Abstract
Purpose
This study investigated the question of whether the addition of natural ingredients (pear fermented solution, celery powder, vitamin C) in curing agents may influence antioxidant activities and nutritional characteristics of smoked duck. Methods: Smoked duck samples with general or natural curing agent containing three additive ingredients were examined to determine total polyphenol contents, antioxidant activities, pH, TBARS, and food additives residue (nitrite ion, antioxidant, sodium glutamate). Results: Smoked duck with natural curing agent showed a higher level of total polyphenol content and antioxidant activities than smoked duck using general curing agent (p < 0.05). The pH and TBARS of smoked duck were significantly decreased by the addition of natural curing ingredients compared to those of smoked duck using general curing agent (p < 0.05). The residues of food additives were not detected in smoked duck using natural curing agent. Conclusion: Findings suggest that the addition of pear fermented solution, celery powder, and vitamin C in natural duck curing agent may improve the antioxidant activities and nutritional characteristics of smoked duck and provides health benefits.
References
1. Kang GH, Jeong TC, Yang HS, Kim SH, Jang BG, Kang HS, Lee DS, Lee SJ, Joo ST, Park GB. Effects of packaging methods on color and lipid oxidation of duck meat during cold storage. Korean J Poult Sci. 2006; 33(1):7–14.
2. Kang G, Cho S, Seong PN, Park K, Kang SM, Park BY. Effect of curing additives on color property of smoked duck meat. Korean J Poult Sci. 2013; 40(3):179–185.

3. Oh JW. Allergic diseases in childhood and food additives. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2010; 20(4):212–218.
4. Kim YW, inventor; Kim JI, assignee. Producing method of smoked duck containing a sea tangle extract. Republic of Korea patent 10–1139514. 2012 Apr 17.
5. Shinchonjayeondock Co., Ltd., inventors; Park YM, assignee. Method for manufacturing smoked duck containing curcuma longa using a curing agent and pyroligneous liquid. Republic of Korea patent 10–0948262. 2010 Mar 11.
6. Shim JH, Shim JH, Kim CH, Shim JR, Kim HJ, inventors; Choi KW, assignee. Method for manufacturing smoked sulfur-containing duck using fermented liquid of wild grass. Republic of Korea patent 10–0988138. 2010 Oct 8.
7. Hansung Food Co. ltd. ., inventors;. Kim JI. assignee.Producing method of smoked duck containing mulberry leaves and mulberry components. Republic of Korea patent 10–1291242.2013 Jul 24.
9. Natural drug research and development promotion 1 of Article 2.
10. National Institute of Horticultural & Herbal Science, Pear Research Station. Industrial condition and activation plan of pear. Suwon: National Institute of Horticultural & Herbal Science;2010.
11. Swain T, Hillis WE. The phenolic constituents of Prunus domestica. I.-The quantitative analysis of phenolic constituents. J Sci Food Agric. 1959; 10(1):63–68.
12. Blois MS. Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature. 1958; 181(4617):1199–1120.

13. Siddhuraju P, Mohan PS, Becker K. Studies on the antioxidant activity of Indian Laburnum (Cassia fistula L.): a preliminary assessment of crude extracts from stem bark, leaves, flowers and fruit pulp. Food Chem. 2002; 79(1):61–67.

14. Witte VC, Krause GF, Bailey ME. A new extraction method for determining 2-thiobarbituric acid values of pork and beef during storage. J Food Sci. 1970; 35(5):582–585.

