Abstract
Background and Objectives
Three-dimensional (3D) imaging is gaining popularity and has been partially used in robotic surgery but not in sinonasal surgery owing to technical problems. This is not only the first pilot study to evaluate the usefulness of newly-developed ‘twin lens’ HD-3D endoscope (Machida), but also the first clinical study to compare this instrument with the pre-existing ‘insect eye’ 3D endoscope (Visionsense).
Materials and Method
A total of 45 surgeries for cerebrospinal fluid leakage, angiofibroma, or sinonasal malignancy were performed using a 3D endoscope between November 2011 and October 2013 (‘insect eye’ Visionsense VSII 3D: 29 cases, ‘twin lens’ Machida HD-3D: 16 cases).
Results
Depth perception and recognition of anatomical structures were all excellent in the two 3D methods. The ‘twin lens’ HD-3D endoscope provided better image resolution and naturalness of color and showed less unfavorable phenomena such as image blurring and blackout than the ‘insect eye’ 3D endoscope.
References
1). Messerklinger W. Technics and possibilities of nasal endoscopy. HNO. 1972; 20(5):133–5.
2). Wigand ME, Steiner W, Jaumann MP. Endonasal sinus surgery with endoscopical control: from radical operation to rehabilitation of the mucosa. Endoscopy. 1978; 10(4):255–60.

3). Tabaee A, Anand VK, Fraser JF, Brown SM, Singh A, Schwartz TH. Three-dimensional endoscopic pituitary surgery. Neurosurgery. 2009; 64:288–95.

4). Wasserzug O, Margalit N, Weizman N, Fliss DM, Gil Z. Utility of a three-dimensional endoscopic system in skull base surgery. Skull base. 2010; 20:223–8.

5). Kari E, Oyesiku NM, Dadashev V, Wise SK. Comparison of traditional 2-dimensional endoscopic pituitary surgery with new 3-di-mensional endoscopic technology: intraoperative and early post-operative fators. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2012; 2:2–8.
6). Manes RP, Barnett S, Batra PS. Utility of novel 3-dimensional stereoscopic vision system for endoscopic sinonasal and skullbase surgery. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011; 1:191–7.

7). Hofmeister J, Frank T, Cuschieri A, Wade N. Perceptual aspects of two dimensional and stereoscopic display techniques in endoscopic surgery: review and current problems. Semin Laprosc Surg. 2001; 8:12–24.
8). Taffinder N, Smith SGT, Huber J, Russell RC, Darzi A. The effect of second generation 3D endoscope on laparoscopic precision of nov-ices and experienced surgeons. Surg Endosc. 1999; 13:1087–92.
9). Menz MD, Freeman RD. Stereoscopic depth processing in the visual cortex: a coarse-to-fine mechanism. Nat Neurosci. 2003; 6:59–65.

10). Hanna GB, Shimi SM, Cuschieri A. Randomised study of influence of two-dimensional versus three-dimensional imaging on performance of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Lancet. 1998; 351:248–51.

11). Buchs NC, Volonte F, Pugin F, Toso C, Morel P. Three-dimensional laparoscopy: a step toward advanced surgical navigation. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:692–3.

12). Byrn JC, Schluender S, Divino CM, Conrad J, Gurland B, Shlasko E, et al. Three-dimensional imaging improves surgical performance for both novice and experienced operators using the da Vinci robot system. Am J Surg. 2007; 193:519–22.

13). Shah RN, Leight WD, Patel MR, Surowirz JB, Wong YT, Wheless SA, et al. A controlled laboratory and clnical evaluation of a three-dimensional endoscope for endonasal sinus and skull base surgery. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; 25:141–4.
14). Brown SM, Tabaee A, Singh A, Schwartz TH, Anand VK. Three-dimensional endoscopic sinus surgery: feasibility and technical aspects. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 138:400–2.

15). Singh A, Saraiya R. Three-dimensional endoscopy in sinus surgery. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013; 21:3–10.

16). Van Gompel JJ, Tabor MH, Youssef AS, Lau T, Carlson AP, Lov-eren HR, et al. Field of view comparison between two-dimensional and three-dimensional endoscopy. Laryngoscope. 2014; 124:387–90.

17). Castelnuovo P, Battaglia P, Turri-Zanoni M, Volpi L, Bignami M, Dallan I. Transnasal skull base reconstruction using a 3-d endoscope: our first impressions. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2012; 73:85–9.

18). Barkhoudarian G, Del Carmen Becerra Romero A, Laws ER. Evaluation of the 3-dimensional Endoscope in transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery. 2013; 73:74–9.

