Abstract
Purpose:
Active learning methods such as problem-based learning have been widely adopted in health professions education, although guided inquiry learning has been used only in limited settings. The objective of this study was to determine students’ learning gain when guided inquiry learning was combined with computer simulation in a basic pharmacology course.
Methods:
The second-year pharmacy students from Fiji National University participated in the study. Following classroom lectures on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, the students used tutor-prepared practice problems in groups of 3-4 to explore their concepts with Cyber Patient and Virtual Organ Bath software. Pre- and posttest assessments were administered to determine the learning gain from the exercises based on Hake’s criteria.
Results:
Forty-two students participated in the study. The average normalized learning gain from the pharmacokinetics exercises was 0.68. Thirty-seven participants (88.1%) achieved a significant learning gain, while 5 (11.90%) did not. The average normalized learning gain from the pharmacodynamics exercises was 0.76. Forty-one participants (97.6%) achieved a significant learning gain, while one participant (2.4%) did not.
Go to : 
Process-oriented guided inquiry learning (POGIL), which had its origin in chemistry education in the 1990s, has been increasingly introduced into health professions education [1]. It was originally based on the three-stage model of the learning cycle proposed by Abraham and Renner [2] in 1986, with the proposition that “the normal learning cycle sequence is the optimum sequence for achievement of content knowledge.” Whereas problem-based learning (PBL) is well established in the curricula of many medical schools and schools of health professions, POGIL is still not widely established, but has been applied increasingly in laboratory courses in medicinal chemistry, anatomy and physiology, and forensic science. POGIL is tutor-led, and builds on a student’s prior knowledge. Through a series of carefully designed questions, it guides a student to develop concepts about a real-life issue. The learner also acquires process skills such as time management, resource exploration, and interpersonal skills. Pharmacology is a mandatory course for pharmacy students at Fiji National University. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are taught early in the pharmacology course. The challenges were how to encourage the students to develop critical thinking and problem solving skills in pharmacology. To this end, guided inquiry learning and computer simulation exercises were introduced for some topics in the pharmacology course for second-year students in the Bachelor of Pharmacy Program. This study assessed the impact of the exercises on the students’ learning gain.
Go to : 
This study was done with second-year bachelor of pharmacy students of the 2011 and 2012 classes of the College of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, Fiji National University,
Suva, Fiji. All of the second year students of the pharmacy program participated in this study.
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are among the first topics addressed in pharmacology class and are usually delivered by traditional lecture-based didactic pedagogy. The lectures are usually supplemented with simulated practical sessions with CyberPatient 2007 software developed by Labsoft Solutions (Simulation Plus, Lancaster, CA, USA) and Virtual Organ Bath computer software from Spider Science, University of Strathclyde, United Kingdom. These software applications could be freely downloaded without licenses from: http://www.labsoft.com/www/software.html and http://spider.science.strath.ac.uk/sipbs/showPage.php?page=software_sims.
Classroom lectures were first given on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics and then followed up with simulation practical classes. The students were briefed on the nature of the practice sessions and the roles of the team members in the process; then the simulation programs were demonstrated to the students by the tutors. They were then separated into groups of 3-4 students in each team. Each team chose a leader, whose roles included ensuring that the sessions were completed on time and that each member of the team was fully engaged in the group activities. A recorder, also chosen by the group, was responsible for all documentation of results and conclusions, as well as the completed report for tutor feedback; an operator from the group carried out the computer simulation activities with the full participation of all team members. The teams used tutor-generated practice problems to explore the concepts. They applied their findings to solve the following: pharmacokinetic problems such as defining types of compartmental models, evaluating the effects of different drug formulations (different Ka’s) on absorption and plasma concentrations; pharmacodynamics problems such as determination of dose-response relationships, defining the types of antagonist used, and bioevaluation of unknown drugs.
