Introduction
Background/rationale
Objectives
Methods
Ethics statement
Study design
Setting
Participants
Variables
Data sources/measurement
Study size
Statistical methods
Results
Participants
Main results
Table 1.
The variables of the effect are as follows: person (p), case (c), and item (i). The model of p*(i:c) were used in G-string ver. 6.3.8 (Ralph Bloch, Hamilton, ON, Canada). Phi-coefficient=0.689. G-coefficient=0.758.
df, degrees of freedom; SS, sum of squares; MS, mean square; VC, variance components.
Table 2.
| Effect | df | T-value | SS | MS | VC | % of VC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | 106 | 52.73098 | 52.73097 | 0.49746 | 0.01289 | 7.32 |
| I | 27 | 80.73565 | 80.73565 | 2.99021 | 0.02667 | 15.14 |
| pi | 2,862 | 524.23098 | 390.76435 | 0.13654 | 0.13654 | 77.54 |
Predicted cut score of each station by the norm-referenced standard setting method, BGM, and BRM
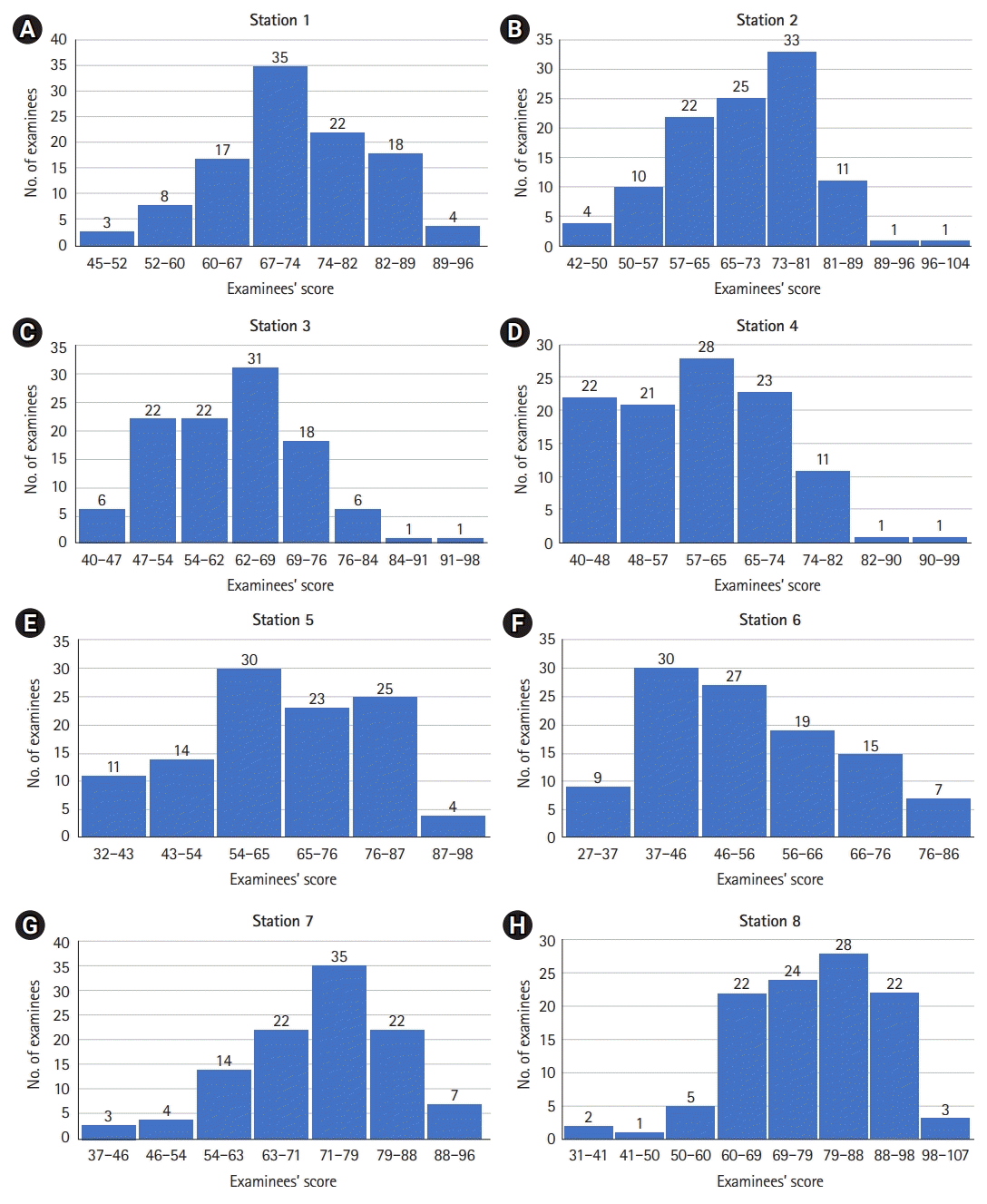 | Fig. 1.(A–H) The histogram of each station in objective structured clinical examination (OSCE). The x-axis is the examinees’ scores, and the y-axis is the number of examinees. A total of 107 examinees participated in each station, and the number indicated on the bar is the number of examinees in the corresponding score section. |
