Abstract
Zinc deficiency is known to be associated with insulin resistance in obese individuals. This study was performed to evaluate the effect of zinc supplementation on insulin resistance and metabolic risk factors in obese Korean women. Forty obese women (body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25 kg/m2) aged 19-28 years were recruited for this study. Twenty women of the study group took 30 mg/day of supplemental zinc as zinc gluconate for 8 weeks and 20 women of control group took placebo. Usual dietary zinc intake was estimated from 3-day diet records. Insulin resistances were measured using Homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) indices, and insulin sensitivities Matsuda indices, which were calculated using oral glucose tolerance test data. Metabolic risk factors, such as waist circumference, blood pressure, fasting glucose, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and adipocyte hormones such as leptin, and adiponectin were also measured. At the beginning of study, dietary zinc averaged 7.31 mg/day and serum zinc averaged 12.98 µmol/L in the study group. Zinc supplementation increased serum zinc by 15% and urinary zinc by 56% (P < 0.05). HOMA values tended to decrease and insulin sensitivity increased slightly in the study group, but not significantly so. BMI, waist circumference, blood pressure, blood glucose, triglyceride, HDL cholesterol, and adipocyte hormones did not change in either the study or control group. These results suggest that zinc status may not affect insulin resistance and metabolic risk factors in obese Korean women. Further research is required on a larger cohort with a longer follow-up to determine the effects of zinc status on insulin resistance and metabolic variables.
Go to : 
Zinc is known to be an essential trace element and a component of hundreds of enzymes [1], and is involved in the synthesis, storage, and release of insulin. Many studies have documented that plasma zinc levels are lower in obese individuals [2,3]. Furthermore, zinc deficiency may predispose glucose intolerance and insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, and coronary artery disease [4-6].
Recent studies have revealed that zinc had beneficial effects on insulin resistance and on glucose and lipid profiles in patients with diabetes or metabolic syndrome [7-10]. For example, a prospective study demonstrated that higher zinc intakesare associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes in U.S. women [10], and other studies have shown that zinc supplementation increases high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and reduces triglyceride (TG) in type 2 diabetes patients [7,8]. Furthermore, in a randomized cross-over trial, supplemental zinc (20 mg per day) significantly decreased insulin resistance in obese children with metabolic syndrome [9]. However, relationships between zinc status and insulin resistance/metabolic risk factors are more controversial among non-diabetic obese and non-obese subjects.
Marreiro et al. [11] found that insulin sensitivity improved, without changes in leptin levels, in non-diabetic obese subjects on zinc supplementation. Whereas Obeid et al. [12] reported that lower plasma zinc concentrations were not related to glycemic status or components of metabolic syndrome in Lebanese adults.
Insulin resistance plays an important role in the pathophysiology of obesity and metabolic syndrome [13], the prevalence of which are rapidly increasing in the Korean population. According to Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III data, an estimated 32% and 30% of Korean adults are obese or have metabolic syndrome, respectively [14]. Thus, it is critical that the relationship between zinc status and insulin resistance or its related metabolic risk factors be determined in obese subjects, because this could allow us to consider zinc intervention for the treatment or prevention of metabolic disease related to insulin resistance.
Therefore, in this study, we evaluated the effects of zinc supplementation at 30 mg/day for 8 weeks on insulin resistance and metabolic risk factors, such as, obesity, blood glucose, and lipid profiles in obese Korean women.
Go to : 
Forty obese women (18-28 years) were recruited from May 2009 to September 2010 in the Daegu and Gyeongbuk regions. Obesity was defined as a body mass index (BMI) of ≥ 25 kg/m2. Participants completed a questionnaire during a face-to-face interview. Information was collected on demographic variables, socioeconomic status, smoking, nutritional supplementation, personal medical history, family history, and medication use. Exclusion criteria included cigarette smoking, vitamin-mineral supplements and/or any other nutritional supplements, the use of oral contraceptives, acute or chronic disease, such as diabetes or a family history of diabetes, and participation in a diet based weight-loss program. Informed written consent was obtained from all 40 study subjects prior to enrollment. The study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and the study protocol was reviewed and approved by the institutional review board of Daegu University.
