Abstract
Objectives
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Prevalence of supplement use across age groups by genderAll analyses including prevalence of dietary supplements accounted for the complex sampling design effect and appropriate sampling weights of the national survey using PROC SURVEY procedure in the SAS program.
Rao-Scott chi-square p values were obtained using PROC SURVEYFREQ, ***0.001, **0.01.
|
Table 1
General characteristics of dietary supplement users among Korean adults aged 20 years or more by gender

Table 2
Lifestyle behavior of supplement users among Korean adults aged 20 years or more by gender

1) All analyses including prevalence of dietary supplements accounted for the complex sampling design effect and appropriate sampling weights of the national survey using PROC SURVEY procedure in the SAS program. Odds Ratios and 95% confidence intervals from multivariate logistic regression analyses adjusted with age, education level, household income, spouse and residential area.
2) Healthy group included subjects having at least one of desirable behaviors with regard to drinking, smoking and physical activity.
Table 3
Health status and disease history of supplement users among Korean adults aged 20 years or more by gender
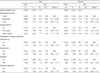
1) All analyses including prevalence of dietary supplements accounted for the complex sampling design effect and appropriate sampling weights of the national survey using PROC SURVEY procedure in the SAS program. Odds Ratios and 95% confidence intervals from multivariate logistic regression analyses adjusted with age, education level, household income, spouse and residential area.
2) Disease history was determined by having all available diseases that had been assessed in the KNHANES, which included cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, respiratory, digestive system, endocrine metabolic, cancer and other chronic conditions.
3) Metabolic disease was determined having at least one disease of dyslipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes.
Table 4
Dietary behaviors of supplement users among Korean adults aged 20 years or more by gender
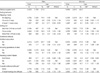
1) All analyses including prevalence of dietary supplements accounted for the complex sampling design effect and appropriate sampling weights of the national survey using PROC SURVEY procedure in the SAS program. Odds Ratios and 95% confidence intervals from multivariate logistic regression analyses adjusted with age, education level, household income, spouse, residential area, smoking, self-assessed health and disease history.
2) It included three attitudes of nutrition education, knowing guidelines of diets, reading nutrient labels.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download