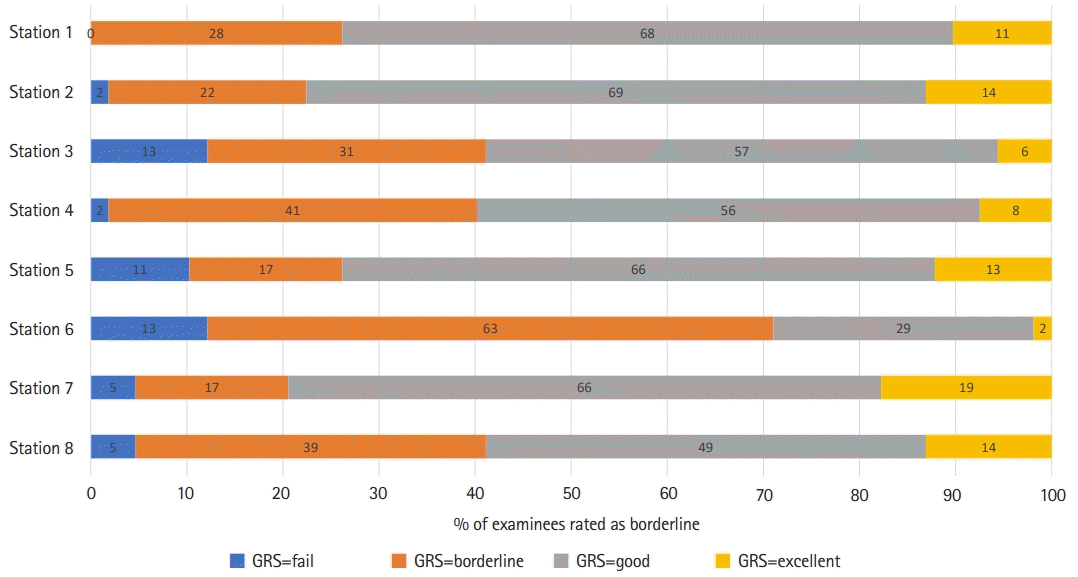 | Fig. 2.The proportion of examinees rated as the borderline group of each station in the objective structured clinical examination. The number presented on the on colored bar is the percentage of examinees rated as borderline. The x-axis is the percentage of rated as borderline and y-axis is station number. GRS, global rating scale. |
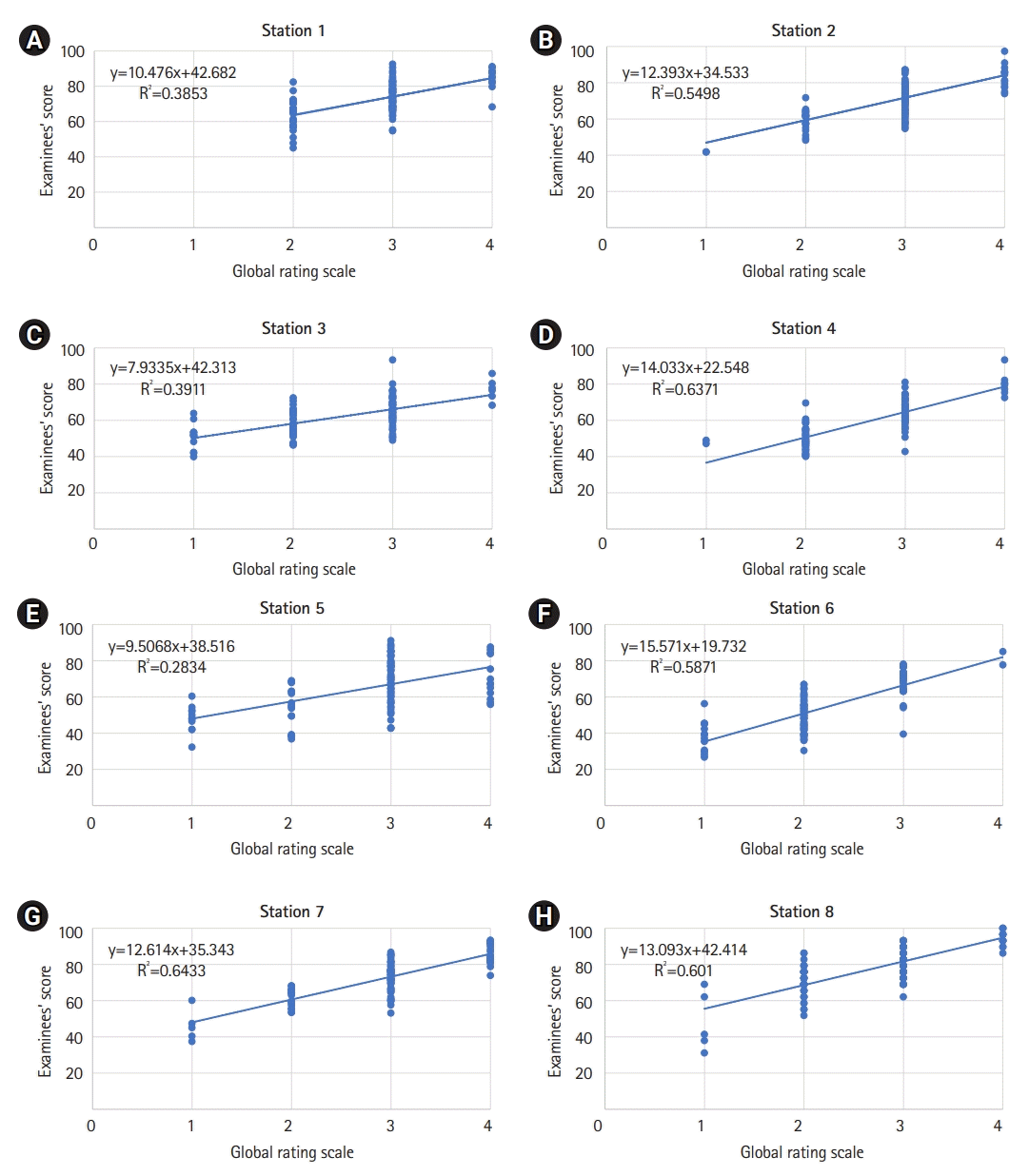 | Fig. 3.(A–H) The regression plot of each station in the objective structured clinical examination. The x-axis is the global rating scale, and the y-axis is the examinees’ score at each station. The regression equation and the correlation of determination (R2) are presented. |
Table 3.
| Variable | Station 1 | Station 2 | Station 3 | Station 4 | Station 5 | Station 6 | Station 7 | Station 8 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSCE score | |||||||||
| Maximum | 92.48 | 97.33 | 93.33 | 93.33 | 91.11 | 85.06 | 93.33 | 92.48 | |
| Minimum | 45.03 | 41.75 | 39.89 | 40 | 32.22 | 26.67 | 37.44 | 45.03 | |
| Mean | 72.45 | 70.32 | 62.33 | 59.8 | 64.73 | 53.78 | 72.24 | 72.45 | |
| SD | 9.88 | 10.6 | 9.91 | 11.35 | 14.27 | 13.43 | 11.37 | 9.88 | |
| Number rated as borderline | 28 | 22 | 31 | 41 | 17 | 63 | 17 | 39 | |