Zinc status, anthropometric measurements, and metabolic variables were measured prior and following zinc supplementation at 30 mg zinc/day (Vitamin House, Korea) or placebo for 8 weeks. Height, weight, waist circumference, and blood pressure were measured mornings before blood collection. After a 12-hour overnight fast, baseline blood was drawn from each subject and then re-drawn at 30, 60, 90, and 120 min after taking 75 g of glucose for oral glucose tolerance testing. After blood collection, twenty women in the study group were discharged with an 8-week supply of 30 mg tablets of zinc supplement as zinc gluconateand the other half in control group were allocated with an 8-week supply of placebo tablets (free zinc starch).The women were told to take the supplement between meals and to remain on their usual diets. For the compliance of supplementation, zinc supplements and placebo tablets were given in plastic weekly pill reminder and the research staff made a call every day to all subjects to check out if they took pills. Usual dietary intakes were estimated from 3-day diet records that included 2 weekdays and 1 weekend day. At first visit, detailed instructions regarding the maintenance of 3-day dietary records were given by trained dietitians. Diet records were collected before the study and while taking supplement or placebo. Nutrient intakes were estimated using a nutrient database developed by the Korean Nutrition Society. After supplementation for 8 weeks, subjects returned to the laboratory for anthropometric measurements and blood collection. Subjects were also asked to collect a 24-hour urine sample the day before each blood collection for urinary zinc analysis.
Physical examinations were performed by trained research staff using standardized procedures. Height was measured by anthropometry (TKK-11252, Japan) and body weight by bioimpedance analysis (Inbody 3.0, Biospace Corp, Korea). BMI was calculated by dividing weight (kg) by height squared (m2). Obesity was defined as a BMI of ≥ 25 kg/m2 according to International Obesity Task Force (IOTF) for Asian adults in the Asia Pacific region [15]. Waist circumference was measured at the midpoint between the lower border of the rib cage and the iliac crest using a non-elastic tape measure [16]. Hip circumference was defined as maximum circumference in the hip region [14]. A trained member of research staff measured systolic blood pressures (SBPs) and diastolic blood pressures (DBPs) after subjects had rested for 10 minutes in a sitting position immediately before blood collection using an automatic sphygmometer (HEM-770A, Japan) [17]. Two SBP and DBP readings were recorded and averages were used in the analysis.
Blood samples for zinc and metabolic variables analyses were collected in plastic syringes, placed on ice for a maximum of 2 h, centrifuged at 1,500 g for 10 min at 4℃ (Allegra 6R, Beckman Coulter, USA), and stored at -70℃ until required for analysis [18]. Urine samples were collected in a polyethylene container and were mixed by shaking vigorously, weighed, and aliquots were stored at -20℃ prior to zinc analysis [19].
Fasting glucose (FG), TG, total cholesterol (TC), and HDL cholesterol were measured enzymatically using an automated analyzer (ADVIA 2400, Japan). Serum fasting insulin (FI) was measured using a chemiluminescent immunoassay method. Insulin resistances were calculated using the following formula according to the homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) method; FG (mmol/L)×FI (µIU/mL)/22.5 [20]. Insulin sensitivity indices were calculated using the formula [21] as follows: Insulin sensitivity index = 10,000 /√[FG/ × FI] × [Mean OGTT glucose × Mean OGTT insulin]
Serum leptin concentrations were determined by radioimmunoassay using a human leptin kit (Linco Research Inc., USA) [22], and plasma adiponectin concentrations were determined by immunoassay using a human adiponectin kit (R&D Systems, USA). Serum alkaline phosphatase levels were determined colorimetrically using an automated analyzer (ADVIA 2400, Japan).Serum superoxide dismutase (SOD) concentrations were measured enzymatically using a SOD assay kit (Cayman Chemical Company, USA).
All results are expressed as means ± standard deviations. Wilcoxon's signed rank test was used to analyze differences before and after zinc supplementation or to compare the zinc supplemented group and the placebo group in terms of zinc status, anthropometric measurements, and metabolic risk factors. Statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.1 (SAS institute Inc. NC, USA). Statistical significance was accepted for P-values of < 0.05.
Go to : 
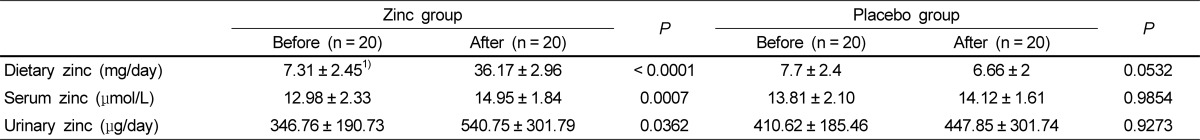
Zinc statuses of the study subjects before and after zinc or placebo supplementation are described in Table 1. At the beginning of study, dietary zinc averaged 7.31 mg/day and serum zinc and urinary zinc concentration averaged 12.98 µmol/L and 346.8 µg/day, respectively, in the study group. Supplementation with 30 mg of zinc daily for 8 weeks significantly increased serum zinc by 15% and urinary zinc by 56% (P < 0.05), whereas no change was observed in the control group.
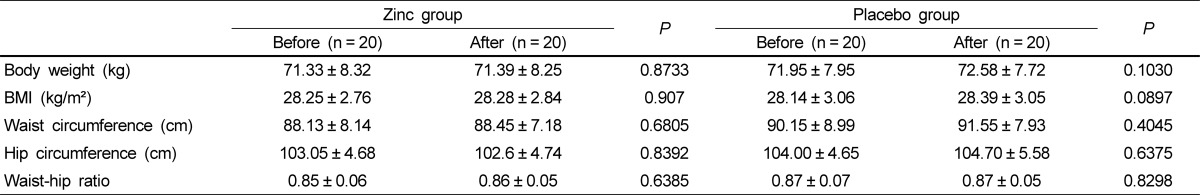
Anthropometric measurements of the study subjects before and after zinc or placebo supplementation are described in Table 2. Mean BMI of subjects was about 28 kg/m2 and waist-hip ratio was averagely 0.86. Body weight, BMI, waist circumference, hip circumference, and waist-hip ratio did not change in either group over the 8-week supplemental period.
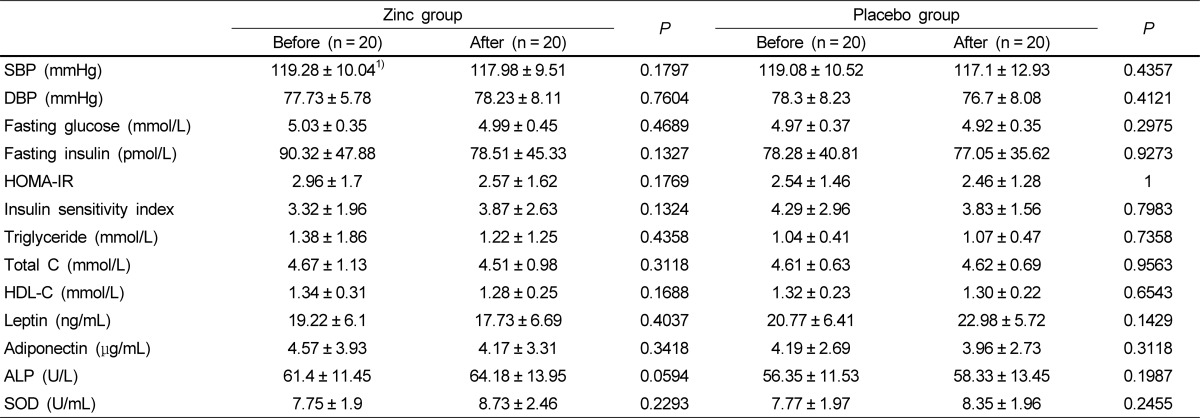
Metabolic risk factors before and after zinc supplementation are described in Table 3. HOMA values tended to decrease and insulin sensitivity increased slightly with zinc supplementation, but it this did not reach significance. Blood pressure, fasting glucose and insulin, TG, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase, and SOD were unchanged after zinc supplementation. Adipocyte hormones such as leptin and adiponectin did not differ with zinc supplementation. Furthermore, no significant differences were found in metabolic risk factors in the control group.
