INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and diets
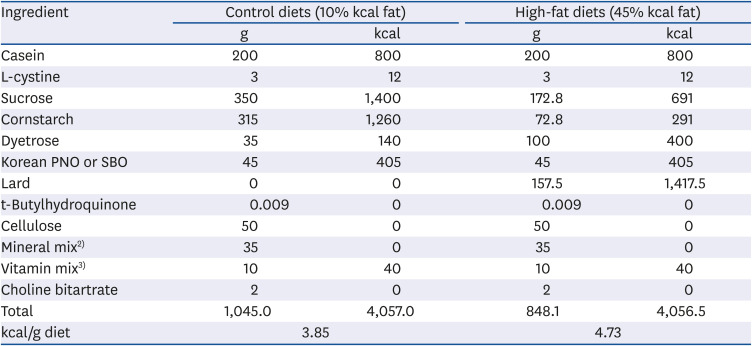
Table 1
Composition of the experimental diet1)
Determination of fecal triacylglycerol (TAG), non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs), and cholesterol concentrations
RNA extraction and complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis
Quantification of gene expression
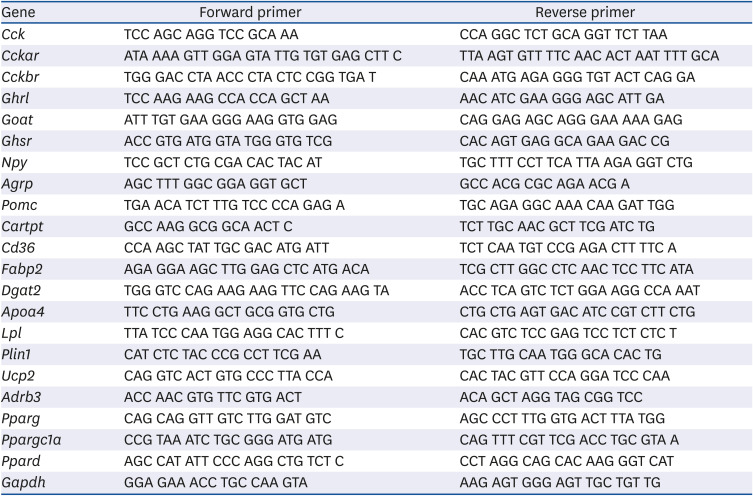
Table 2
The primer sequences used for real-time polymerase chain reaction
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Body weight change, food intake, feed efficiency, and WAT weight
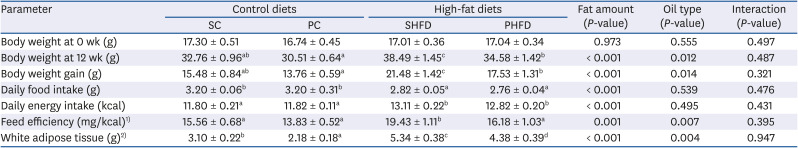
Table 3
Body weight, weight gain, food intake, feed efficiency, white adipose tissue weight, and serum leptin level
Fecal lipid concentrations
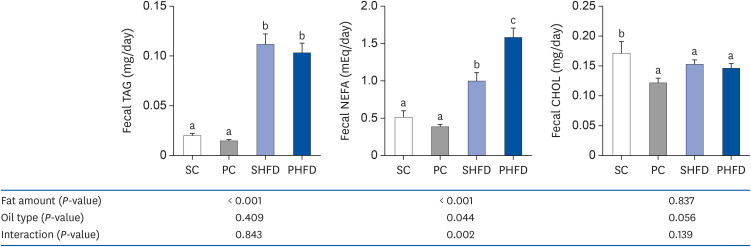 | Fig. 1Fecal triacylglycerol, non-esterified fatty acid, and cholesterol levels. Data are presented as means ± SEM, n= 7–14 for each group. Two-way analysis of variance was used to determine the significant effect of fat amount and oil type. Different letters indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 by Fisher's LSD multiple comparison test.SC, 10% soybean oil; PC, 10% pine nut oil; SHFD, 10% soybean oil + 35% lard; PHFD, 10% pine nut oil + 35% lard; TAG, triacylglycerol; NEFA, non-esterified fatty acid; CHOL, cholesterol.