19). Bolzoni Villaret A, Battaglia P, Tschabitscher M, Mattavelli D, Tur-ri-Zanoni M, Castelnuovo P, et al. A 3-dimensional transnasal endoscopic journey through the paranasal sinuses and adjacent skull base: a practical and surgery-oriented perspective. Neurosurgery. 2014; 10(Suppl 1):116–20. discussion 120.

Fig. 1.
Visionsense ‘insect eye’ VSII video tower combining with 32” high-resolution display monitor and 3D imaging processing unit (A1). 4-mm 0º, 30º 3D endoscope and cable with LED light source (A2). 40” high-definition display monitor (Sony, Tokyo, Japan), Machida ‘twin lens’ 3D video camera unit and 3D converter (B1). 4.7-mm 0º 3D endoscope consisting of twin-lens (B2). 0º, 30º 3D endoscope and xenon light cable (B3).
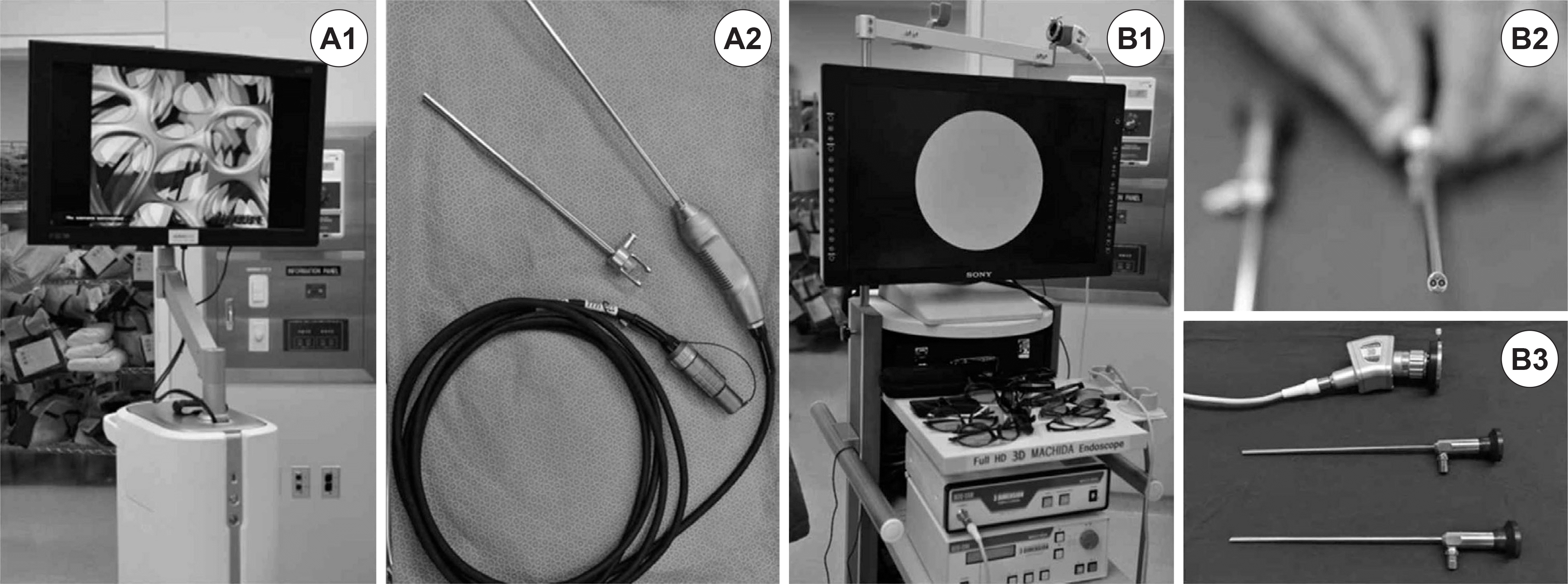
Fig. 2.
Left ethmoid sinus view in 2 different patients with ‘insect eye’ 3D endoscope (Visionsense) (A) and ‘twin lens’ HD-3D endoscope (Machida) (B). Reconstructed