INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Participants
Clinical characteristics
Laboratory measurements
Assessment of β-cell function and insulin resistance
Autoantibody grouping
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Positive distribution of islet autoantibodies
Comparison of the clinical characteristics between either autoantibody positive group and autoantibody negative group
Table 2.
| Characteristic | Either autoantibody positive group (n=209) | Autoantibody negative group (n=300) | P valuea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male/female | 115 (55.0)/94 (45.0) | 188 (62.7)/112 (37.3) | 0.084 |
| Age, yr | 58.8±14.4 | 56.22±14.2 | 0.038b |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 8 (2–13) | 7 (1–13) | 0.453 |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 131±17.5 | 135.61±18.1 | 0.004c |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 76.0±11.4 | 78.1±10.5 | 0.037b |
| Weight, kg | 65 (58–74.5) | 70 (61–79.8) | 0.000c |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.8 (21.4–26.1) | 24.7 (22.6–27.7) | 0.001c |
| Waist, cm | 88 (80–95) | 90 (84–97) | 0.008c |
| Family history of diabetes | 17 (8.1) | 47 (15.7) | 0.012b |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 81 (38.8) | 84 (28) | 0.011b |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 21 (10) | 25 (8.3) | 0.507 |
| Macrovascular complications | 16 (7.7) | 20 (6.7) | 0.397 |
| HbA1c, % | 9.4 (7.9–11.7) | 9.9 (8–11.5) | 0.555 |
| TC, mmol/L | 4.4 (3.6–5.4) | 4.7 (3.9–5.5) | 0.035b |
| TG, mmol/L | 1.3 (0.9–2.2) | 1.6 (1.0–2.5) | 0.029b |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 0.163 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 2.6±0.9 | 2.8±1.0 | 0.005c |
| UA, μmol/L | 280 (219.5–335) | 283 (229.3–349) | 0.227 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 113.5±37.8 | 118.8±37.4 | 0.116 |
| UACR, mg/mmol | 1.5 (0.8–7.0) | 1.5 (0.7–7.3) | 0.585 |
| Whole body fat mass, kg | 19.9±7.2 | 21.6±7.7 | 0.015b |
| Visceral fat mass, kg | 1.1±0.6 | 1.3±0.6 | 0.000c |
| FINS, pmol/L | 45.9 (21.8–113.1) | 51.3 (29.9–83.9) | 0.560 |
| 120minINS, pmol/L | 147.8 (73.2–367.2) | 169.5 (90.4–274.1) | 0.741 |
| FCP, nmol/L | 0.6 (0.4–1.0) | 0.7 (0.5–0.9) | 0.009c |
| 120minCP, nmol/L | 1.4 (0.8–2.1) | 1.6 (1.1–2.2) | 0.007c |
| FPG, mmol/L | 10.2 (8.6–12.7) | 10.5 (8.9–13.2) | 0.272 |
| 120minPG, mmol/L | 22.6±5.2 | 22.2±4.9 | 0.421 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.0 (1.4–7.5) | 3.5 (2.0–5.9) | 0.450 |
| HOMA-β | 18.3 (9.1–52.2) | 20.6 (11.7–33.7) | 0.907 |
| ΔI30/ΔG30 | 1.4 (0.4–3.7) | 1.9 (0.7–3.5) | 0.111 |
| Matsuda index | 79.1 (32.3–159.8) | 67.4 (43.3–115.8) | 0.568 |
| DI | 0.4 (0.1–1.5) | 0.5 (0.2–1.5) | 0.250 |
| AUCCP | 602.9 (359.0–896.8) | 677.0 (475.3–935.2) | 0.011b |
| AUCINS/AUCGlu | 0.9 (0.4–2.4) | 1.0 (0.5–1.6) | 0.990 |
| Medical treatment | |||
| Insulin | 46 (22.0) | 38 (12.7) | |
| Oral agents | 40 (19.1) | 72 (24.0) | |
| Insulin+oral agents | 123 (58.9) | 190 (63.3) | |
| Lipid-lowering agents | 111 (53.1) | 162 (54.0) | 0.457 |
Values are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (range).