|
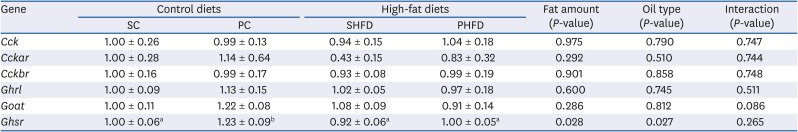
Expression of genes involved in appetite control
Table 4
The mRNA expression levels of cholecystokinin- and ghrelin-related genes
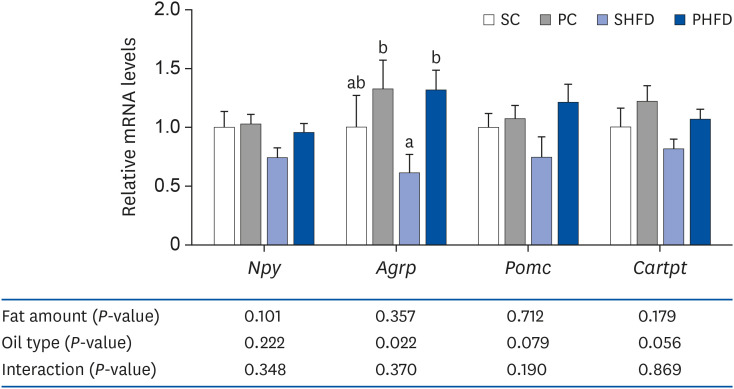 | Fig. 2The mRNA expression levels of neuropeptides (hypothalamic Npy, Agrp, Pomc, and Cartpt). Data are presented as means ± SEM, n= 5-6 for each group. Two-way analysis of variance was used to determine the significant effect of fat amount and oil type. Different letters indicate significant difference at P < 0.05 by Fisher's LSD multiple comparison test. All values are normalized to the levels of house-keeping gene Gapdh and expressed as relative mRNA level compared to the average expression level of SC group.mRNA, messenger RNA; SC, 10% soybean oil; PC, 10% pine nut oil; SHFD, 10% soybean oil + 35% lard; PHFD, 10% pine nut oil + 35% lard; Npy, neuropeptide Y; Agrp, agouti-related peptide; Pomc, pro-opiomelanocortin-alpha; Cartpt, cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript prepropeptide; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|
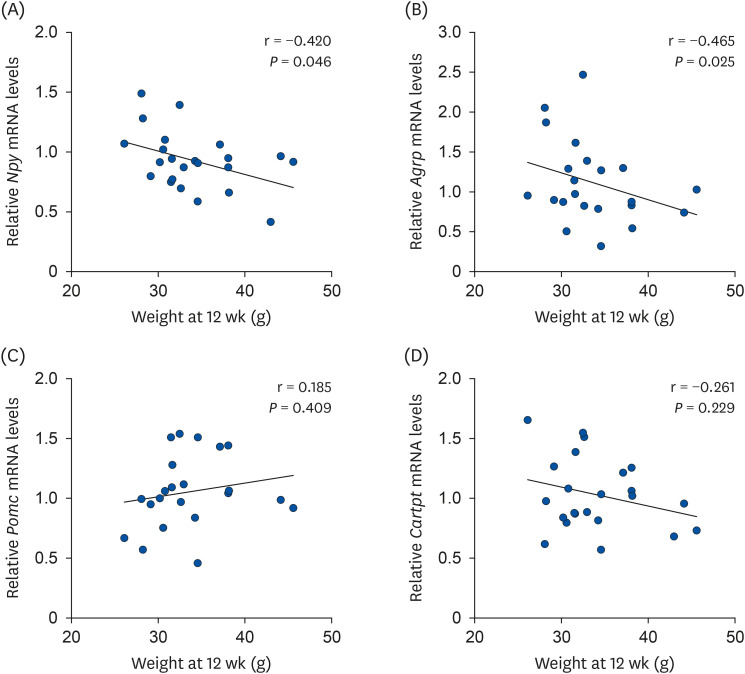 | Fig. 3Correlation between body weight and hypothalamic neuropeptide mRNA levels. Correlation between body weight and (A) Npy, (B) Agrp, (C) Pomc, and (D) Cartpt mRNA levels. Pearson's correlation was used to determine the linear relationship between variables.mRNA, messenger RNA; Npy, neuropeptide Y; Agrp, agouti-related peptide; Pomc, pro-opiomelanocortin-alpha; Cartpt, cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript prepropeptide.