Go to : 
Zinc supplementation at 30 mg daily for 8 weeks increased serum zinc by 15% and urinary zinc by 56%, but no significant difference was found for any anthropometric measurement, insulin resistance, or any other metabolic risk factors, such as blood pressure, blood glucose, triglyceride, and HDL cholesterol after zinc supplementation.
Several experimental and clinical studies have explored the effect of zinc intervention on insulin resistance and other metabolic risk factors in obese individuals [11,23-25], and some studies have reported results similar to our findings. Gómez-García et al. [24] showed zinc intervention at 100 mg/day for one month significantly increased mean serum zinc concentration from 11.8 to 16.9 µmol/L, but found that it did not modify insulin sensitivity in seven Spanish obese men (BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2) between 21 and 30 years old. Similarly, Beletate et al. [23] reported that zinc supplementation for 4 weeks did not have a beneficial effect on insulin resistance, fasting glucose, or on lipid levels in normal glucose tolerant obese women aged 25 to 45 years. However, other studies have produced contrasting results. In one randomized, placebo-control study, it was found that zinc supplementation at 30 mg daily for 4 weeks significantly decreased fasting insulin and HOMA values in Brazilian obese women aged 25 to 45 years, but that plasma zinc, BMI, fasting glucose, and leptin levels were unaffected by zinc supplementation [11]. In a cross-over study conducted on obese Iranian children, fasting glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR were found to significantly decrease after zinc supplementation at 20 mg/d for 8 weeks, while BMI, waist circumference, triglyceride, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol did not significantly change [25].
However, results cannot be directly compared because study conditions differed in several ways. First, we defined obesity as a BMI of ≥ 25 kg/m2 according the IOTF criterion for Asians, whereas in the Brazilian study mentioned above BMI was defined as ≥ 30 kg/m2, and this definitional difference might have affected responses of insulin resistance or metabolic risk factors to zinc supplementation. Second, the studies were conducted in different ethnic groups or different age groups. Diet compositions and dietary patterns vary according to age, gender, and ethnicity [26], and previous studies have demonstrated that food compositions and dietary patterns are associated with components of metabolic syndrome, that is, abdominal obesity, blood pressure, and lipid levels [16,27]. Furthermore, serum HOMA-IR levels measured at the beginning of this study were not as high as those reported in other studies [11,25]. Given that much differences, if the subjects were more obese with higher insulin resistance, supplemental zinc might have affected insulin resistance or other metabolic risk factors in this study. Thus it will be interesting to observe the relationship between zinc status and metabolic risk factors including insulin resistance in various subjects according to different age group or the degree of obesity for the future study.
Several mechanisms have been suggested to explain the association between zinc and insulin resistance. Zinc is known to play a major role in the stabilization of insulin hexamers and in the pancreatic storage of insulin because it can enhance insulin binding to hepatocyte membranes [28]. In fact, reduced hepatic insulin binding to hepatocyte membranes during zinc deficiency may be associated with the contribution of zinc during insulin receptor synthesis [29]. Furthermore, zinc is an efficient antioxidant, and oxidative stress is considered to be a primary contributor to the initiation and progression of insulin resistance and diabetes [30]. In addition, zinc is a component of SOD and is required for optimum SOD activity [29].
Our study has several limitations that require consideration. First, we did not control for potential confounders such as diet or physical activity during zinc supplementation. Second, the supplementation period may have been insufficient in terms of significantly changing metabolic risk factors. Thus, we suggest a longer follow-up study be conducted on zinc supplementation in obese individuals.
In conclusion, zinc supplementation at 30 mg daily for 8 weeks improved serum zinc and urinary zinc concentrations in obese Korean women. However, zinc supplementation did not improve insulin resistance or any metabolic risk factor examined. Further research on the effect of zinc on insulin resistance and metabolic risk factors should be performed in a larger cohort with a longer follow-up period to determine the potential merits of zinc-based intervention in patients with metabolic disease.
Go to : 
Acknowledgment
We are grateful to study participants, the nurses, dieticians, and research members of staff that contributed to this study.
Go to : 
Notes
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (grant no. NRF-2009-0068869).
Go to : 
References
1. Haase H, Overbeck S, Rink L. Zinc supplementation for the treatment or prevention of disease: current status and future perspectives. Exp Gerontol. 2008; 43:394–408. PMID: 18221847.

