INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study population
Use of RAAS inhibitors
Study outcomes
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Characteristics of the study participants
Fig. 1.
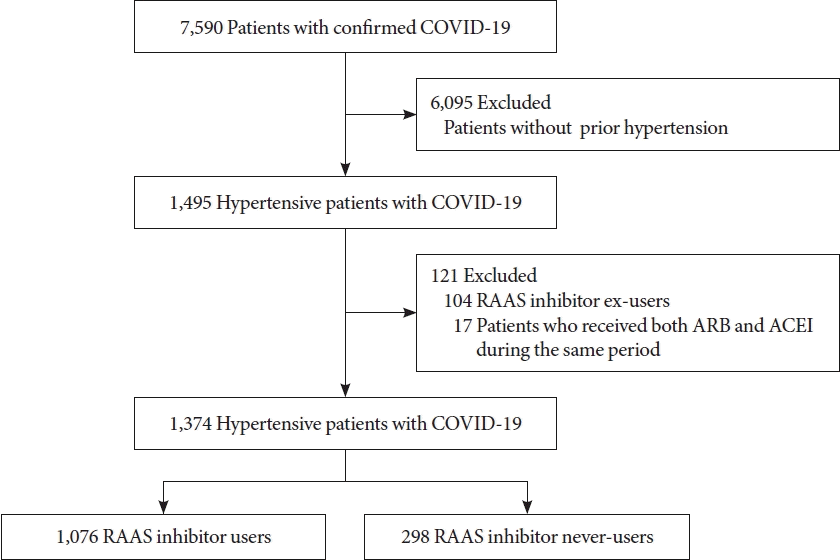
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Total (n=1,374) | RAAS inhibitor users (n=1,076) | RAAS inhibitor never-users (n=298) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 65.0±13.2 | 64.5±12.8 | 66.7±14.9 | 0.017 | |
| <65 | 727 (52.9) | 599 (55.7) | 128 (43.0) | ||
| ≥65 | 647 (47.1) | 477 (44.3) | 170 (57.0) | ||
| Men | 569 (41.4) | 459 (42.7) | 110 (36.9) | 0.075 | |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 799 (58.2) | 653 (60.7) | 146 (49.0) | <0.001 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 699 (50.9) | 581 (54.0) | 118 (39.6) | <0.001 | |
| Cardiovascular diseasea | 594 (43.2) | 454 (42.2) | 140 (47.0) | 0.140 | |
| Chronic kidney disease | 55 (4.0) | 46 (4.3) | 9 (3.0) | 0.328 | |
| Chronic pulmonary diseaseb | 275 (20.0) | 210 (19.5) | 65 (21.8) | 0.381 | |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 2.00±1.57 | 2.01±1.56 | 1.95±1.58 | 0.813 | |
| Medications | |||||
| Diuretics | 366 (26.6) | 323 (30.0) | 43 (14.4) | <0.001 | |
| Calcium channel blocker | 705 (51.3) | 539 (50.1) | 166 (55.7) | 0.086 | |
| β-Blocker | 204 (14.9) | 143 (13.3) | 61 (20.5) | 0.002 | |
| Metformin | 326 (23.7) | 279 (25.9) | 47 (15.8) | <0.001 | |
| Sulfonylurea | 140 (10.2) | 123 (11.4) | 17 (5.7) | 0.004 | |
| Thiazolidinedione | 35 (2.6) | 29 (2.7) | 6 (2.0) | 0.509 | |
| DPP-4 inhibitor | 199 (14.5) | 174 (16.2) | 25 (8.4) | 0.001 | |
| SGLT2 inhibitor | 31 (2.3) | 28 (2.6) | 3 (1.0) | 0.101 | |
| GLP-1 receptor agonist | 7 (0.5) | 7 (0.7) | 0 | 0.358 | |
| Insulin | 26 (1.9) | 23 (2.1) | 3 (1.0) | 0.205 | |
| Statin | 654 (47.6) | 542 (50.4) | 112 (37.6) | <0.001 | |
| Antithrombotic agent | 389 (28.3) | 305 (28.4) | 84 (28.2) | 0.957 | |
| Inhaled corticosteroids | 102 (7.4) | 77 (7.2) | 25 (8.4) | 0.472 | |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1.
