Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Notes
References
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 2
Supplementary Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Study participants. DG, distal gastrectomy; PPG, pylorus-preserving gastrectomy; TG, total gastrectomy; QOL, quality of life.
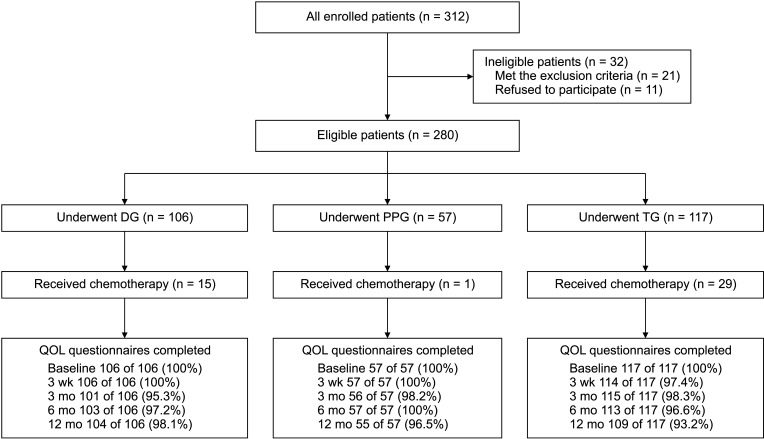
Fig. 2
Analysis of body weight loss. (A) Comparison of DGBI (n = 67) and DGBII/DGRY (n = 24). (B) Comparison of DG (n = 91), PPG (n = 56), and TG (n = 88). (C) Comparison of partial gastrectomy (n = 147) and partial gastrectomy with chemotherapy (n = 16). (D) Comparison of TG (n = 88) and TG with chemotherapy (n = 29). DGBI, DG with Billroth-I anastomosis; DGBII/DGRY, DG with Billroth-II/Roux-en-Y anastomosis; DG, distal gastrectomy; PPG, pylorus-preserving gastrectomy; TG, total gastrectomy; Chemo, chemotherapy. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
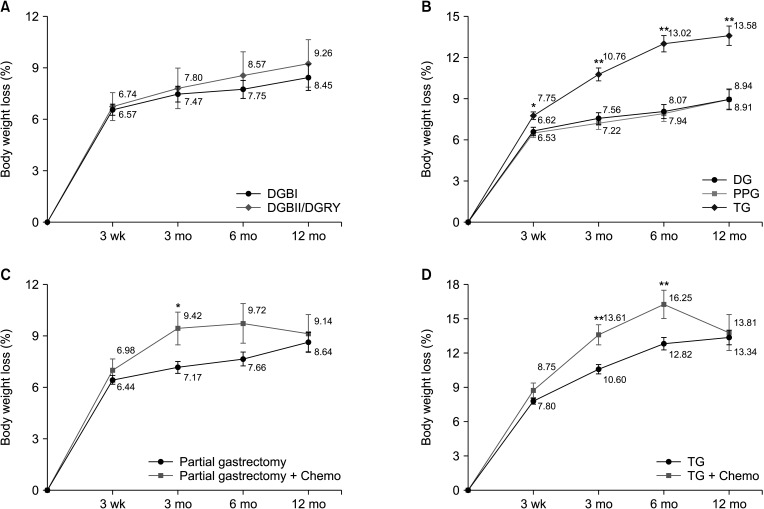
Fig. 3
(A) Radar chart representing mean scores of the EORTC QLQ-C30 global and functional scales among (a) DG, (b) PPG, and (c) TG (higher scores represent better QOL). (B) Radar chart representing mean scores of the EORTC QLQ-C30 symptoms scales among (a) DG, (b) PPG, and (c) TG (lower scores represent better QOL). DG, distal gastrectomy; PPG, pylorus-preserving gastrectomy; TG, total gastrectomy; EORTC QLQ, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QOL questionnaires; QOL, quality of life.