15. Cunniff P. AOAC International. Official methods of analysis. 16th edition.Washington, D.C.: Association of Official Analytical Chemist;1995.
16. Tanimura A, Fujii M, Yoshihira K, Ito Y, Shiro T. Analytical methods for additives in foodstuff. Tokyo: Kodan Scientific Co.;1992.
17. Kang HK, Yoo YK, Lee SK. Effects of prestorage heat treatment on changes of phenolic compound contents and incidence of skin blackening in ‘Niitaka' pear fruits during cold storage. Korean J Hort Sci Technol. 2003; 44(2):197–200.
18. National Korean Medicine Laboratory. Private oriental medicine. Hongcheon: National Korean Medicine Laboratory;2006.
19. Koo JO, Lim HS, Yoon JS, Lee AR, Seo JS, Lee JH, Sohn CM. Advanced nutrition. Goyang: Powerbook;2013.
20. Keskinel A, Ayres JC, Hnyer HE. Determination of oxidative changes of meats by the 2-thiobarbituric acid method. J Food Technol. 1964; 18:223–228.
Fig. 1.
Comparison of the pH and TBARS change in the S.D.G and S.D.N during the storage days ∗Asterisks present the significant differences between two independent groups as determined by Mann-Whitney test at a confidence level of 95%. ※S.D.G: smoked duck with general curing agent, S.D.N: smoked duck with natural curing agent
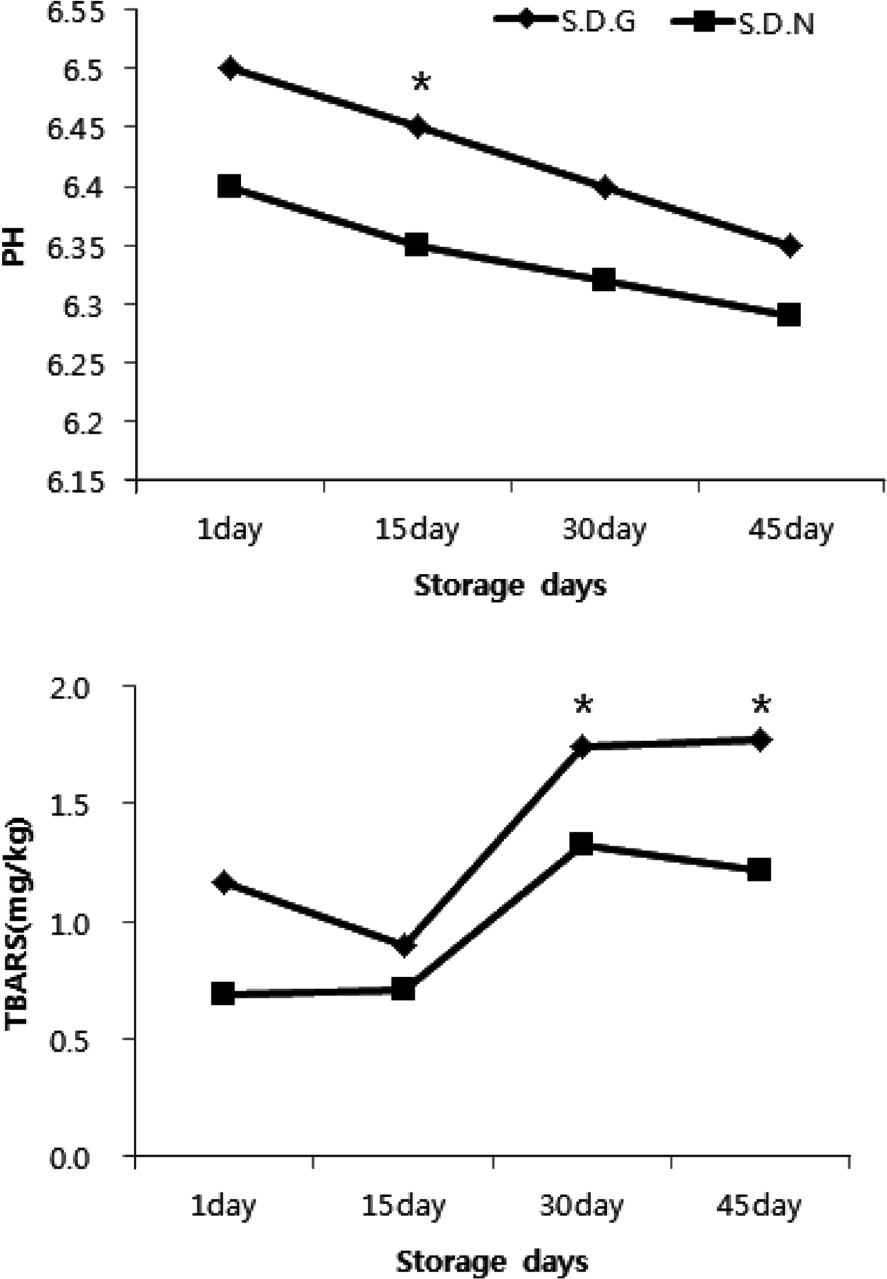
Table 1.
Total polyphenol contents (mg/100g) of two smoke uck, pear fermented solution and celery powder 10
| Inspection item | Value (mg/100g) |
|---|---|
| S.D.G | 55 ± 3.5 |
| S.D.N | 107 ± 2.4∗ |
| Pear fermented solution | 71.2 ± 5.0 |
| Celery powder 10 | 120.9 ± 2.0 |
Table 2.
Antioxidant activities(%) of two smoked duck, pear fermented solution and celery powder 10
a-d Means with different superscripts significantly differ by ANOVA with Duncan's multiple range test at a confidence level of 95%. ※S.D.G: smoked duck with general curing agent, S.D.G 10: decuple dilution of smoked duck with general curing agent, S.D.N: smoked duck with natural curing agent, S.D.N 10: decuple dilution of smoked duck with natural curing agent, BHT 100: centuple dilution of BHT




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download