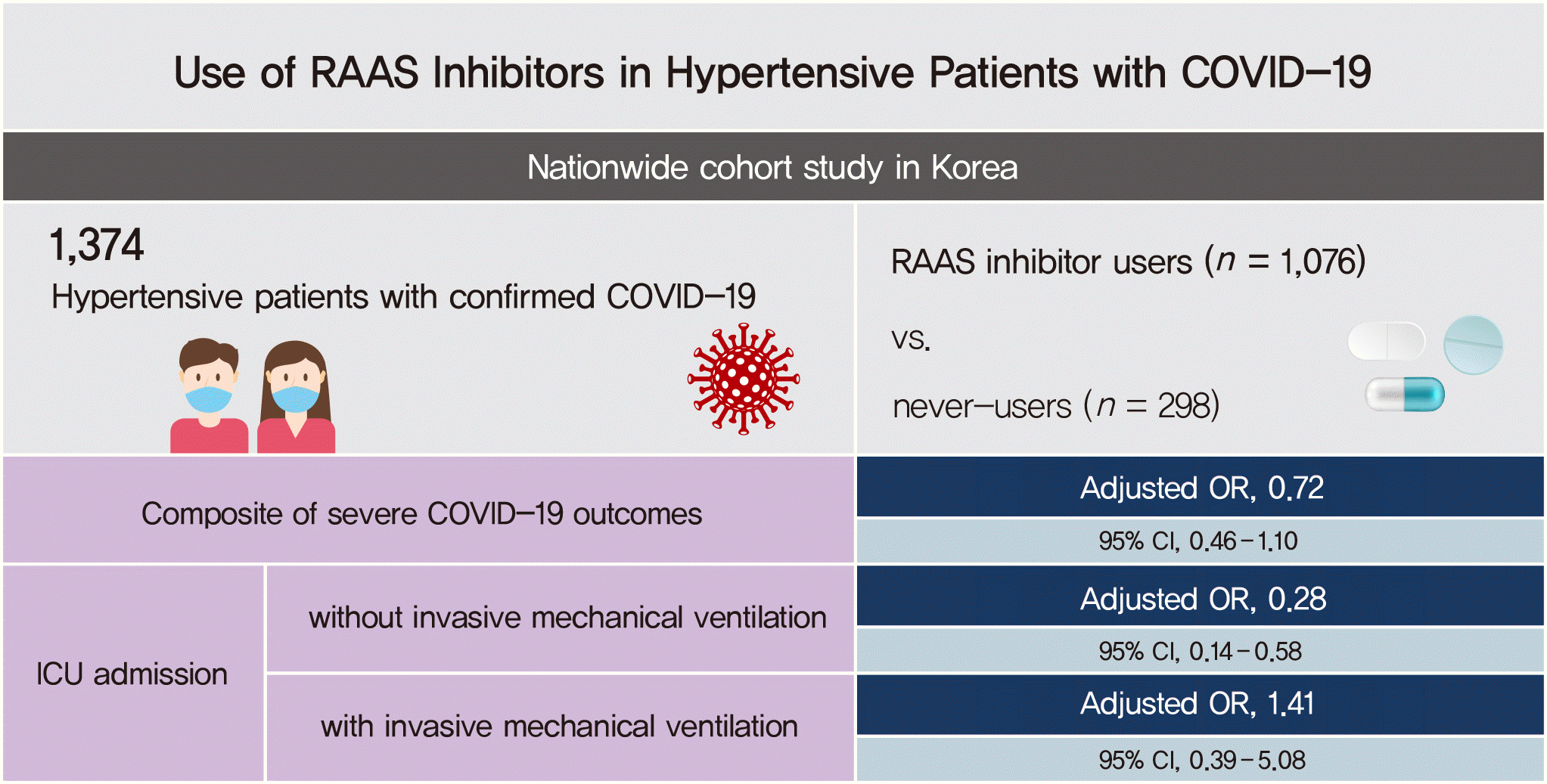
Severe outcomes of COVID-19
Table 2.
