INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Cell viability assay
In vitro immunocytochemistry
Animal care
In vivo energy metabolism test
In vivo antifatigue experimental design
Forced swimming test
In vivo measurement of biochemical parameters
Analysis of mRNA expression
Analysis of protein expression in vivo
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Effects of TR and GSE on the viability of L6 cells
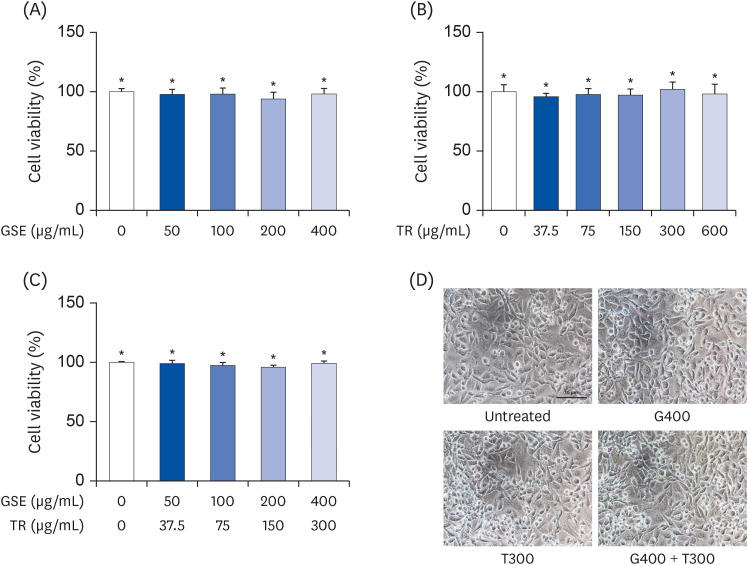 | Fig. 1Effects of TR and GSE on the viability of L6 cells. (A) The cells were treated with different concentrations (50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL) of GSE for 24 h. (B) L6 cells were incubated with different concentrations (37.5, 75, 150, 300, and 600 µg/mL) of TR for 24 h. (C) Cells were co- treated with different concentrations of GSE and TR for 24 h. (D) Cell morphology was observed using light microscopy. Data are expressed as the mean percentages (± SD) relative to the untreated group.GSE, ginseng extract; TR, taurine; G400, 400 µg/mL GSE; T300, 300 µg/mL TR.
*Denote no significant difference (P < 0.05; Tukey's multiple range test).
|
Effects of TR and GSE against exogenous H2O2-induced oxidative stress in L6 cells
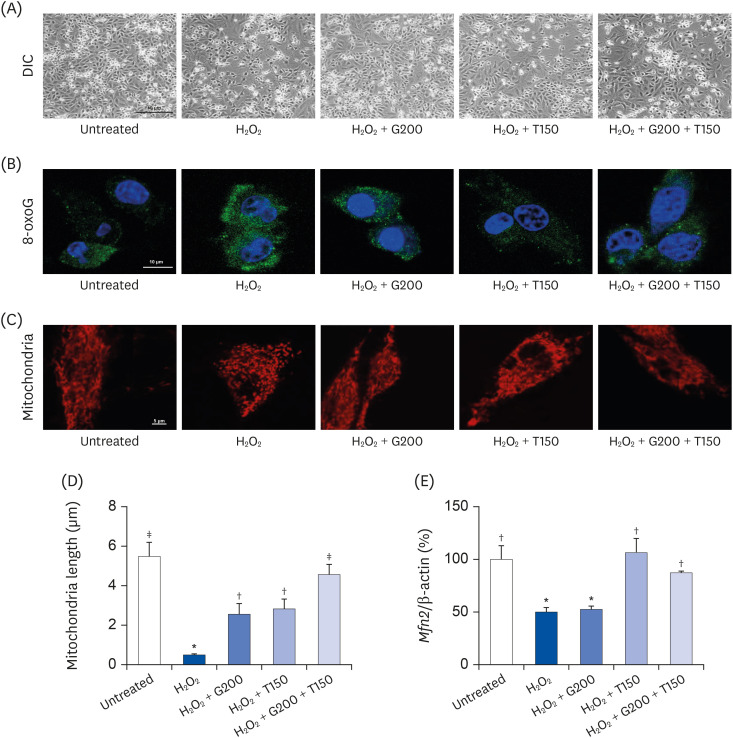 | Fig. 2Effects of TR and GSE on H2O2-stimulated L6 cells. (A) The images represent the cell morphology observed using light microscopy (200×). (B) Immunocytochemistry staining for 8-oxoG (green color). The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue color). (C) Fluorescence microscopy detection of mitochondria stained with Mito Tracker™ Red FM for 30 min. (D) The lengths of mitochondria measured in the panel (C) photographs. (E) Mfn2 mRNA expression. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD.TR, taurine; GSE, ginseng extract; 8-oxoG, 8-oxoguanine; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Mfn2, mitofusin-2; G200, 200 µg/mL GSE; T150, 150 µg/mL TR; DIC, differential interference contrast; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide.
