Abstract
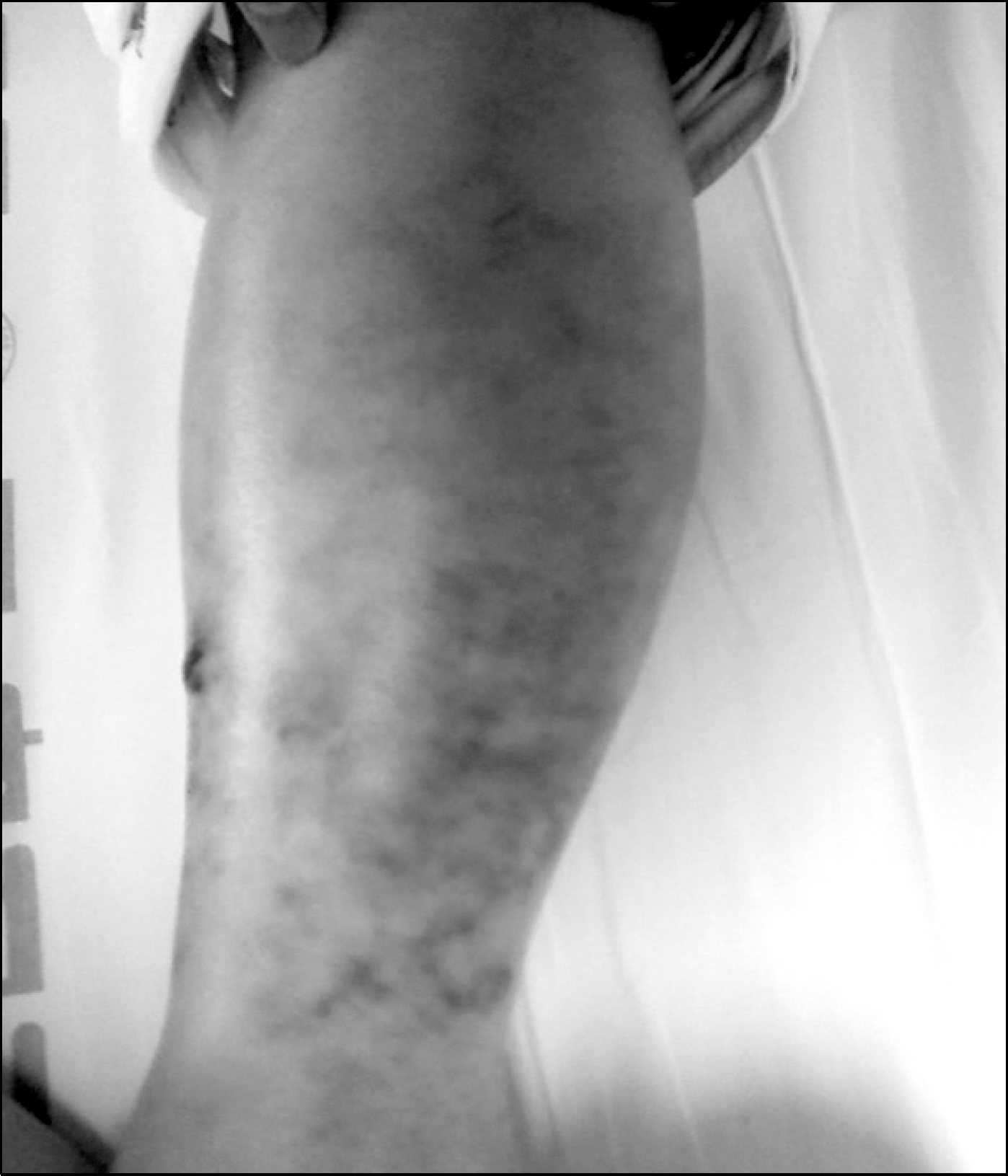
Necrotizing fasciitis (NF) is an uncommon, life-threatening infection of the subcutaneous tissue and superficial fascia. The clinical course of NF is rapid and progressive, and it is often fatal despite the appropriate therapy. The prognosis of NF depends on a timely diagnosis and then proper treatment. At onset it may not be possible to clearly dis-tinguish NF from minor soft-tissue infections. Although infection are common due to the use of steroids and immunosuppressive agents in patients with systemic lupus erythematous (SLE), it is interesting that NF has rarely been reported with SLE. Here, we present two cases of NF with SLE.
References
1. Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, Sebastiani GD, Gil A, Lavilla P, et al. European Working Party on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 10-year period: a comparison of early and late manifestations in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003; 82:299–308.
2. Iliopoulos AG, Tsokos GC. Immunopathogenesis and spectrum of infections in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 25:318–36.
3. Zonana-Nacach A, Camargo-Coronel A, Yañez P, Sánchez L, Jimenez-Balderas FJ, Fraga A. Infections in outpatients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective study. Lupus. 2001; 10:505–10.