| Outcomes (vs. RAAS inhibitor never-users) |
RAAS inhibitors (n=1,076) |
ARB (n=1,037) |
ACEI (n=39) |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of events (%) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI)b | No. of events (%) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI)b | No. of events (%) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI)b | |||
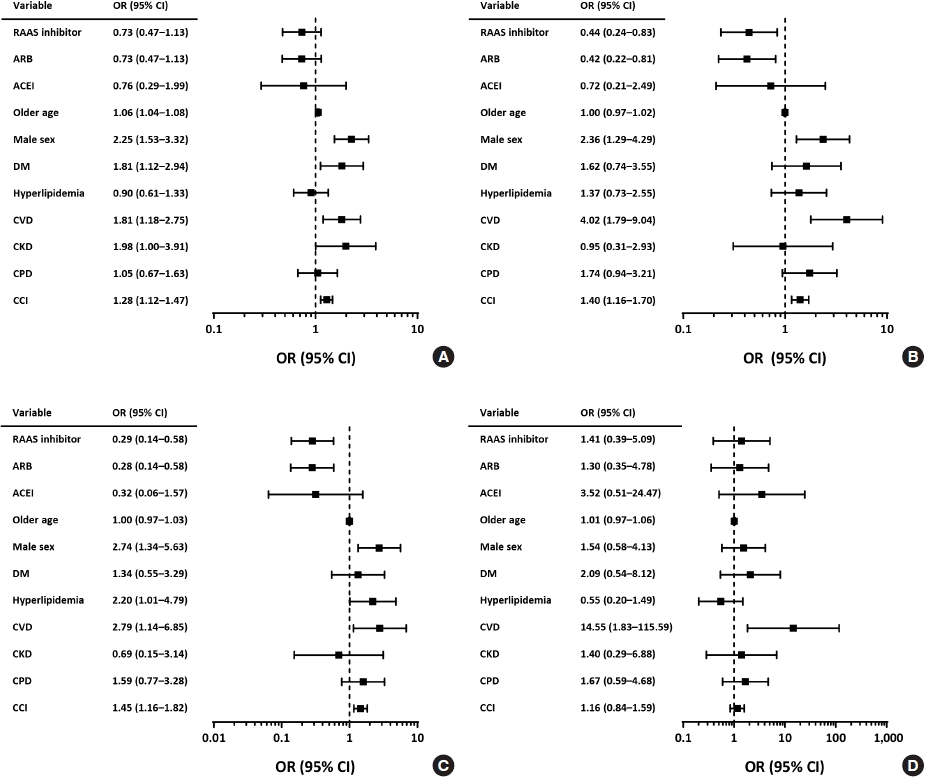
| Primary outcomea (n=144) | 106 (9.9) | 0.75 (0.50–1.11) | 0.72 (0.46-1.10) | 99 (9.6) | 0.72 (0.49–1.08) | 0.71 (0.46–1.10) | 7 (18.0) | 1.50 (0.62–3.63) | 0.81 (0.31–2.11) | ||
| Secondary outcomes | |||||||||||
| ICU admission (n=52) | 34 (3.2) | 0.51 (0.28–0.91) | 0.44 (0.24–0.84) | 30 (2.9) | 0.46 (0.26–0.84) | 0.42 (0.22–0.81) | 4 (10.3) | 1.78 (0.57–5.55) | 0.72 (0.21–2.48) | ||
| Not requiring IMV (n=34) | 21 (2.0) | 0.35 (0.18–0.68) | 0.28 (0.14–0.58) | 19 (1.8) | 0.33 (0.17–0.65) | 0.28 (0.14–0.58) | 2 (5.1) | 0.96 (0.21–4.31) | 0.31 (0.06–1.56) | ||
| Requiring IMV (n=17) | 14 (1.3) | 1.30 (0.37–4.54) | 1.41 (0.39–5.08) | 12 (1.2) | 1.15 (0.32–4.11) | 1.30 (0.36–4.76) | 2 (5.1) | 5.32 (0.86–32.86) | 3.57 (0.52–24.71) | ||
| IMV (n=17) | 14 (1.3) | 1.30 (0.37–4.54) | 1.41 (0.39–5.08) | 12 (1.2) | 1.15 (0.31–4.11) | 1.30 (0.36–4.76) | 2 (5.1) | 5.32 (0.86–32.86) | 3.57 (0.52–24.71) | ||
| CRRT (n=0) | 0 | NA | NA | 0 | NA | NA | 0 | NA | NA | ||
| ECMO (n=1) | 1 (0.1) | NA | NA | 1 (0.1) | NA | NA | 0 | NA | NA | ||
| Death (n=106) | 82 (7.6) | 0.94 (0.59–1.51) | 1.09 (0.64–1.85) | 79 (7.6) | 0·94 (0.59–1.52) | 1.12 (0.66–1.90) | 3 (7.7) | 0.95 (0.27–3.32) | 0.62 (0.17–2.35) | ||
RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; ARB, angiotensin-receptor blocker; ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ICU, intensive care unit; IMV, invasive mechanical ventilation; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy; NA, not applicable; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
a The primary outcome was defined as the composite of ICU admission, IMV, CRRT, ECMO, and death from coronavirus disease 2019,
b Adjusted variables included age; sex; comorbidities, including diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and chronic pulmonary disease; medications, including antihypertensive, glucose-lowering, lipid-lowering, and antithrombotic agents; and the Charlson Comorbidity Index.
Risk factors for the primary composite outcome and ICU admission
Fig. 2.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download