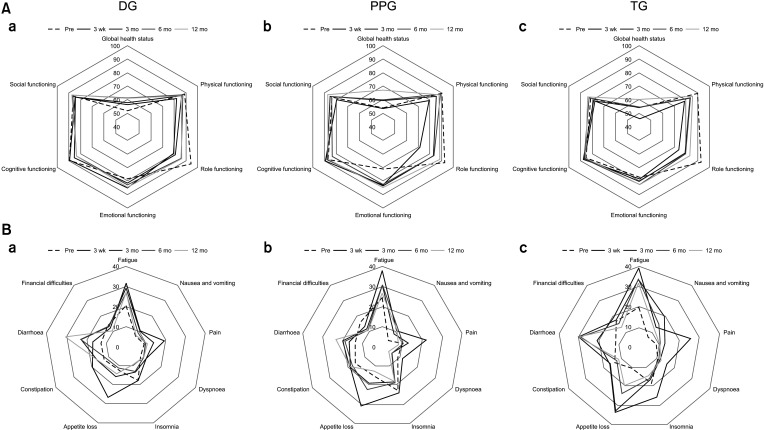
Fig. 4
(A) Radar chart representing mean scores of the EORTC QLQ-OG25 scales among (a) DG, (b) PPG, and (c) TG. (B) Radar chart representing mean scores of the EORTC QLQ-STO22 scales among (a) DG, (b) PPG, and (c) TG. Score of ‘body image’ = 100 – initial score of ‘body image.’ DG, distal gastrectomy; PPG, pylorus-preserving gastrectomy; TG, total gastrectomy; EORTC QLQ, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer quality of life questionnaires.
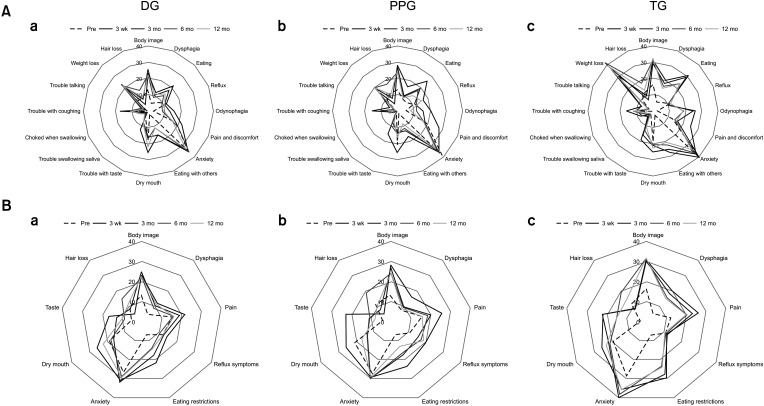
Table 1
Demographic features and clinical information of patients
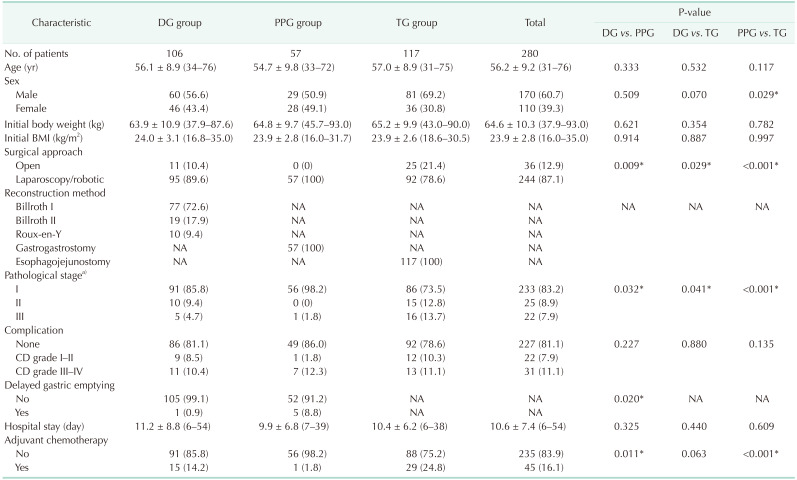
Values are presented as number only, mean ± standard deviation (range), or number (%).
DG, distal gastrectomy; PPG, pylorus-preserving gastrectomy; TG, total gastrectomy; BMI, body mass index; NA, not applicable; CD, Clavien-Dindo classification.
a)Classification according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer 8th edition.
*P < 0.05, statistically significant.
Table 2
Comparison of mean scores on EORTC QLQ-C30 among DG (n = 91), PPG (n = 56), and TG (n = 88), without chemotherapy
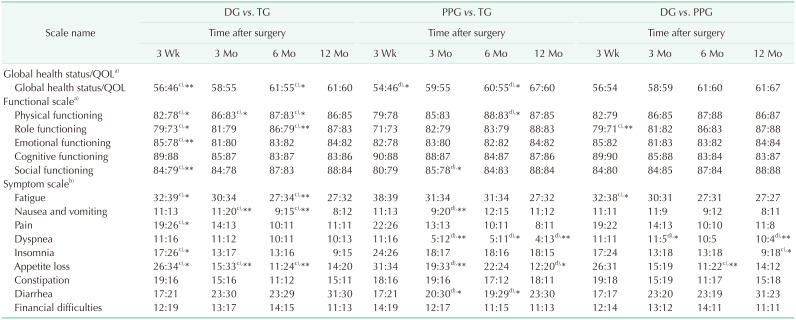
Values are presented as mean scores.
