Abstract
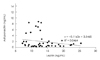
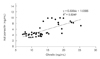
We investigated the effects of short-term food restriction and repeated fasting and refeeding on appetite regulating hormones and adiponectin activity in rats. To investigate the acute and chronic effects of food restriction in vivo, Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into a control group (CON), a 1 day fasting group, a 2 days fasting gruop, a 3 days fasting gruop, a fasting and refeeding for 1 week gruoup and a fasting and refeeding for 2 weeks group. Blood glucose, triglyceride and total cholesterol decreased in all fasting groups compared to those in the CON group. Free fatty acid of all fasting groups was higher than those in the CON, and were lowest in the three cycle fasting and refeeding group. Blood insulin following short-term food restriction was lower than that in the CON. blood ghrelin increased significantly (p < 0.01) following the short-term food restriction, However, blood ghrelin in the repeated fasting and refeeding groups decreased significantly decreased (p < 0.01) compared to that in the CON and short-term food restriction group. In contrast, blood leptin decreased significantly (p < 0.01) in the short term food restriction group and the three cycle of fasting and refeeding group but increased in the six cycle of fasting and refeeding group. No significant differences in adiponectin contents were observed in the short-term food restriction group. But, adiponectin increased significantly (p < 0.01) following the fasting and refeeding cycles. Blood adiponectin and blood leptin levels were showed positively correlated (r2 = 0.469) when all samples were analysed together.
References
1. Ernsberger P, Koletsky RJ, Baskin JS, Collins LA. Consequences of weight cycling in obese spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1996. 270(4 Pt 2):R864–R872.

2. Jen KL, Lu H, Savona L, Watkins A, Shaw M. Long-term weight cycling reduces body weight and fat free mass, but not fat mass in female Wistar rats. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1995. 19(10):699–708.
3. Stein LJ, Stellar E, West DB, Greenwood MR, Foster GD, Feurer I, Brown J, Mullen JL, Brownell KD. Early-onset repeated dieting reduces food intake and body weight but not adiposity in dietary-obese female rats. Physiol Behav. 1992. 51(1):1–6.

4. Graham B, Chang S, Lin D, Yakubu F, Hill JO. Effect of weight cycling on susceptibility to dietary obesity. Am J Physiol. 1990. 259(6 Pt 2):R1096–R1102.

5. Wang H, Zhang H, Jia Y, Zhang Z, Craig R, Wang X, Elbein SC. Adiponectin receptor 1 gene (ADIPOR1) as a candidate for type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2004. 53(8):2132–2136.

6. Tschöp M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000. 407(6806):908–913.

7. Hellsten Y, Nielsen JJ, Lykkesfeldt J, Bruhn M, Silveira L, Pilegaard H, Bangsbo J. Antioxidant supplementation enhances the exercise-induced increase in mitochondrial uncoupling protein 3 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA content in human skeletal muscle. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007. 43(3):353–361.

8. Seki Y, Berggren JR, Houmard JA, Charron MJ. Glucose transporter expression in skeletal muscle of endurance-trained individuals. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006. 38(6):1088–1092.

9. Yang WS, Lee WJ, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Matsuzawa Y, Chao CL, Chen CL, Tai TY, Chuang LM. Weight reduction increases plasma levels of an adipose-derived anti-inflammatory protein, adiponectin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86(8):3815–3819.

10. Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. 257(1):79–83.

11. Fasshauer M, Klein J, Neumann S, Eszlinger M, Paschke R. Hormonal regulation of adiponectin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. 290(3):1084–1089.

12. Azuma K, Katsukawa F, Oguchi S, Murata M, Yamazaki H, Shimada A, Saruta T. Correlation between serum resistin level and adiposity in obese individuals. Obes Res. 2003. 11(8):997–1001.

13. Benson JD, Bensadoun A. Response of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase to fasting in the chicken and the rat--a species difference. J Nutr. 1977. 107(6):990–997.

14. Bergö M, Wu G, Ruge T, Olivecrona T. Down-regulation of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase during fasting requires that a gene, separate from the lipase gene, is switched on. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277(14):11927–11932.

15. Lee JJ, Smith PJ, Fried SK. Mechanisms of decreased lipoprotein lipase activity in adipocytes of starved rats depend on duration of starvation. J Nutr. 1998. 128(6):940–946.

