1. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The state of food insecurity in the world 2001. 2002. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization in the United Nations.
2. Radimer KL. Measurement of household food security in the USA and other industrialised countries. Public Health Nutr. 2002. 5(6A):859–864.

3. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Measurement and assessment of food deprivation and undernutrition. 2002. In : International Scientific Symposium; Rome. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
4. United Nations. Report of the World Food Conference. 1975. 1974 November 5-16; New York and Rome. United Nations.
5. Wunderlich GS, Norwood JL. Food insecurity and hunger in the United States: An assessment of the measure. Panel to Review U.S. Department of Agriculture's Measurement of Food Insecurity and Hunger. 2006. National Research Council.
6. Kim K, Kim MK, Shin YJ. The concept and measurement of food security. J Prev Med Public Health. 2008. 41(6):387–396.

7. Anderson SA. Core indicators of nutritional state for difficult-to-sample populations. J Nutr. 1990. 120:Suppl 11. 1559–1600.
8. Radimer KL, Olson CM, Campbell CC. Development of indicators to assess hunger. J Nutr. 1990. 120:Suppl 11. 1544–1548.

9. Wehlar CA, Scott RI, Anderson JJ. The community childhood hunger identification project: A model of domestic hunger-demonstration project in Seattle, Washington. J Nutr Educ. 1992. 24:Suppl 1. 29S–35S.
10. Bickel G, Nord M, Price C, Hamilton WL, Cook JT. Measuring food security in the United States. Guide to measuring household food security. 2000. Office of Analysis, Nutrition, and Evaluation, Food and Nutrition Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture;Available from URL:
http://www.fns.usda.gov/fsec/FILES/FSGuide.pdf.
11. Keenan DP, Olson C, Hersey JC, Parmer SM. Measures of food insecurity/security. J Nutr Educ. 2001. 33:Suppl 1. S49–S58.

12. Hamilton WL, Cook JT, Thompson WW, Buron LF, Frongillo EA, Olson CM, Wehler CA. Household food security in the United States in 1995. Summary report of the food security measurement project. 1997. Washington, DC: US Department of Agriculture.
13. Nord M, Andrews M, Carlson S. Household food security in the United States in 2007. 2008. Washington, DC: US Department of Agriculture.
14. Shim JS, Oh K, Nam CM. Association of household food security with dietary intake - Based on the third (2005) Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES III). Korean J Nutr. 2008. 41(2):174–183.
15. Kim K, Hong SA, Kim MK. Nutritional status and food insufficiency of Korean population through the life-course by education level based on 2005 national health and nutrition survey. Korean J Nutr. 2008. 41(7):667–681.
16. Kim K, Kim MK. Development and validation of food security measure. Korean J Nutr. 2009. 42(4):374–385.

17. Oh SY, Hong MJ. Food insecurity is associated with dietary intake and body size of Korean children from low-income families in urban areas. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003. 57(12):1598–1604.

18. Kwon SO, Oh SY. Associations of household food insecurity with socioeconomic measures, health status and nutrient intake in low income elderly. Korean J Nutr. 2007. 40(8):762–768.
19. Rose D, Oliveira V. Nutrient intakes of individuals from food-insufficient households in the United States. Am J Public Health. 1997. 87(12):1956–1961.

20. Rose D, Oliveira V. Validation of a self-reported measure of household food insufficiency with nutrient intake data. Technical bulletin 1863. 1997. Alexandria, VA: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service, Food and Consumer Economics Division.
21. Swindale A, Bilinsky P. Development of a universally applicable household food insecurity measurement tool: process, current status, and outstanding issues. J Nutr. 2006. 136:1449S–1452S.

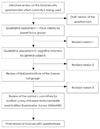
22. Oh SY. Development and validation of the Korean food insecurity measures. 2009. Seoul: Korean Research Foundation.
23. Jobe JB, Mingay DJ. Cognitive research improves questionnaires. Am J Public Health. 1989. 79(8):1053–1055.

24. Willis GB. Cognitive interviewing - A "How to" guide. Research Triangle Institute. 1999. National Cancer Institute.
25. Fowler FJ. Wiley SP, editor. Getting beyond pretesting and cognitive interviews: The case for more experimental pilot studies. Questionnaire development evaluation and testing methods. 2004. New York: Wiley.
26. Groves RM, Graham K, K. RJN, Norbert S, Christopher S. Forsyth BH, Rothgeb , Willis G, editors. Methods for testing and evaluating survey questionnaires. Does pretesting make a difference? An Experimental est. 2004. John Wiley & Sons;525–546.
27. Coates J, Frongillo EA, Rogers BL, Webb P, Wilde PE, Houser R. Commonalities in the experience of household food insecurity across cultures: what are measures missing? J Nutr. 2006. 136(5):1438S–1448S.

28. Harrison GG, Stormer A, Herman DR, Winham DM. Development of a Spanish-language version of the U.S. household food security survey module. J Nutr. 2003. 133(4):1192–1197.

29. Pérez-Escamilla R, Segall-Corréa AM, Kurdian Maranha L, Sampaio Md Mde F, Marin-León L, Panigassi G. An adapted version of the U.S. department of agriculture food insecurity module is a valid tool for assessing household food insecurity in Campinas, Brazil. J Nutr. 2004. 134(8):1923–1928.

30. Derrickson JP, Fisher AG, Anderson JE. The core food security module scale measure is valid and reliable when used with Asians and Pacific islanders. J Nutr. 2000. 130(11):2666–2674.

31. Gulliford MC, Nunes C, Rocke B. The 18 household food security survey items provide valid foods security classifications for adults and children in the Caribbean. BMC Public Health. 2006. 6:26.






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download