INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant material
Animals
Histological examinations
Serum parameter analysis
Ex vivo fluorescence imaging
Western blot analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
CzE regulates lipid profile in blood of ApoE−/− mice
Table 1
Body weight changes in ApoE−/− mice after 12 weeks of CzE administration
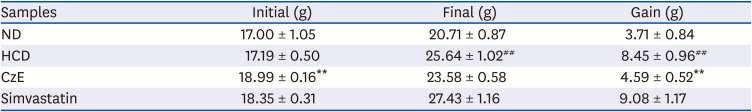
Table 2
Effect of CzE on serum lipid profile levels in ApoE−/− mice
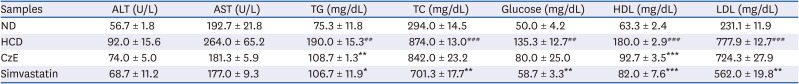
Anti-atherogenic effect of CzE on ApoE−/− mice
 | Fig. 1Representative images of Oil Red O-stained gross atherosclerotic lesions in HCD-fed and control mice (A-C). Typical cross-sections of aortic valves (× 100) in hearts from control (ND) (A), HCD (B), and CzE-treated HCD (C) mice. Treatment with CzE (100 mg·kg−1·d−1) for 12 weeks affects atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice. (D) Mean atherosclerotic lesion area in the aortic sinus was determined; data are expressed as mean ± SD values (n = 6 for each group).ND, normal diet; HCD, high-cholesterol diet; CzE, Curcuma zedoaria extract; ApoE−/−, apolipoprotein E-deficient.
**P < 0.01 vs. HCD group.
|
Expressions of TNF-α, CX3CL1, and HMGB-1 induced by CzE in normal intima and atherosclerotic lesions of ApoE−/− mice
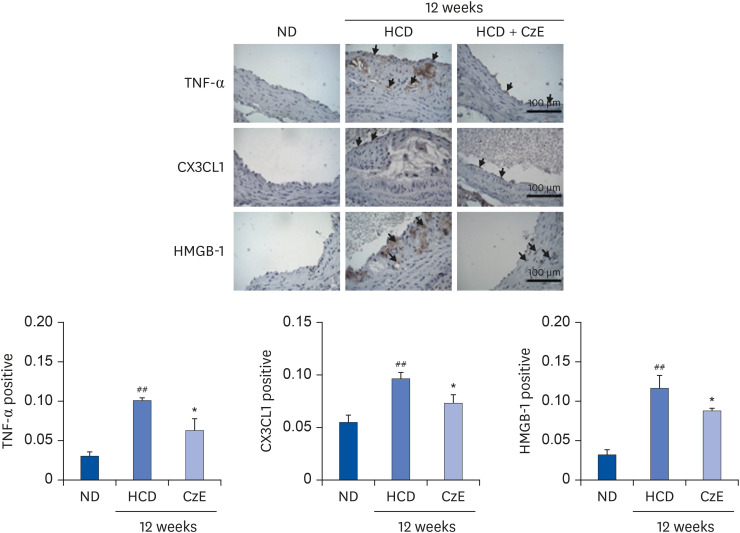 | Fig. 2Immunohistochemical identification of inflammatory molecules in ApoE−/− mouse aortas. ApoE−/− mice were fed an HCD for 12 weeks, after which, inflammatory molecules in plaques in the aortic sinuses were assessed histologically and immunohistochemically. In the control aorta, TNF-α, CX3CL1, and HMGB-1 showed negligible staining (brown staining). HCD-fed ApoE−/− mice showed over-expression of TNF-α, CX3CL1, and HMGB-1 not only in endothelial cells, including in some intimal areas, but also in smooth muscle cells (dark-brown staining: black arrows). However, in HCD–CzE-fed ApoE−/− mice, the expressions of these inflammatory molecules were significantly inhibited. Arrowheads indicate TNF-α-, CX3CL1-, or HMGB-1-positive cells. All results are shown as mean ± SD values.ND, normal diet; HCD, high-cholesterol diet; CzE, Curcuma zedoaria extract; ApoE−/−, apolipoprotein E-deficient; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; CX3CL1, chemokine (C-X3-C-motif) ligand 1; HMGB-1, high mobility group box-1.
