA, Palta P, Rippon B, Sherwood G, Soto L, Ceballos F, et al. Pre-diabetes, but not type 2 diabetes, is related to brain amyloid in late middle-age. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020; 75:1241–52.
62. Maldjian JA, Whitlow CT, Saha BN, Kota G, Vandergriff C, Davenport EM, et al. Automated white matter total lesion volume segmentation in diabetes. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34:2265–70.

63. Manor B, Newton E, Abduljalil A, Novak V. The relationship between brain volume and walking outcomes in older adults with and without diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1907–12.

64. Moran C, Beare R, Phan TG, Bruce DG, Callisaya ML, Srikanth V, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and biomarkers of neurodegeneration. Neurology. 2015; 85:1123–30.

65. Moran C, Tapp RJ, Hughes AD, Magnussen CG, Blizzard L, Phan TG, et al. The association of type 2 diabetes mellitus with cerebral gray matter volume is independent of retinal vascular architecture and retinopathy. J Diabetes Res. 2016; 2016:6328953.

66. Musen G, Jacobson AM, Bolo NR, Simonson DC, Shenton ME, McCartney RL, et al. Resting-state brain functional connectivity is altered in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2012; 61:2375–9.

67. Novak V, Zhao P, Manor B, Sejdic E, Alsop D, Abduljalil A, et al. Adhesion molecules, altered vasoreactivity, and brain atrophy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:2438–41.

68. Peng B, Chen Z, Ma L, Dai Y. Cerebral alterations of type 2 diabetes mellitus on MRI: a pilot study. Neurosci Lett. 2015; 606:100–5.

69. Qiu C, Sigurdsson S, Zhang Q, Jonsdottir MK, Kjartansson O, Eiriksdottir G, et al. Diabetes, markers of brain pathology and cognitive function: the Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility-Reykjavik Study. Ann Neurol. 2014; 75:138–46.
70. Raffield LM, Cox AJ, Freedman BI, Hugenschmidt CE, Hsu FC, Wagner BC, et al. Analysis of the relationships between type 2 diabetes status, glycemic control, and neuroimaging measures in the Diabetes Heart Study Mind. Acta Diabetol. 2016; 53:439–47.

71. Redel JM, DiFrancesco M, Vannest J, Altaye M, Beebe D, Khoury J, et al. Brain gray matter volume differences in obese youth with type 2 diabetes: a pilot study. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018; 31:261–8.

72. Reinhard H, Garde E, Skimminge A, Akeson P, Ramsoy TZ, Winther K, et al. Plasma NT-proBNP and white matter hyperintensities in type 2 diabetic patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012; 11:119.

73. Rensma SP, van Sloten TT, Ding J, Sigurdsson S, Stehouwer CD, Gudnason V, et al. Type 2 diabetes, change in depressive symptoms over time, and cerebral small vessel disease: longitudinal data of the AGES-Reykjavik Study. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:1781–7.

74. Roberts RO, Knopman DS, Przybelski SA, Mielke MM, Kantarci K, Preboske GM, et al. Association of type 2 diabetes with brain atrophy and cognitive impairment. Neurology. 2014; 82:1132–41.

75. Roy B, Ehlert L, Mullur R, Freeby MJ, Woo MA, Kumar R, et al. Regional brain gray matter changes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:9925.

76. Saczynski JS, Siggurdsson S, Jonsson PV, Eiriksdottir G, Olafsdottir E, Kjartansson O, et al. Glycemic status and brain injury in older individuals: the age gene/environment susceptibility-Reykjavik study. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1608–13.
77. Shibata D, Suchy-Dicey A, Carty CL, Madhyastha T, Ali T, Best L, et al. Vascular risk factors and findings on brain MRI of elderly adult American Indians: the Strong Heart Study. Neuroepidemiology. 2019; 52:173–80.

78. Sun Q, Chen GQ, Wang XB, Yu Y, Hu YC, Yan LF, et al. Alterations of white matter integrity and hippocampal functional connectivity in type 2 diabetes without mild cognitive impairment. Front Neuroanat. 2018; 12:21.

79. Suzuki H, Venkataraman AV, Bai W, Guitton F, Guo Y, Dehghan A, et al. Associations of regional brain structural differences with aging, modifiable risk factors for dementia, and cognitive performance. JAMA Netw Open. 2019; 2:e1917257.

80. Walsh EI, Shaw M, Sachdev P, Anstey KJ, Cherbuin N. The impact of type 2 diabetes and body mass index on cerebral structure is modulated by brain reserve. Eur J Neurol. 2019; 26:121–7.

81. Wood AG, Chen J, Moran C, Phan T, Beare R, Cooper K, et al. Brain activation during memory encoding in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a discordant twin pair study. J Diabetes Res. 2016; 2016:3978428.

82. Yau PL, Kluger A, Borod JC, Convit A. Neural substrates of verbal memory impairments in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2014; 36:74–87.

83. Zhang Y, Zhang X, Zhang J, Liu C, Yuan Q, Yin X, et al. Gray matter volume abnormalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without mild cognitive impairment. Neurosci Lett. 2014; 562:1–6.

84. Zhang YW, Zhang JQ, Liu C, Wei P, Zhang X, Yuan QY, et al. Memory dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus correlates with reduced hippocampal CA1 and subiculum volumes. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015; 128:465–71.

85. Peters R. Ageing and the brain. Postgrad Med J. 2006; 82:84–8.

86. Tabatabaei-Jafari H, Shaw ME, Cherbuin N. Cerebral atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2015; 1:487–504.

87. Henneman WJ, Sluimer JD, Barnes J, van der Flier WM, Sluimer IC, Fox NC, et al. Hippocampal atrophy rates in Alzheimer disease: added value over whole brain volume measures. Neurology. 2009; 72:999–1007.

88. Cherbuin N, Sachdev P, Anstey KJ. Higher normal fasting plasma glucose is associated with hippocampal atrophy: the PATH Study. Neurology. 2012; 79:1019–26.

89. Garfield V, Farmaki AE, Eastwood SV, Mathur R, Rentsch CT, Bhaskaran K, et al. HbA1c and brain health across the entire glycaemic spectrum. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021; 23:1140–9.

90. Li J, Shao YH, Gong YP, Lu YH, Liu Y, Li CL. Diabetes mellitus and dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014; 18:1778–89.
91. Vincent C, Hall PA. Executive function in adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analytic review. Psychosom Med. 2015; 77:631–42.
92. Zhou JB, Tang X, Han M, Yang J, Simo R. Impact of antidiabetic agents on dementia risk: a Bayesian network meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2020; 109:154265.

93. Srikanth V, Sinclair AJ, Hill-Briggs F, Moran C, Biessels GJ. Type 2 diabetes and cognitive dysfunction-towards effective management of both comorbidities. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020; 8:535–45.






 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download