Analysis: Their observations and conclusions were recorded and the reports were submitted to the tutors for marking and tutor feedback. Pre- and posttests of 10 pharmacokinetics and 10 pharmacodynamics items were used to assess the learning gain of the students after the simulation exercises. A paired sample Student’s t-test was used to compare the pretest and posttest scores of the students using Prism Graph Pad 6 statistical software, and a P-value<0.01 was considered statistically significant. The learning gain for the whole study group was determined based on Hake’s criteria, with a class average normalized gain (g) ≥ 0.30 considered significant. Individual students’ learning gain values (gi) were calculated as follows [2-4]:
gi=(%posttest-%pretest)/(100-%pretest), while the class average normalized gain was calculated as: g=1/NΣ gi=1/NΣ (%posttest-%pretest)/(100-%pretest).
Go to : 
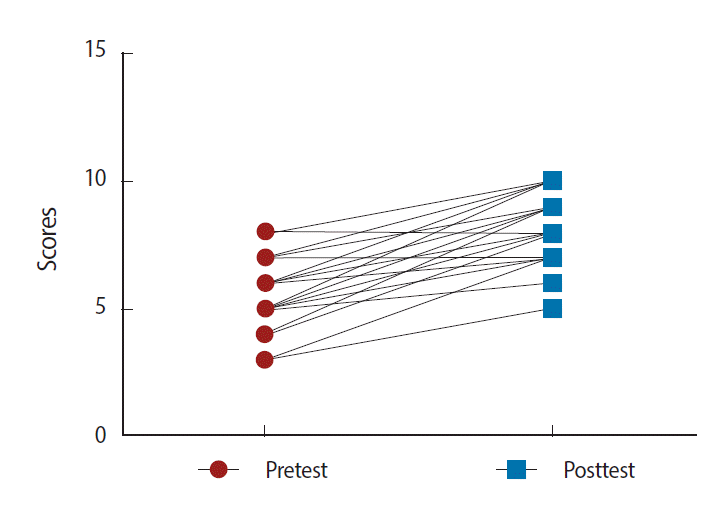
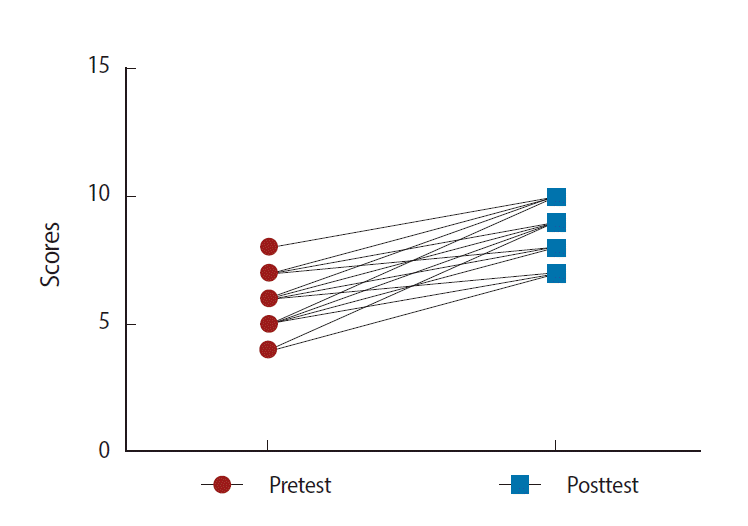
Forty-two students comprising 20 students from the 2011 class and 22 students from the 2012 class participated in the study. The mean posttest score for pharmacokinetics (8.57± 1.192) was significantly higher than the mean pretest score (5.643±1.322; Fig. 1, P<0.001). The average normalized learning gain of the students was 0.68 (SD=0.27) with learning gain values for individual students ranging from 0.00 to 1.00, a median value of 0.67, a 25th percentile value of 0.50 and 75th percentile value of 1.00. Based on Hake’s criteria, 88.1% of the students (37/42) achieved significant learning gains (≥0.30), while only 11.90% (5/42) did not. Similarly, the mean posttest score for pharmacodynamics (8.98±0.92) was significantly higher than the mean pretest score (6.24±0.95; Fig. 2, P<0.001). The average normalized learning gain from the pharmacodynamics exercises was 0.76 with values ranging from 0.25 to 1.00. Forty-one of the participants (97.6%) achieved a significant learning gain (≥0.30), with only 1 participant (2.4%) not achieving a significant learning gain by Hake’s criteria.
Go to : 
Several research reports have demonstrated successful application of active learning methodologies in teaching pharmacology courses to health science students [1, 5]. Together with the adoption of active learning methods, there has come increasing application of technology in education, and several studies have demonstrated good outcomes when educational experience with these technologies was measured in terms of user satisfaction [6, 7]. The results of this study demonstrated significant learning gains when process-oriented guided inquiry learning was integrated with computer simulations in basic pharmacology education in our setting. The students’ performances on the pretest and posttest assessments showed that they achieved deep learning through the exercises and were able to apply these concepts to solving pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics problems. By Kirkpatrick’s four-level model of training evaluation, the pretest and posttest assessments represent level 2 evaluation, which measures “learning” or more precisely, the increase in knowledge that is attributable to the educational experience [8, 9]. This level is presumably a higher order measure of learning outcomes compared to measures of participants’ reactions to an educational exercise, which has been assigned to level 1 in this model.
The possible limitation of this study is that the data were obtained from students in a pharmacy program whose pharmacology content is different from those of other health professions programs, so that the results may not be generalized to those other programs. However, it does demonstrate that the combination of guided inquiry learning and computer simulations could significantly improve students’ pharmacology learning outcomes in any pharmacy program. The software programs used in the study were obtained free of charge or license commitments, and the practice sessions were simple to administer, making this an attractive instructional method for health professional education institutions. Furthermore, we recommend this model not only for other pharmacology modules but also for other science programs with substantial pharmacology content.
In conclusion, the use of the process-oriented guided inquiry technique further enhanced the students’ process and team skills, enabling them to take greater possession of their learning and enhanced their analytical abilities. The continued participation of all the students in the exercises up to the end, and their enthusiastic quest to explore the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics issues was an eloquent expression of their interest in the computer exercises, which some of them likened to a computer game.
Go to : 
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are thankful to the staff of the Information Technology Unit and library of the Fiji School of Medicine for installing the software applications.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Stewart DW, Brown SD, Clavier CW, Wyatt J. Active-learning processes used in US pharmacy education. Am J Pharm Educ. 2011; 75:68. http://dx.doi.org/10.5688/ajpe75468.