| % rated as borderline | 26.17 | 20.56 | 28.97 | 38.32 | 15.89 | 58.88 | 15.89 | 36.45 | |
| Norm-referenced method (below one SD from mean) | |||||||||
| Predicted cut score | 62.57 | 59.72 | 52.42 | 48.44 | 50.46 | 40.36 | 60.87 | 64.54 | |
| Number below standard | 15 | 17 | 19 | 22 | 18 | 21 | 19 | 13 | |
| % below standard | 14.02 | 15.89 | 17.76 | 20.56 | 16.82 | 19.63 | 17.76 | 12.15 | |
| Borderline group method | |||||||||
| Predicted cut score | 65.64 | 61.5 | 56.08 | 48.49 | 54.67 | 51.07 | 63 | 68.97 | <0.01a) |
| Number below standard | 20 | 20 | 33 | 22 | 29 | 48 | 21 | 30 | |
| % below standard | 18.69 | 18.69 | 30.84 | 20.56 | 27.1 | 44.86 | 19.63 | 28.04 | |
| Borderline regression method | |||||||||
| Predicted cut score | 63.63 | 59.32 | 58.18 | 50.61 | 57.53 | 50.87 | 60.57 | 68.6 | <0.02a) |
| Number below standard | 17 | 17 | 37 | 27 | 36 | 47 | 18 | 16 | 0.99b) |
| % below standard | 14.85 | 14.85 | 32.32 | 22.71 | 20.09 | 38.43 | 17.47 | 12.15 |
OSCE stations 1–7 were interview-based examination and OSCE station 8 was skill-based examination. The P-value of <0.05 was considered significant.
OSCE, objective structured clinical examination, SD, standard deviation.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download