Abstract
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is one of the most common complications of diabetes and is diagnosed as the presence of symptoms and/or signs of peripheral nerve dysfunction in people with diabetes. The prevalence of DPN was reported at 33.5% of type 2 diabetes patients by the Korean diabetes neuropathy study group. Early diagnosis is recommended to prevent diabetic foot ulcers, amputation, or disability. A questionnaire asking about symptoms and neurologic examination of feet is commonly used as a screening tool. However, complete diagnostic tests for DPN are not well established because of incomplete understanding of the pathogenetic mechanisms leading to the nerve injury, the various clinical manifestations, and the unclear natural history. Therefore, DPN has not been paid sufficient attention by clinicians. The roles of glycemic control and management of cardiovascular risk factors in the prevention and treatment of neuropathic complications are well known. Pathogenetically oriented or symptomatic agents are other options, though such treatments do not always produce a satisfactory outcome. Therefore, DPN remains a challenge for physicians to screen, diagnose, and treat. There have been recent advances in understanding the mechanisms underlying DPN and in the development of new diagnostic modalities and treatments. In this review, diagnosis and management of DPN will be discussed.
Figures and Tables
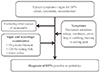 | Fig. 1Diagnostic approach to diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) proposed by the Korean Diabetes Association. Adapted from the book of the Korean Diabetes Association (Treatment guideline for diabetes 2015. 5th ed.) [7] with original copyright holder's permission. |
References
1. Won JC, Kwon HS, Kim CH, Lee JH, Park TS, Ko KS, Cha BY. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in hospital patients with Type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabet Med. 2012; 29:e290–e296.
2. Tesfaye S, Chaturvedi N, Eaton SE, Ward JD, Manes C, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, Witte DR, Fuller JH. EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study Group. Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:341–350.

3. Ziegler D, Rathmann W, Dickhaus T, Meisinger C, Mielck A. KORA Study Group. Neuropathic pain in diabetes, prediabetes and normal glucose tolerance: the MONICA/KORA Augsburg surveys S2 and S3. Pain Med. 2009; 10:393–400.

4. Van Acker K, Bouhassira D, De Bacquer D, Weiss S, Matthys K, Raemen H, Mathieu C, Colin IM. Prevalence and impact on quality of life of peripheral neuropathy with or without neuropathic pain in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients attending hospital outpatients clinics. Diabetes Metab. 2009; 35:206–213.

5. Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ. Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2009; 32:1–32.

6. Won JC, Kim SS, Ko KS, Cha BY. Current status of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Korea: report of a hospital-based study of type 2 diabetic patients in Korea by the diabetic neuropathy study group of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:25–31.

7. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes 2015. 5th ed. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2015. p. S109–S112.
8. Kim SS, Won JC, Kwon HS, Kim CH, Lee JH, Park TS, Ko KS, Cha BY. Prevalence and clinical implications of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: results from a nationwide hospital-based study of diabetic neuropathy in Korea. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014; 103:522–529.

9. American Diabetes Association. 10. Microvascular complications and foot care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:Suppl 1. S105–S118.
10. Jensen TS, Backonja MM, Hernández Jiménez S, Tesfaye S, Valensi P, Ziegler D. New perspectives on the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2006; 3:108–119.

11. Tsuji M, Yasuda T, Kaneto H, Matsuoka TA, Hirose T, Kawamori R, Iseki M, Shimomura I, Shibata M. Painful diabetic neuropathy in Japanese diabetic patients is common but underrecognized. Pain Res Treat. 2013; 2013:318352.

12. Dyck PJ, Albers JW, Andersen H, Arezzo JC, Biessels GJ, Bril V, Feldman EL, Litchy WJ, O'Brien PC, Russell JW. Toronto Expert Panel on Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetic polyneuropathies: update on research definition, diagnostic criteria and estimation of severity. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011; 27:620–628.

13. Won JC, Park TS. Recent advances in diagnostic strategies for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2016; 31:230–238.

14. Vinik AI, Nevoret ML, Casellini C, Parson H. Diabetic neuropathy. Endocr inol Metab Clin Nor th Am. 2013; 42:747–787.

15. Ahmed A, Bril V, Orszag A, Paulson J, Yeung E, Ngo M, Orlov S, Perkins BA. Detection of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy by corneal confocal microscopy in type 1 diabetes: a concurrent validity study. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:821–828.

16. Devigili G, Tugnoli V, Penza P, Camozzi F, Lombardi R, Melli G, Broglio L, Granieri E, Lauria G. The diagnostic criteria for small fibre neuropathy: from symptoms to neuropathology. Brain. 2008; 131(Pt 7):1912–1925.

17. Vinik A, Ullal J, Parson HK, Casellini CM. Diabetic neuropathies: clinical manifestations and current treatment options. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 2:269–281.

18. Boulton AJ, Kempler P, Ametov A, Ziegler D. Whither pathogenetic treatments for diabetic polyneuropathy? Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2013; 29:327–333.

19. Callaghan BC, Little AA, Feldman EL, Hughes RA. Enhanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; (6):CD007543.

21. Iqbal Z, Azmi S, Yadav R, Ferdousi M, Kumar M, Cuthbertson DJ, Lim J, Malik RA, Alam U. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: epidemiology, diagnosis, and pharmacotherapy. Clin Ther. 2018; 40:828–849.

22. Griebeler ML, Tsapas A, Brito JP, Wang Z, Phung OJ, Montori VM, Murad MH. Pharmacologic interventions for painful diabetic neuropathy: an umbrella systematic review and comparative effectiveness network meta-analysis (Protocol). Syst Rev. 2012; 1:61.

23. Shakher J, Stevens MJ. Update on the management of diabetic polyneuropathies. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2011; 4:289–305.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download