*,†,‡Denote significant differences (P < 0.05; Tukey's multiple range test).
|
Effects of TR and GSE on mouse metabolism during acute exercise
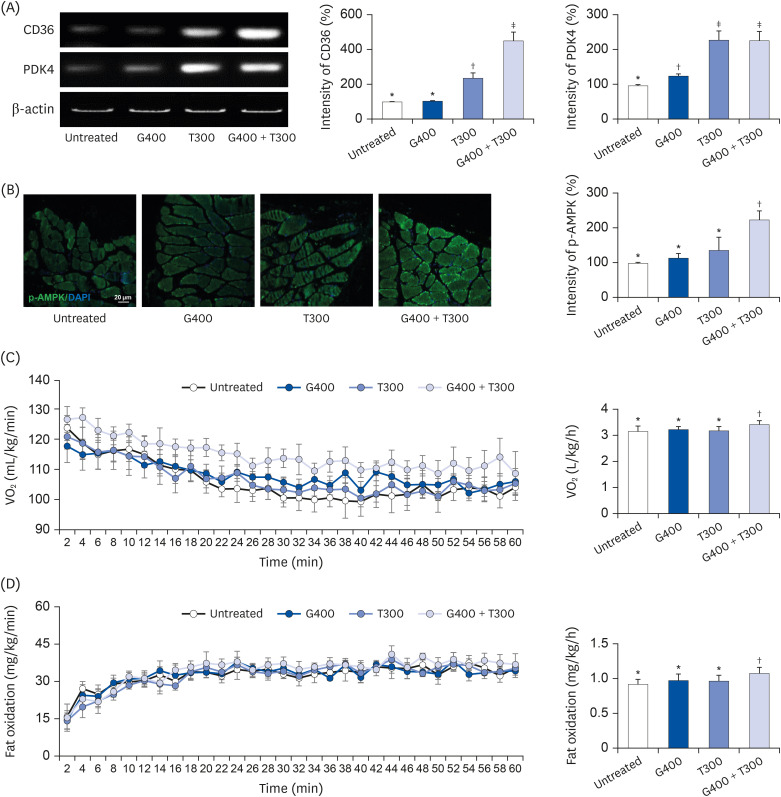 | Fig. 3Effects of TR and GSE on oxygen uptake and fat metabolism in mice during acute exercise. (A) CD36 and Pdk4 mRNA expression measured using reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction. The graphs indicate the band intensity relative to that in the untreated group. (B) Immunohistochemical staining for p-AMPK. The graph shows the intensity of p-AMPK in muscle tissue. (C) Oxygen uptake data using an open-circuit method at 2-min intervals during exercise for 1 h. (D) Measurement of fat metabolism using the open-circuit method during exercise for 1 h. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD.TR, taurine; GSE, ginseng extract; CD36, cluster of differentiation 36; Pdk4, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4; p-AMPK, phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase; G400, 400 mg/kg GSE; T300, 300 mg/kg TR; VO2, volume of oxygen.