right (A1) and left (A2) images using single video chip. Separate, independent right (B1) and left (B2) images using twin lens and dual video chip.
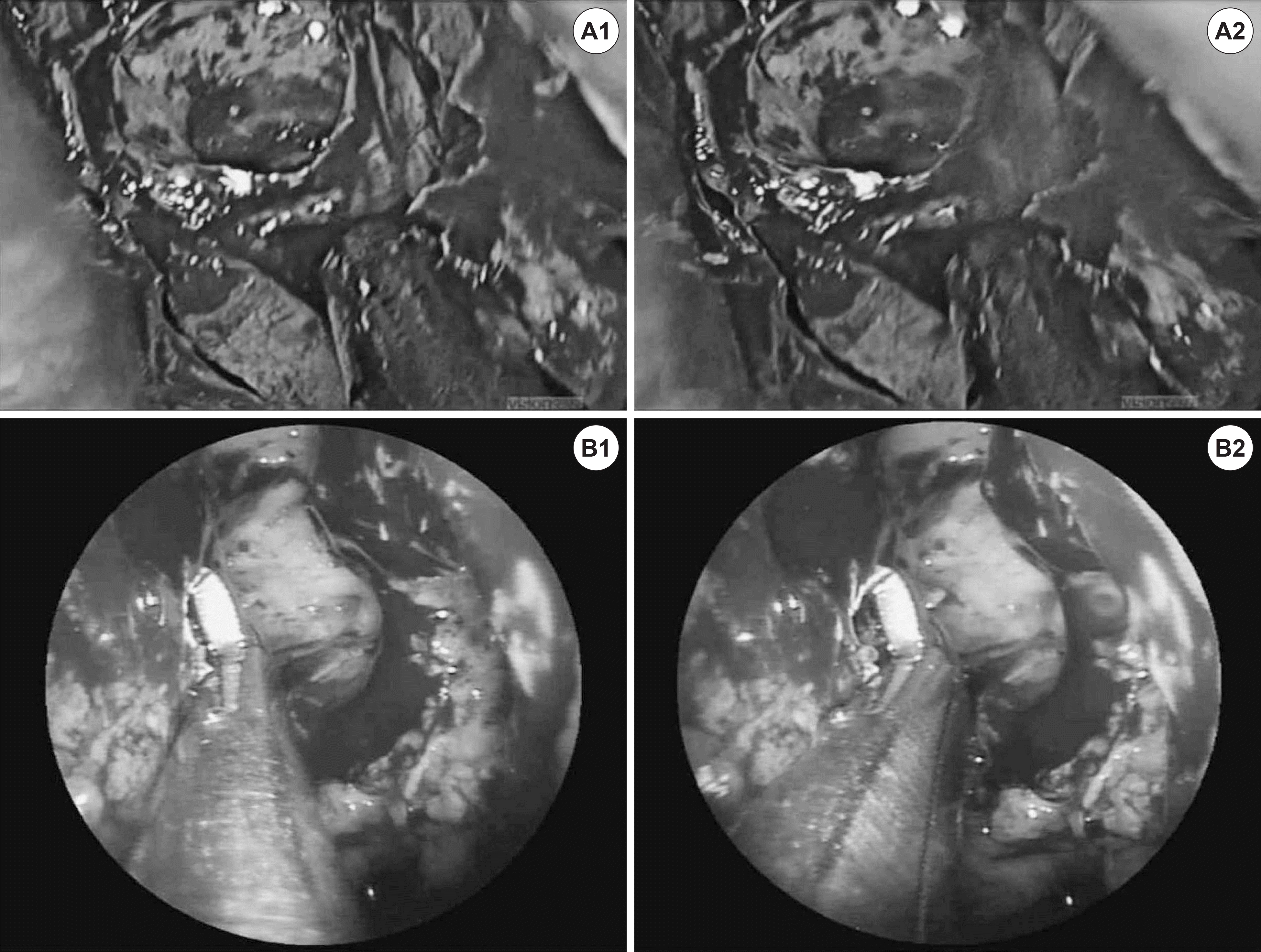
Table 1.
Specification comparison of 3D endoscopes
Table 2.
Patients’ demographic and procedural details for ‘insect eye’ Visionsense VSII 3D endoscope
Pt: patient, Op.: operation, Navi: navigation, L: left, R: right, B: both, CSF: cerebrospinal fluid, CCRTx: concurrent chemoradiation, SCC: squamous cell carcinoma, CFR: craniofacial resection, MM: medial maxillectomy, MFDA: midfacial degloving approach, w/: with, lumbar D: lumbar drainage, SRP: septorhinoplasty
Table 3.
Patients’ demographic and procedural details for ‘twin lens’ Machida HD-3D endoscope
Table 4.
Causes of switch from 3D to 2D endoscope
Table 5.
Comparison of qualitative assessments for 3D endoscopes




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download