Abstract
Koreans have undergone many changes in dietary patterns with economic growth. The purpose of this research was to examine changes in dietary patterns using data from the 1998, 2001, and 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The study included 21,525 subjects (8,295 from 1998, 6,880 from 2001, and 6,350 from 2005) who were 20 years or older and who participated in a 24-h diet recall. The percentage energy intake from 22 food groups was calculated, and a cluster analysis was applied to identify dietary patterns. Two dietary patterns emerged; the first pattern was characterized by high intake of white rice, legumes, vegetables, kimchi, and seaweeds, the so-called "traditional" pattern (53%), whereas the other pattern was characterized by high intake of other grains, noodle dumplings, floured bread, pizza, hamburgers, cereals and snacks, potatoes, sugared sweets, nuts, fruits, meat·its products, eggs, fish, milk and dairy products, oils, beverages and seasoning, or the so-called "modified" pattern. The modified pattern comprised a higher proportion of younger aged, metropolitan residents with more education and higher incomes. However, the gender distribution was not significantly different. The modified pattern had a significantly higher intake of all nutrients except carbohydrates and had a higher proportion of energy from fat and protein. No association with a risk for metabolic syndrome was found for either dietary pattern. After age was standardized, the traditional pattern included 52% of the respondents in 1998, 54% in 2001, and 50% in 2005. However, the modified pattern was significantly more prevalent in the younger age group (20-29 yr), whereas the traditional pattern increased significantly in the older age group (≥ 65 yr). In conclusion, a secular trend was found for dietary pattern by age group, suggesting that it is necessary to monitor the changes in dietary pattern by age group and to develop appropriate dietary education and guidelines.
Figures and Tables
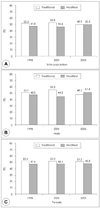
Fig. 2
Secular trends of dietary patterns by age groups. *: P from logistic analysis including gender, region, education level, study year, and income as covariates in each age group.
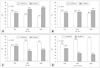
Table 2
Dietary pattern analysis: mean percent energy intake from each food group by cluster analysis using data from three KNHANES

Table 5
Metabolic syndrome and its components by pattern groups

All the models were tested using general linear regression models by cluster group (*: p < 0.05, *: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001) Multivariate models were included with age, gender, education level, income, region, and study year. Logistic analyses used age, gender, region, education level, income, and study year as covariates. OR: odds ratio
References
1. Paik HY. Dietary intakes and disease in Korean. 1997. Seoul: Seoul National University.
2. In-Depth Analysis on the 3rd (2005) Korea Health and Nutrition Examination Survey - Nutrition Survey -. 2007. Korea Health Industry Development Institute.
3. Lee HS, Kim BH, Jang YA, Kim CI. 2001 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey -The change of dietary intakes and the intakes of fat. In : Proceedings of 26th Korean Soc Lipid Atherosclerosis conference; 2003. Sep. 26-27.; Seoul, Korea.
4. Yoon KH. Comparisons of dietary atherogenicity and nutrient intakes between college students and their parents. Korean J Food Nutr. 2000. 13(2):111–117.
5. Kant AK, BI Graubard. Secular trends in patterns of self-reported food consumption of adult Americans: NHANES 1971-1975 to NHANES 1999-2002. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006. 84(5):1215–1223.

6. Valdes J, Grau M, Subirana I, Marrugat J, Covas MI, Schroder H. Secular trends in energy intake and diet quality in a Mediterranean population. Ann Nutr Metab. 2009. 54(3):177–183.

7. Zhai F, Wang H, Du S, He Y, Wang Z, Ge K, Popkin BM. Lifespan nutrition and changing socio-economic conditions in China. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007. 16:Suppl 1. 374–382.
8. Newby PK, Tucker KL. Empirically derived eating patterns using factor or cluster analysis: a review. Nutr Rev. 2004. 62(5):177–203.

10. Mishra GD, McNaughton SA, Bramwell GD, Wadsworth ME. Longitudinal changes in dietary patterns during adult life. Br J Nutr. 2006. 96(4):735–744.
11. Weismayer C, JG Anderson, A Wolk. Changes in the stability of dietary patterns in a study of middle-aged Swedish women. J Nutr. 2006. 136(6):1582–1587.

12. Borland SE, Robinson S M, Crozier SR, Inskip HM. Stability of dietary patterns in young women over a 2-year period. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008. 62(1):119–126.

13. Song Y, Park MJ, Paik HY, Joung H. Secular trends in dietary patterns and obesity-related risk factors in Korean adolescents aged 10-19 years. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010. 34(1):48–56.

14. National health and nutrition examination survey report 1998. 1999. Ministry of Health and Welfare.
15. National health and nutrition examination survey report 2001. 2002. Ministry of Health and Welfare.
16. National health and nutrition examination survey report 2005. 2006. Ministry of Health and Welfare.
17. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC, Spertus JA, Costa F. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute scientific statement: Executive summary. Crit Pathw Cardiol. 2005. 4(4):198–203.
18. Song YJ, Paik HY, Joung HJ. A comparision of cluster and factor analysis to derive dietary patterns in Korean adults using data from the 2005 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009. 14(6):722–733.
19. Song YJ, Joung HJ, Paik HY. Socioeconomic, nutrient, and health risk factors associated with dietary patterns in adult population from 2001 Korean national health and nutrition survey. Korean J Nutr. 2005. 38(3):219–225.
20. Park SH, Lee KS, Park HY. Dietary carbohydrate intake is associated with cardiovascular disease risk in Korean: Analysis of the third Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES III). Int J Cardiol. 2010. 139(3):234–240.

21. Choi J, Se-Young O, Lee D, Tak S, Hong M, Park SM, Cho B, Park M. Characteristics of diet patterns in metabolically obese, normal weight adults (Korean national health and nutrition examination survey III, 2005). Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2010.09.001.

22. Wirfalt AK, RW Jeffery. Using cluster analysis to examine dietary patterns: nutrient intakes, gender, and weight status differ across food pattern clusters. J Am Diet Assoc. 1997. 97(3):272–279.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download