BP, blood pressure; BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; UA, uric acid; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; UACR, urine albumin/creatinine ratio; FINS, fasting insulin; 120minINS, 120 minutes insulin; FCP, fasting C-peptide; 120minCP, 120 minutes C-peptide; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; 120minPG, 120 minutes plasma glucose; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostatic model assessment for β-cell function; ΔI30, increase of insulin concentration at the 30th minute after the sugar load; ΔG30, increase of glucose concentration at the 30th minute after the sugar load; DI, glucose disposition index; AUCCP, the area under the C-peptide curve; AUCINS, the area under the insulin curve; AUCGlu, the area under the glucose curve.
Comparison of the clinical characteristics between GADA negative group and GADA positive group
Table 3.
| Characteristic | GADA negative group (n=418) | GADA positive group (n=91) | P valuea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male/female | 261 (62.4)/157 (37.6) | 42 (46.2)/49 (53.8) | 0.006b |
| Age, yr | 57.3±14.3 | 57.5±14.8 | 0.882 |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 7 (1–13) | 8 (1.8–15) | 0.337 |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 134.7±18.4 | 129.3±15.2 | 0.004b |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 77.3±10.9 | 76.8±10.5 | 0.713 |
| Weight, kg | 69.2±12.6 | 65.1±12.0 | 0.005b |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.8±4.0 | 24.0±4.0 | 0.065 |
| Waist, cm | 90.2±10.4 | 87.9±11.3 | 0.055 |
| Family history of diabetes | 57 (13.6) | 7 (7.8) | 0.130 |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 135 (32.2) | 30 (33.3) | 0.838 |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 38 (9.1) | 8 (8.9) | 0.957 |
| Macrovascular complications | 29 (6.9) | 7 (7.7) | 0.472 |
| HbA1c, % | 9.7 (7.9–11.4) | 9.5 (8.1–12.2) | 0.459 |
| TC, mmol/L | 4.8±1.4 | 4.5±1.5 | 0.037c |
| TG, mmol/L | 1.5 (1.0–2.4) | 1.3 (0.9–2.3) | 0.117 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 0.715 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 2.8±0.9 | 2.5±0.9 | 0.028c |
| UA, μmol/L | 296.0±108.8 | 283.4±97.9 | 0.291 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 116.8±36.7 | 115.7±41.6 | 0.798 |
| UACR, mg/mmol | 1.6 (0.7–7.4) | 1.5 (0.6–4.8) | 0.469 |
| Whole body fat mass, kg | 21.1±7.6 | 20.0±7.2 | 0.201 |