EORTC QLQ, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QOL questionnaires; DG, distal gastrectomy; TG, total gastrectomy; PPG, pylorus-preserving gastrectomy; QOL, quality of life.
a)Higher scores represent better QOL; b)lower scores represent better QOL; c)DG obtains better QOL in the comparison; d)PPG obtains better QOL in the comparison.
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Table 3
Comparison of mean scores on EORTC QLQ-OG25 and -STO22 among DG (n = 91), PPG (n = 56), and TG (n = 88), without chemotherapy
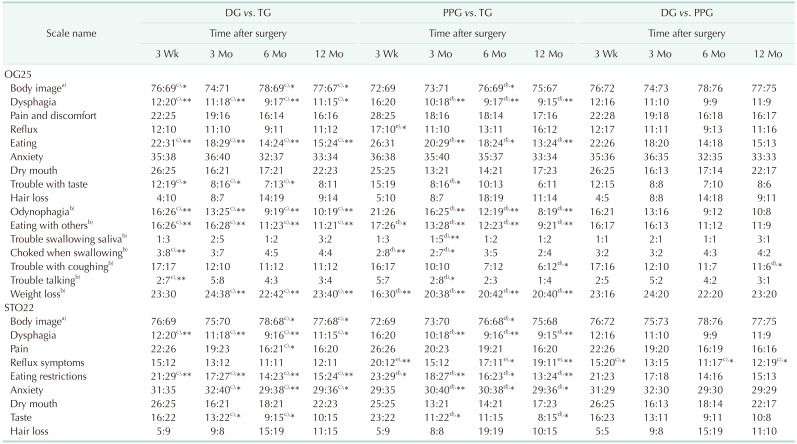
Values are presented as mean score.
EORTC QLQ, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QOL questionnaires; DG, distal gastrectomy; PPG, pylorus-preserving gastrectomy; TG, total gastrectomy; QOL, quality of life.
a)Higher scores represent better QOL; Others: lower scores represent better QOL. b)New scales in OG25 compared with STO22. c)DG obtains better QOL in the comparison; d)PPG obtains better QOL in the comparison; e)TG obtains better QOL in the comparison.
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Table 4
Comparison of mean scores on EORTC QLQ-C30 and -OG25 between chemotherapy group and chemo-free group
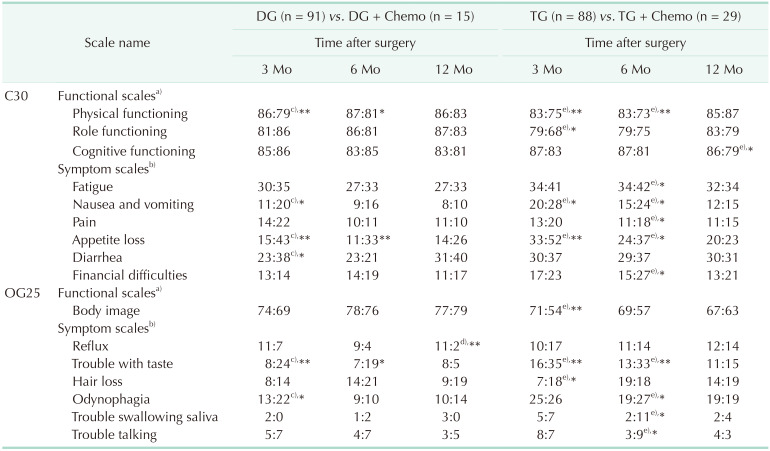
Values are presented as mean score.
EORTC QLQ, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QOL questionnaires; DG, distal gastrectomy; TG, total gastrectomy; Chemo, chemotherapy; QOL, quality of life.
a)Higher scores represent better QOL; b)Lower scores represent better QOL. c)DG obtains better QOL in the comparison; d)DG + Chemo obtains better QOL in the comparison; e)TG obtains better QOL in the comparison.
Only scales with statistical difference were showed; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download