|
Expression of genes involved in lipid absorption
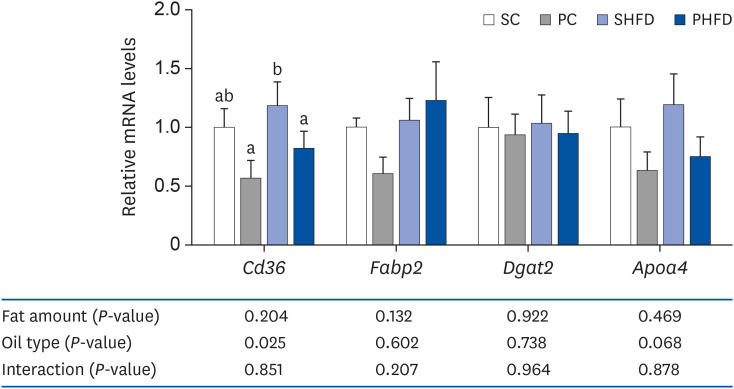 | Fig. 4The mRNA expression levels of genes associated with intestinal lipid metabolism (jejunal Cd36, Fabp2, Dgat2, and Apoa4). Data are presented as means ± SEM, n= 5–6 for each group. Two-way analysis of variance was used to determine the significant effect of fat amount and oil type. Different letters indicate significant difference, P < 0.05. All values are normalized to the levels of house-keeping gene Gapdh and expressed as relative mRNA level compared to the average expression level of SC group.mRNA, messenger RNA; SC, 10% soybean oil; PC, 10% pine nut oil; SHFD, 10% soybean oil + 35% lard; PHFD, 10% pine nut oil + 35% lard; Cd36, fatty acid translocase; Fabp2, fatty acid binding protein 2, intestinal; Dgat2, diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2; Apoa4, apolipoprotein A-IV; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|
Expression of genes involved in body fat accumulation
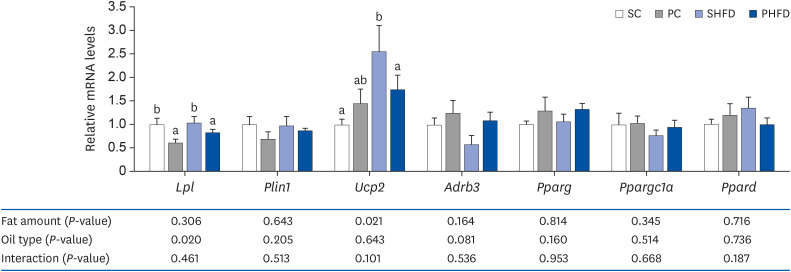 | Fig. 5The mRNA expression levels of genes associated with lipid metabolism in the white adipose tissue (epididymal Lpl, Plin1, Udp2, Adrb3, Pparg, Ppargc1a, and Ppard). Data are presented as means ± SEM, n = 5–6 for each group. Different letters indicate significant difference, P < 0.05. All values are normalized to the levels of house-keeping gene Gapdh and expressed as relative mRNA level compared to the average expression level of SC group.mRNA, messenger RNA; SC, 10% soybean oil; PC, 10% pine nut oil; SHFD, 10% soybean oil + 35% lard; PHFD, 10% pine nut oil + 35% lard; Lpl, lipoprotein lipase; Plin1, perilipin 1; Ucp2, mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2; Adrb3, β3 adrenergic receptor; Pparg, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; Ppargc1a, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha; Ppard, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download