| Visceral fat mass, kg | 1.2±0.6 | 1.1±0.7 | 0.018c |
| ICA, IU/mL | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 0.9 (0.4–2.6) | 0.000b |
| GADA, IU/mL | 2.1 (0.6–4.5) | 20.5 (12.7–43.2) | 0.000b |
| IAA, IU/mL | 0.3 (0.1–1.5) | 0.4 (0.2–1.6) | 0.009b |
| Total autoantibody, IU/mL | 3.9 (2.0–7.3) | 25.1 (15.5–68.7) | 0.000b |
| FINS, pmol/L | 50.6 (27.9–90.7) | 41.8 (19.9–111.8) | 0.245 |
| 120minINS, pmol/L | 169.2 (88.2–301.7) | 119.0 (54.4–315.0) | 0.110 |
| FCP, nmol/L | 0.7 (0.4–0.9) | 0.5 (0.2–0.7) | 0.000b |
| 120minCP, nmol/L | 1.5 (1.0–2.2) | 1.1 (0.6–1.7) | 0.000b |
| FPG, mmol/L | 10.5 (8.9–12.9) | 10.3 (8.3–13.1) | 0.344 |
| 120minPG, mmol/L | 22.2±4.9 | 23.0±5.6 | 0.171 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.5 (1.8–6.0) | 2.6 (1.3–7.8) | 0.235 |
| HOMA-β | 20.5 (10.6–36.5) | 17.9 (8.3–59.8) | 0.770 |
| ΔI30/ΔG30 | 1.7 (0.7–3.6) | 1.3 (0.3–3.7) | 0.199 |
| Matsuda index | 67.9 (40.9–124.2) | 87.8 (31.6–183.9) | 0.233 |
| DI | 0.5 (0.2–1.4) | 0.3 (0.1–1.8) | 0.337 |
| AUCCP | 671.5 (458.7–938.4) | 506.2 (292.6–729.9) | 0.000b |
| AUCINS/AUCGlu | 1.0 (0.5–1.8) | 0.7 (0.3–2.1) | 0.038c |
| Medical treatment | |||
| Insulin | 56 (13.4) | 28 (30.8) | |
| Oral agents | 97 (23.2) | 15 (16.5) | |
| Insulin+oral agents | 265 (63.4) | 48 (52.7) | |
| Lipid-lowering agents | 227 (54.3) | 46 (50.5) | 0.296 |
Values are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (range).
GADA, glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody; BP, blood pressure; BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; UA, uric acid; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; UACR, urine albumin/creatinine ratio; ICA, islet cell antibody; IAA, insulin autoantibody; FINS, fasting insulin; 120minINS, 120 minutes insulin; FCP, fasting C-peptide; 120minCP, 120 minutes C-peptide; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; 120minPG, 120 minutes plasma glucose; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostatic model assessment for β-cell function; ΔI30, increase of insulin concentration at the 30th minute after the sugar load; ΔG30, increase of glucose concentration at the 30th minute after the sugar load; DI, glucose disposition index; AUCCP, the area under the C-peptide curve; AUCINS, the area under the insulin curve; AUCGlu, the area under the glucose curve.
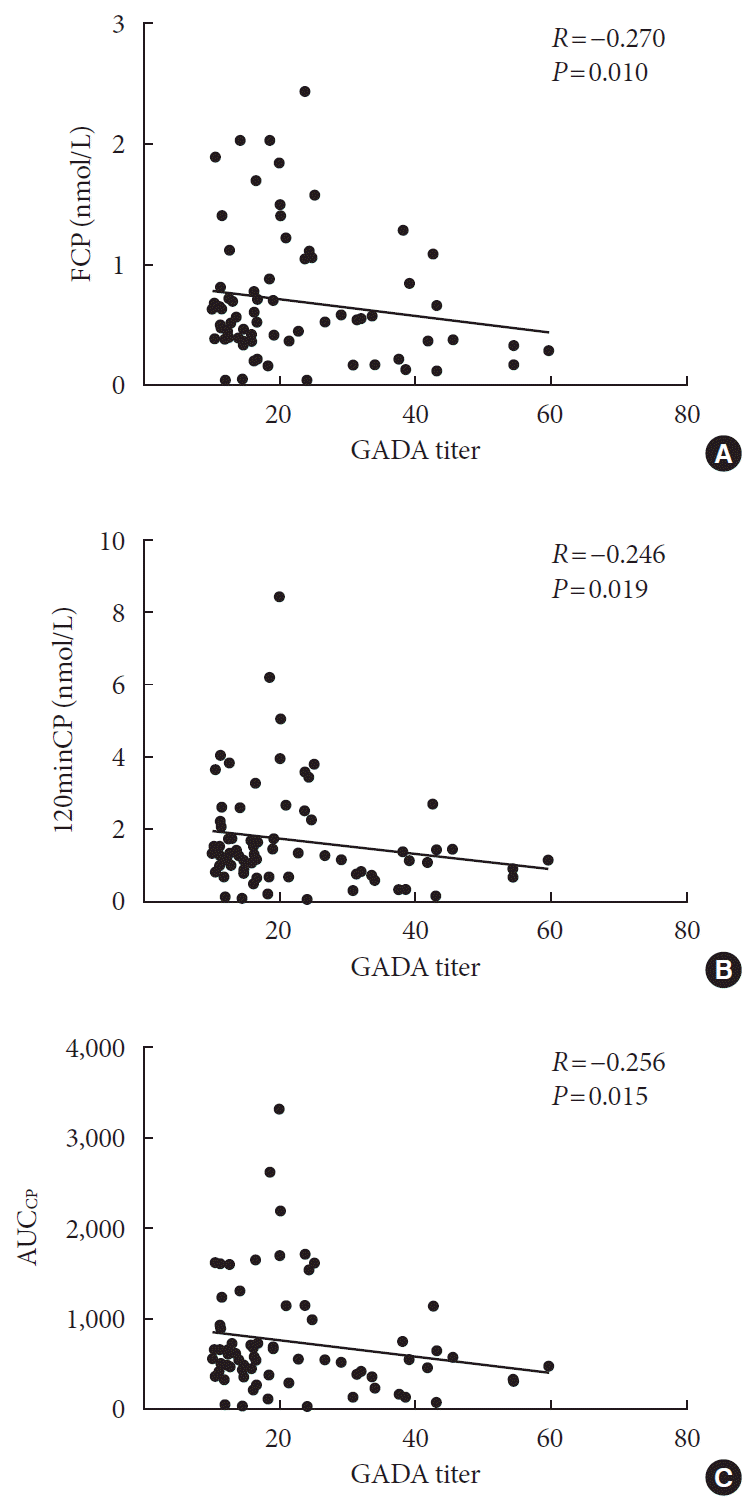
Correlation analysis
Table 4.
| Variable |
GADA titer |
ICA titer |