2. Marreiro DN, Fisberg M, Cozzolino SM. Zinc nutritional status and its relationships with hyperinsulinemia in obese children and adolescents. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2004; 100:137–149. PMID: 15326363.

3. Tungtrongchitr R, Pongpaew P, Phonrat B, Tungtrongchitr A, Viroonudomphol D, Vudhivai N, Schelp FP. Serum copper, zinc, ceruloplasmin and superoxide dismutase in Thai overweight and obese. J Med Assoc Thai. 2003; 86:543–551. PMID: 12924803.
4. Afridi HI, Kazi TG, Kazi N, Baig JA, Jamali MK, Arain MB, Sarfraz RA, Sheikh HU, Kandhro GA, Shah AQ. Status of essential trace metals in biological samples of diabetic mother and their neonates. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2009; 280:415–423. PMID: 19169697.

5. Singh RB, Niaz MA, Rastogi SS, Bajaj S, Gaoli Z, Shoumin Z. Current zinc intake and risk of diabetes and coronary artery disease and factors associated with insulin resistance in rural and urban populations of North India. J Am Coll Nutr. 1998; 17:564–570. PMID: 9853535.

6. Viktorínová A, Toserová E, Krizko M, Duracková Z. Altered metabolism of copper, zinc, and magnesium is associated with increased levels of glycated hemoglobin in patients with diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2009; 58:1477–1482. PMID: 19592053.

7. Farvid MS, Siassi F, Jalali M, Hosseini M, Saadat N. The impact of vitamin and/or mineral supplementation on lipid profiles in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004; 65:21–28. PMID: 15163474.

