Abstract
Although flexor tendon triggering due to stenosing flexor tenosynovitis is common clinically, extensor triggering is quite rare. Known common causes are impingement between extensor tendon and extensor retinaculum, stenosis of the tendon sheath, and impingement between extensor tendon and osteophyte. We report rare case of triggering in the little finger caused by impingement between extensor digiti minimi and synovial septum.
Go to : 
References
1. Ambrose J, Goldstone R. Anomalous extensor digiti minimi proprius causing tunnel syndrome in the dorsal compartment. Report of a case. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975; 57:706–7.

2. Khazzam M, Patillo D, Gainor BJ. Extensor tendon triggering by impingement on the extensor retinaculum: a report of 5 cases. J Hand Surg Am. 2008; 33:1397–400.

3. Panwar J, Thomas BP, Sreekanth R. Sonographic findings of extensor digiti minimi triggering caused by thickened extensor retinaculum. J Ultrasound. 2015; 18:79–82.

4. Park SE, Kim YY, Ji JH, Lee HH, Jeong JJ. Double triggering of extensor digiti minimi: a case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133:429–32.

5. Park HS, Kim YH, Kim SS. Treatment of extensor digiti minimi triggering: two cases report. J Korean Soc Surg Hand. 2010; 15:44–6.
6. Wilson SM, Dubert T, Rozenblat M. Extensor tendon impingement in a gymnast. J Hand Surg Br. 2006; 31:66–7.

7. O’Rourke PJ, O’Sullivan T, Stephens M. Extensor tendon sheath stenosis resulting in triggering of the little finger. J Hand Surg Br. 1994; 19:662–3.

8. Durand S, Gaujoux G, Macquillan A. Triggering of the lateral slip of the extensor mechanism on a Bouchard’s node. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2011; 36:340–1.