*,†,‡Denote significant differences (P < 0.05; Tukey's multiple range test).
|
Effects of TR and GSE on tissue glycogen content in mice
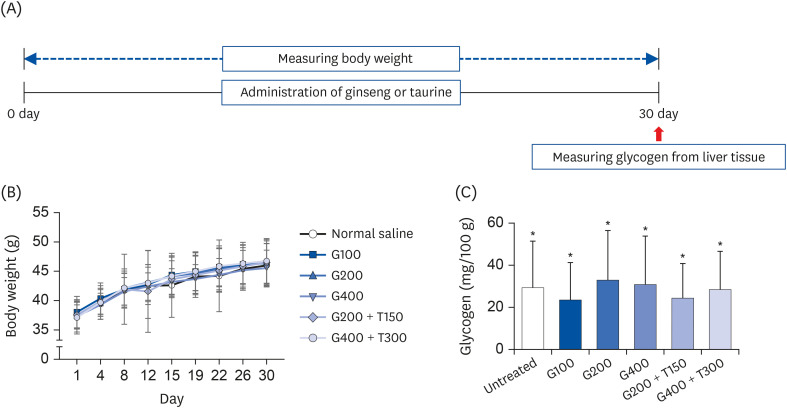 | Fig. 4Body weight and tissue glycogen levels in mice. (A) Schematic workflow for the 30-day experiment. (B) Body weight changes in mice over a period of 30 days. (C) The bar graphs indicate the glycogen levels. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD.TR, taurine; GSE, ginseng extract; G100, 100 mg/kg/day GSE; G200, 200 mg/kg/day GSE; G400, 400 mg/kg/day GSE; T150, 300 mg/kg/day TR; T300, 300 mg/kg/day TR.
*Denote no significant difference (P < 0.05; Tukey's multiple range test).
|
Effects of TR and GSE on fatigue-related parameters in mice after swimming
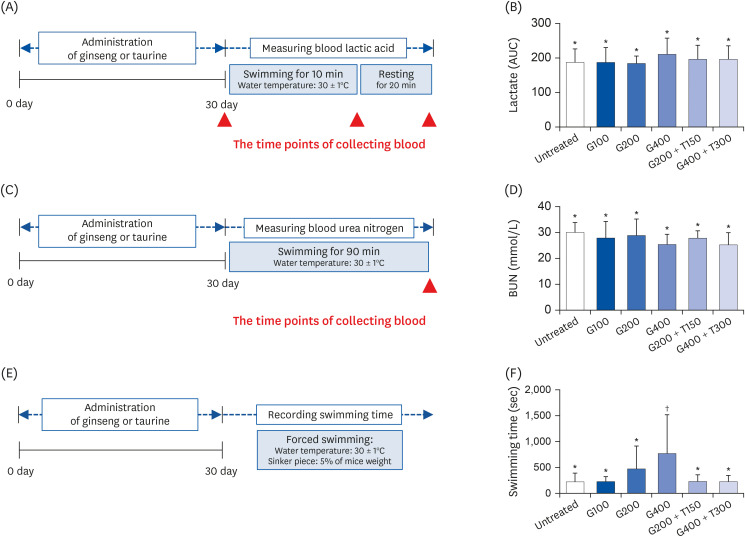 | Fig. 5Analysis of biochemical parameters after the swimming exercise in mice treated for 30 days. (A) Schematic workflow for measuring the blood lactic acid levels. (B) Blood lactic acid levels in each group. (C) Schematic workflow for measuring the BUN levels. (D) BUN levels in each group after swimming. (E) Schematic workflow for recording the duration of forced swimming. (F) Duration of forced swimming in each group. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD.TR, taurine; GSE, ginseng extract; G100, 100 mg/kg/day GSE; G200, 200 mg/kg/day GSE; G400, 400 mg/kg/day GSE; T150, 150 mg/kg/day TR; T300, 300 mg/kg/day TR; AUC, area under the curve; BUN, blood urea nitrogen.
*,†Denote significant differences (P < 0.05; Tukey's multiple range test).
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download