8. Kadhim HM, Ismail SH, Hussein KI, Bakir IH, Sahib AS, Khalaf BH, Hussain SA. Effects of melatonin and zinc on lipid profile and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients poorly controlled with metformin. J Pineal Res. 2006; 41:189–193. PMID: 16879326.

9. Kelishadi R, Hashemipour M, Adeli K, Tavakoli N, Movahedian-Attar A, Shapouri J, Poursafa P, Rouzbahani A. Effect of zinc supplementation on markers of insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammation among prepubescent children with metabolic syndrome. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2010; 8:505–510. PMID: 21028969.

10. Sun Q, van Dam RM, Willett WC, Hu FB. Prospective study of zinc intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:629–634. PMID: 19171718.

11. Marreiro DN, Geloneze B, Tambascia MA, Lerário AC, Halpern A, Cozzolino SM. Effect of zinc supplementation on serum leptin levels and insulin resistance of obese women. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2006; 112:109–118. PMID: 17028377.

12. Obeid O, Elfakhani M, Hlais S, Iskandar M, Batal M, Mouneimne Y, Adra N, Hwalla N. Plasma copper, zinc, and selenium levels and correlates with metabolic syndrome components of lebanese adults. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2008; 123:58–65. PMID: 18288450.

13. Mikhail N. The metabolic syndrome: insulin resistance. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2009; 11:156–158. PMID: 19278606.

14. Ministry of Health and Welfare. National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey Report 2005. 2005. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare.
15. Kim J, Jo I. Relationship between body mass index and alanine aminotransferase concentration in non-diabetic Korean adults. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010; 64:169–175. PMID: 19904291.

16. Kim J, Jo I. Grains, vegetables, and fish dietary pattern is inversely associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome in South Korean adults. J Am Diet Assoc. 2011; 111:1141–1149. PMID: 21802559.

17. Kim J, Jo I. Age-dependent association between sleep duration and hypertension in the adult Korean population. Am J Hypertens. 2010; 23:1286–1291. PMID: 20706198.

18. Kim J, Paik HY, Joung H, Woodhouse LR, Li S, King JC. Zinc supplementation reduces fractional zinc absorption in young and elderly Korean women. J Am Coll Nutr. 2004; 23:309–315. PMID: 15310734.

19. Meret S, Henkin RI. Simultaneous direct estimation by atomic absorption spectrophotometry of copper and zinc in serum, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 1971; 17:369–373. PMID: 5573399.

20. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–419. PMID: 3899825.
21. Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22:1462–1470. PMID: 10480510.

22. Ma Z, Gingerich RL, Santiago JV, Klein S, Smith CH, Landt M. Radioimmunoassay of leptin in human plasma. Clin Chem. 1996; 42:942–946. PMID: 8665687.

23. Beletate V, El Dib RP, Atallah AN. Zinc supplementation for the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; CD005525. PMID: 17253560.

24. Gómez-García A, Hernández-Salazar E, González-Ortiz M, Martínez-Abundis E. Effect of oral zinc administration on insulin sensitivity, leptin and androgens in obese males. Rev Med Chil. 2006; 134:279–284. PMID: 16676098.
25. Hashemipour M, Kelishadi R, Shapouri J, Sarrafzadegan N, Amini M, Tavakoli N, Movahedian-Attar A, Mirmoghtadaee P, Poursafa P. Effect of zinc supplementation on insulin resistance and components of the metabolic syndrome in prepubertal obese children. Hormones (Athens). 2009; 8:279–285. PMID: 20045801.

26. Mishra G, Ball K, Arbuckle J, Crawford D. Dietary patterns of Australian adults and their association with socioeconomic status: results from the 1995 National Nutrition Survey. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002; 56:687–693. PMID: 12080411.

27. Rumawas ME, Meigs JB, Dwyer JT, McKeown NM, Jacques PF. Mediterranean-style dietary pattern, reduced risk of metabolic syndrome traits, and incidence in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009; 90:1608–1614. PMID: 19828705.

28. Wijesekara N, Chimienti F, Wheeler MB. Zinc, a regulator of islet function and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009; 11(Suppl 4):202–214. PMID: 19817803.

29. Faure P, Roussel A, Coudray C, Richard MJ, Halimi S, Favier A. Zinc and insulin sensitivity. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1992; 32:305–310. PMID: 1375070.

30. Wiernsperger NF. Oxidative stress as a therapeutic target in diabetes: revisiting the controversy. Diabetes Metab. 2003; 29:579–585. PMID: 14707886.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download