IAA titer |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | P valuea | R | P valuea | R | P valuea | |
| Age, yr | 0.007 | 0.878 | 0.139 | 0.002b | 0.193 | 0.000b |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 0.087 | 0.050 | 0.084 | 0.059 | 0.120 | 0.007b |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | –0.046 | 0.305 | –0.013 | 0.765 | –0.039 | 0.380 |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 0.042 | 0.348 | –0.023 | 0.610 | –0.110 | 0.013c |
| Weight, kg | –0.047 | 0.292 | –0.155 | 0.000b | –0.138 | 0.002b |
| BMI , kg/m2 | 0.003 | 0.937 | –0.108 | 0.015c | –0.108 | 0.015c |
| Waist, cm | –0.015 | 0.731 | –0.120 | 0.007b | –0.064 | 0.149 |
| HbA1c, % | –0.035 | 0.432 | –0.068 | 0.128 | –0.108 | 0.015c |
| TC, mmol/L | –0.116 | 0.009b | –0.150 | 0.001b | –0.127 | 0.004b |
| TG, mmol/L | –0.017 | 0.710 | –0.137 | 0.002b | –0.092 | 0.037c |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | –0.063 | 0.153 | –0.013 | 0.767 | 0.037 | 0.406 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | –0.088 | 0.047c | –0.134 | 0.002b | –0.167 | 0.000b |
| UA, μmol/L | –0.032 | 0.469 | –0.035 | 0.435 | –0.025 | 0.577 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 0.004 | 0.936 | –0.113 | 0.011c | –0.120 | 0.077 |
| UACR, mg/mmol | –0.050 | 0.260 | –0.061 | 0.172 | 0.084 | 0.059 |
| Diabetic retinopathy | –0.019 | 0.669 | 0.017 | 0.701 | 0.121 | 0.006b |
| Diabetic nephropathy | –0.030 | 0.494 | 0.023 | 0.612 | 0.028 | 0.530 |
| Whole body fat mass, kg | 0.029 | 0.509 | –0.082 | 0.064 | –0.081 | 0.069 |
| Visceral fat mass, kg | –0.054 | 0.227 | –0.144 | 0.001b | –0.088 | 0.048c |
| GADA, IU/mL | - | - | 0.458 | 0.000b | –0.005 | 0.911 |
| ICA, IU/mL | 0.458 | 0.000b | - | - | 0.554 | 0.000b |
| IAA, IU/mL | –0.005 | 0.911 | 0.554 | 0.000b | - | - |
| FINS, pmol/L | 0.008 | 0.861 | –0.046 | 0.303 | 0.070 | 0.116 |
| 120minINS, pmol/L | –0.028 | 0.533 | –0.041 | 0.361 | 0.077 | 0.082 |
| FCP, nmol/L | –0.152 | 0.001b | –0.169 | 0.000b | –0.029 | 0.515 |
| 120minCP, nmol/L | –0.144 | 0.001b | –0.150 | 0.001b | –0.030 | 0.500 |
| FPG, mmol/L | –0.034 | 0.444 | –0.023 | 0.600 | –0.036 | 0.418 |
| 120minPG, mmol/L | 0.013 | 0.766 | 0.071 | 0.108 | 0.025 | 0.579 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.009 | 0.838 | –0.044 | 0.316 | 0.063 | 0.159 |
| HOMA-β | 0.028 | 0.521 | –0.032 | 0.469 | 0.071 | 0.109 |
| ΔI30/ΔG30 | –0.006 | 0.890 | –0.075 | 0.092 | 0.000 | 0.997 |