5. Wong CH, Chang HC, Pasupathy S, Khin LW, Tan JL, Low CO. Necrotizing fasciitis: clinical presentation, mi-crobiology, and determinants of mortality. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85-A:1454–60.
6. Chong JH, Yoo WH. Necrotizing fasciitis in a patient with overlap syndrome of systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2009; [Epub ahead of print].

7. Lee MW, Kim TH, Choo EJ, Kang JH, Kim DW, Kim DK, et al. Characteristics of necrotizing fasciitis in three university hospitals in Korea. Korean J Med. 2006; 70:681–7.
8. Mok MY, Wong SY, Chan TM, Tang WM, Wong WS, Lau CS. Necrotizing fasciitis in rheumatic diseases. Lupus. 2006; 15:380–3.

9. Isik A, Koca SS. Necrotizing fasciitis resulting from Streptococcus pneumoniae in recently diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus case: a case report. Clin Rheumatol. 2007; 26:999–1001.

10. Son GS, Choi IS, Kim KH, Jung KH, Hong YS. MRI for the early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 1997; 52:766–70.
11. Seok JH, Jee WH, Chun KA, Kim JY, Jung CK, Kim YR, et al. Necrotizing fasciitis versus pyomyositis: dis-crimination with using MR imaging. Korean J Radiol. 2009; 10:121–8.

12. Kamran M, Wachs J, Putterman C. Necrotizing fasciitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 37:236–42.

13. Hwang JE, Woo H, Kim SH, Lee WS, Hwang JH, Kim JC, et al. Successful treatment of necrotizing fasciitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2006; 13:155–9.
14. Hashimoto N, Sugiyama H, Asagoe K, Hara K, Yamasaki O, Yamasaki Y, et al. Fulminant necrotising fasciitis developing during longterm corticosteroid treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61:848–9.
Figure 2.
A hypointensive signal is seen in the anterior, lateral and posterior compartments (Right lower leg T1 image: A, white arrow). Thickening and enhanced fasciitis lesion is seen in the anterior, lateral and posterior compartments (T2 image: B, black arrow). Edematous change and enhanced myositis is seen in the tibialis anterior muscle (white arrow) and the extensor digitorum muscle (black arrow) (T2 image: C).
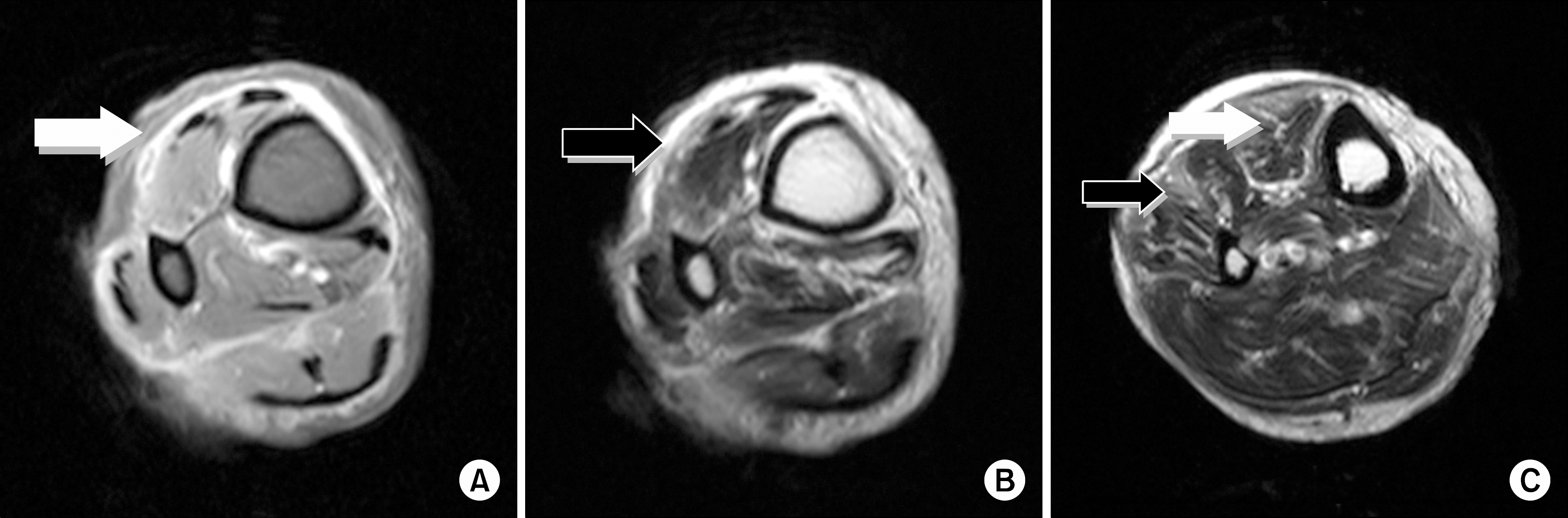
Table 1.
Comparisons of case 1 and case 2




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download