Go to : 
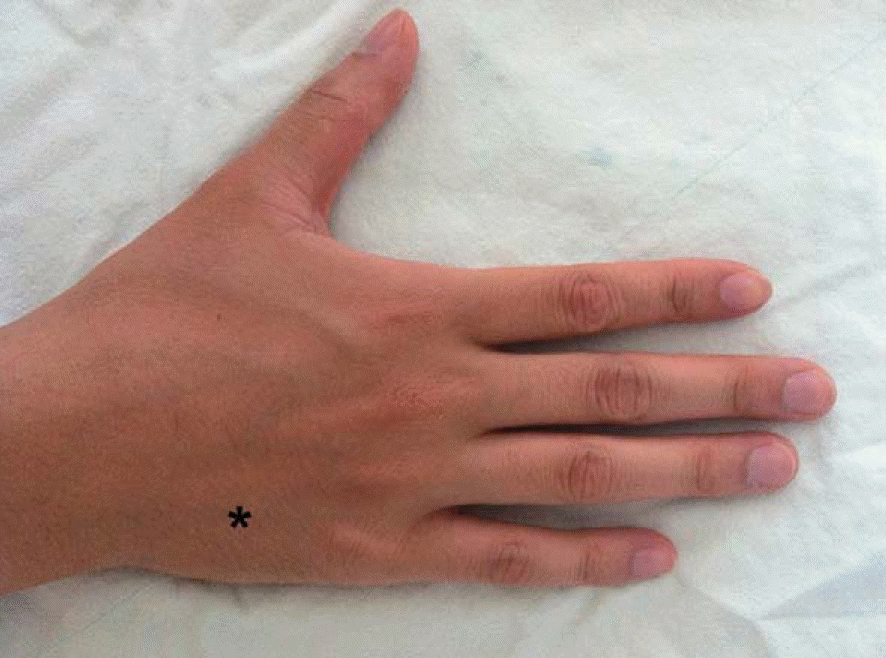 | Fig. 1.A 22-year-old male student presented a mass and triggering according to the motion of the finger which were palpated on the base of fifth metacarpal bone (black asterisk). |
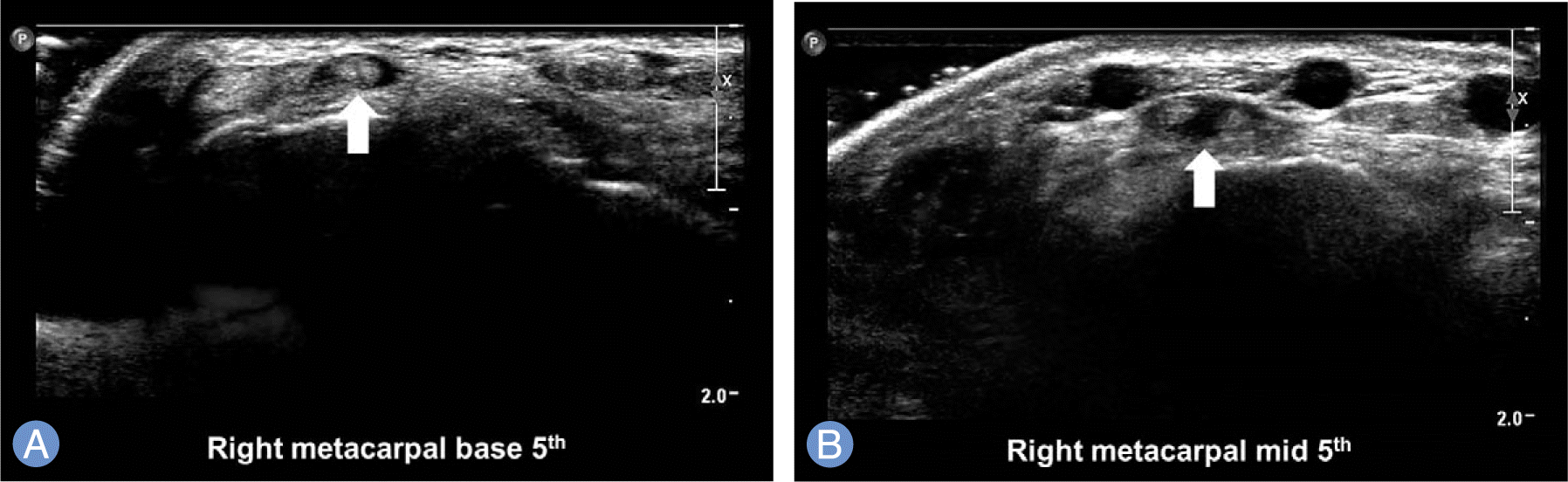 | Fig. 2.In real time ultrasonography, extensor digiti minimi (white arrow) was observed as a single tendon at the base of fifth metacarpalbone (A), but it was divided into two slips as it progressed distally (B). |
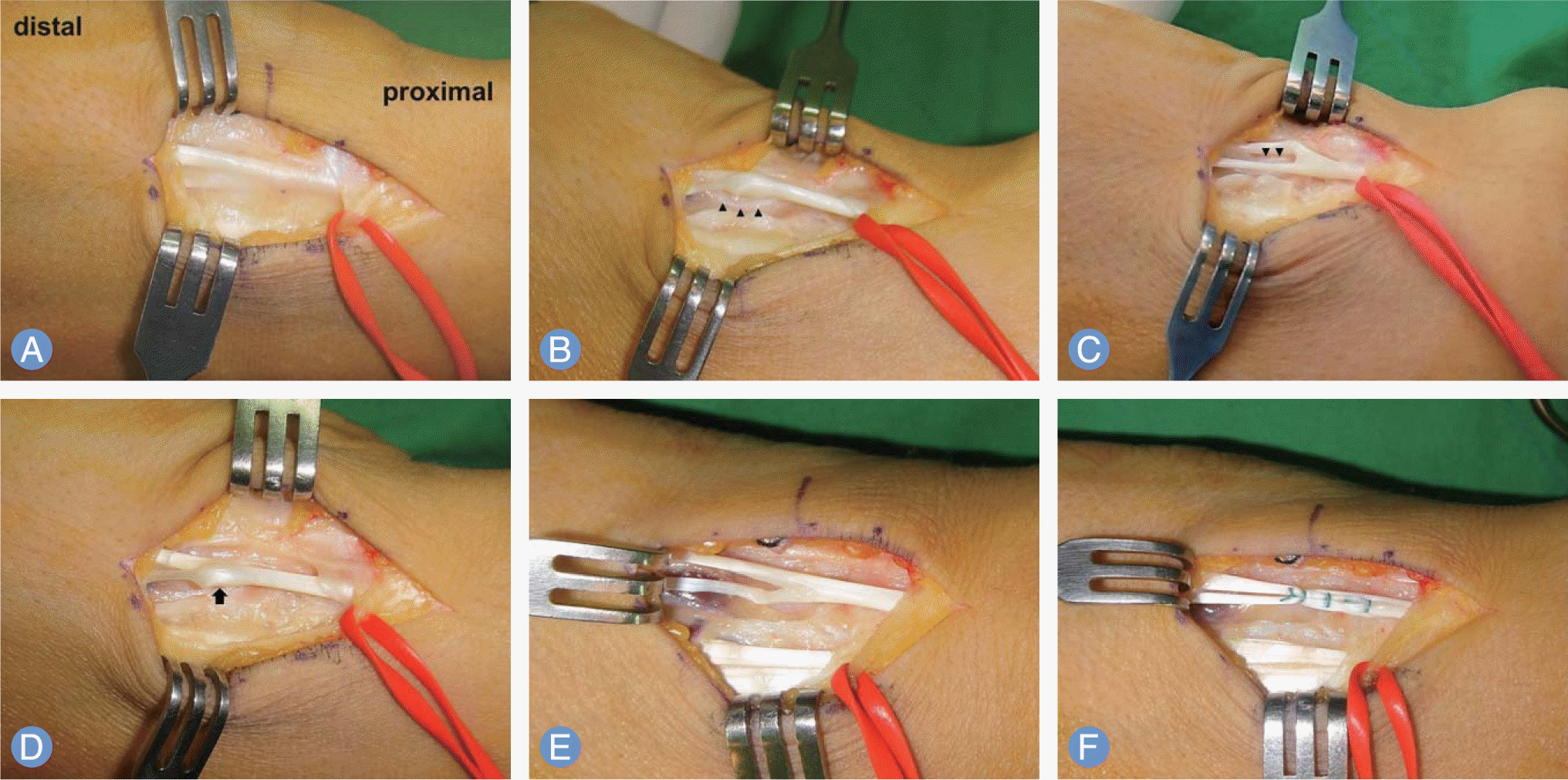 | Fig. 3.Intra-operative photographs. (A) Duplicated EDM originated distal to the retinaculum. (B, C) Synovial septum (black arrowhead) was present between the radial and ulnar EDM slip. (D) Bifurcated area of EDM tendon (black arrow) was more thickened than surrounding tendon. (E) When the little finger was flexed, impingement between bifurcated area and synovial septum resulted in tightening of the ulnar side EDM slip, with laxity of the radial slip. (F) Two EDM slips were sutured after excision of synovial septum, and then triggering was disappeared. EDM, extensor digiti minimi. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download