16. Park SC, Park YH, Park SY, Kim JY, Park YK, Lee TH, Won KC, Kim YW. The effect of leptin level fluctuations by a repeated fasting/refeeding on the leptin sensitivity in OLETF rats. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008. 23(5):310–318.

17. Bence KK, Delibegovic M, Xue B, Gorgun CZ, Hotamisligil GS, Neel BG, Kahn BB. Neuronal PTP1B regulates body weight, adiposity and leptin action. Nat Med. 2006. 12(8):917–924.

18. Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995. 270(45):26746–26749.

19. Festa A, D'Agostino R Jr, Howard G, Mykkänen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM. Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Circulation. 2000. 102(1):42–47.

20. Motoshima H, Wu X, Sinha MK, Hardy VE, Rosato EL, Barbot DJ, Rosato FE, Goldstein BJ. Differential regulation of adiponectin secretion from cultured human omental and subcutaneous adipocytes: effects of insulin and rosiglitazone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 87(12):5662–5667.

21. Wolfe BE, Jimerson DC, Orlova C, Mantzoros CS. Effect of dieting on plasma leptin, soluble leptin receptor, adiponectin and resistin levels in healthy volunteers. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2004. 61(3):332–338.

22. Numao S, Suzuki M, Matsuo T, Nomata Y, Nakata Y, Tanaka K. Effects of acute aerobic exercise on high-molecular-weight adiponectin. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008. 40(7):1271–1276.

23. O'Leary VB, Jorett AE, Marchetti CM, Gonzalez F, Phillips SA, Ciaraldi TP, Kirwan JP. Enhanced adiponectin multimer ratio and skeletal muscle adiponectin receptor expression following exercise training and diet in older insulin-resistant adults. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007. 293(1):E421–E427.
24. Hara T, Fujiwara H, Nakao H, Mimura T, Yoshikawa T, Fujimoto S. Body composition is related to increase in plasma adiponectin levels rather than training in young obese men. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2005. 94(5-6):520–526.

25. Ryan AS, Berman DM, Nicklas BJ, Sinha M, Gingerich RL, Meneilly GS, Egan JM, Elahi D. Plasma adiponectin and leptin levels, body composition, and glucose utilization in adult women with wide ranges of age and obesity. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26(8):2383–2388.

26. Tschöp M, Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Devanarayan V, Ravussin E, Heiman ML. Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes. 2001. 50(4):707–709.

27. Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999. 402(6762):656–660.

28. Takaya K, Ariyasu H, Kanamoto N, Iwakura H, Yoshimoto A, Harada M, Mori K, Komatsu Y, Usui T, Shimatsu A, Ogawa Y, Hosoda K, Akamizu T, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K. Ghrelin strongly stimulates growth hormone release in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85(12):4908–4911.

29. Hataya Y, Akamizu T, Takaya K, Kanamoto N, Ariyasu H, Saijo M, Moriyama K, Shimatsu A, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K. A low dose of ghrelin stimulates growth hormone (GH) release synergistically with GH-releasing hormone in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86(9):4552–4555.

30. Nakazato M, Murakami N, Date Y, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K, Matsukura S. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature. 2001. 409(6817):194–198.

31. Shintani M, Ogawa Y, Ebihara K, Aizawa-Abe M, Miyanaga F, Takaya K, Hayashi T, Inoue G, Hosoda K, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K. Ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, is a novel orexigenic peptide that antagonizes leptin action through the activation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y/Y1 receptor pathway. Diabetes. 2001. 50(2):227–232.

32. Kraemer RR, Castracane VD. Exercise and humoral mediators of peripheral energy balance: ghrelin and adiponectin. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2007. 232(2):184–194.
33. Zhang Y, Matheny M, Zolotukhin S, Tumer N, Scarpace PJ. Regulation of adiponectin and leptin gene expression in white and brown adipose tissues: influence of beta3-adrenergic agonists, retinoic acid, leptin and fasting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. 1584(2-3):115–122.

34. Maeda N, Takahashi M, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Nishizawa H, Kishida K, Nagaretani H, Matsuda M, Komuro R, Ouchi N, Kuriyama H, Hotta K, Nakamura T, Shimomura I, Matsuzawa Y. PPARgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes. 2001. 50(9):2094–2099.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download