| Matsuda index | –0.010 | 0.828 | 0.027 | 0.545 | –0.075 | 0.090 |
| DI | –0.024 | 0.586 | –0.059 | 0.183 | –0.009 | 0.843 |
| AUCCP | –0.140 | 0.002b | –0.143 | 0.001b | –0.018 | 0.681 |
| AUCINS/AUCGlu | –0.015 | 0.730 | –0.035 | 0.425 | 0.080 | 0.072 |
GADA, glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody; ICA, islet cell antibody; IAA, insulin autoantibody; BP, blood pressure; BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; UA, uric acid; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; UACR, urine albumin/creatinine ratio; FINS, fasting insulin; 120minINS, 120 minutes insulin; FCP, fasting C-peptide; 120minCP, 120 minutes C-peptide; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; 120minPG, 120 minutes plasma glucose; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostatic model assessment for β-cell function; ΔI30, increase of insulin concentration at the 30th minute after the sugar load; ΔG30, increase of glucose concentration at the 30th minute after the sugar load; DI, glucose disposition index; AUCCP, the area under the C-peptide curve; AUCINS, the area under the insulin curve; AUCGlu, the area under the glucose curve.
Multiple linear regression analysis of the influencing factors of the GADA, ICA, and IAA titers
Table 5.
| Variable |
Model 1 |
Model 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | P value | β | P value | |
| TC, mmol/L | –6.507 | 0.213 | –8.061 | 0.217 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | –16.770 | 0.033a | –41.981 | 0.013a |
| ICA, IU/mL | 12.326 | 0.000a | 12.287 | 0.000a |
| FCP, nmol/L | –41.293 | 0.022a | –40.560 | 0.040a |
| 120minCP, nmol/L | –14.823 | 0.040a | –13.838 | 0.085 |
| AUCCP | –0.038 | 0.032a | –0.036 | 0.067 |
Model 1 adjusted for age, gender, duration of diabetes, systolic blood pressure (BP), diastolic BP, weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference; Model 2 adjusted for age, gender, duration of diabetes, systolic BP, diastolic BP, weight, BMI, waist circumference, glycosylated hemoglobin, TC, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and urine albumin/creatinine ratio.
GADA, glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody; TC, total cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; ICA, islet cell antibody; FCP, fasting C-peptide; 120minCP, 120 minutes C-peptide; AUCCP, the area under the C-peptide curve.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download