2. Abraham MR, Renner JW. The sequence of learning cycle activities in high school chemistry. J Res Sci Teach. 1986; 23:121–143. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/tea.3660230205.

3. Colt HG, Davoudi M, Murgu S, Zamanian Rohani N. Measuring learning gain during a one day introductory bronchoscopy course. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:207–216. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1161-4.
4. Hake RR. Interactive-engagement versus traditional methods: a six-thousand-student survey of mechanics test data for introductory physics courses. Am J Phys. 1998; 66:64–74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1119/1.18809.

5. Kwan CY. Problem-based learning and teaching of medical pharmacology. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002; 366:10–17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00210-002-0561-y.

6. Persky AM. Multi-faceted approach to improve learning in pharmacokinetics. Am J Pharm Educ. 2008; 72:36. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2384211/.

7. Premkumar K, Coupal C. Rules of engagement-12 tips for successful use of “clickers” in the classroom. Med Teach. 2008; 30:146–149. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01421590801965111.

8. Alliger GM, Janak EA. Kirkpatrick’s levels of training criteria: thirty years later . Pers Psychol. 1989; 42:331–342. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.1989.tb00661.x.

9. Blanchard PN, Thacker JW, Way SA. Training evaluation: perspectives and evidence from Canada. Int J Train Dev. 2000; 4:295–304. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/1468-2419.00115.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download