*P < 0.05 vs. HCD group; ##P < 0.01 vs. ND group.
|
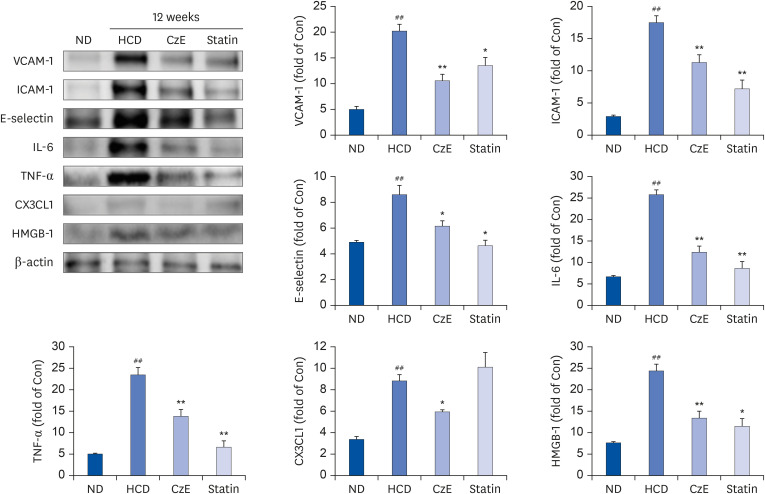 | Fig. 4Effect of CzE on adhesion molecules and inflammatory mediators in the aortas of ApoE−/− mice. The data were collected from ND, HFD with CzE (100 mg/kg), and HFD with simvastatin (10 mg/kg) fed mice (treated orally for 12 weeks). Representative photomicrographs of western blot results and densitometric analysis show the relative protein expression levels of adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin) and inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, IL-6, CX3CL1, and HMGB-1), normalized to β-actin. Values are mean ± SD.ND, normal diet; HCD, high-cholesterol diet; CzE, Curcuma zedoaria extract; ApoE−/−, apolipoprotein E-deficient; ICAM-1, intracellular adhesion molecule-1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-6, interleukin-6; CX3CL1, chemokine (C-X3-C-motif) ligand 1; HMGB-1, high mobility group box-1.
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. HCD group; ##P < 0.01 vs. ND group.
|
CzE treatment decreases arterial cathepsin activity in HCD-fed ApoE−/− mice
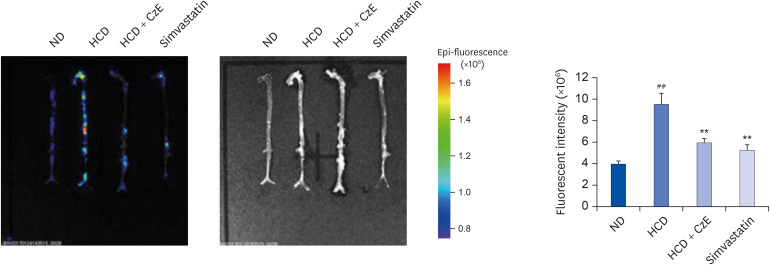 | Fig. 3Visualization of cathepsin activity in atherosclerotic mouse aortas. Visible light images show that the aortas of ApoE−/− mice appear normal, whereas those of ApoE−/− mice fed an HCD exhibit increased proteolytic fluorescence in the carotid arteries. The fluorescent density distributed from the ascending aorta to the infrarenal aorta in each group indicates the location of cathepsin activity. In the ApoE−/− mice fed the HCD with CzE diet (100 mg·kg−1·d−1), the inflammatory cathepsin expression level was significantly inhibited. The presence of internally quenched fluorogenic peptides containing Abz-Dnp, which are activatable by pan-cathepsin, confirmed the inhibition of inflammatory cardiovascular disease by CzE treatment in ApoE−/− mice. Values presented are mean ± SD.ND, normal diet; HCD, high-cholesterol diet; CzE, Curcuma zedoaria extract; ApoE−/−, apolipoprotein E-deficient.
**P < 0.01 vs. HCD group; ##P < 0.01 vs. ND group.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download