Abstract
Objectives
This study was performed to investigate health-related factors, nutrition knowledge and food habits of college students in Wonju.
Methods
A total of 442 (male: 221, female: 221) college students were recruited and a questionnaire-based survey was conducted. The general characteristics, health-related factors, nutrition knowledge, and food habits were investigated and data were analyzed using SPSS WIN (ver 21.0).
Results
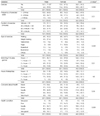
The body mass index (22.9 kg/m2 vs 20.9 kg/m2, p < 0.001) was significantly higher in the males. The ratio of weight (p < 0.001) was significantly different between males and females. Health-related factor scores 'Exercise (p < 0.001)', 'Number of exercise (p < 0.001)', 'Times of exercise (p < 0.01)', 'Concerns about health (p < 0.05)', 'Health condition (p < 0.001)' were significantly higher in the males. 'Type of exercise (p < 0.001)' was significantly different between males and females. Score on 'Watching TV & computer games (p < 0.01)' was significantly higher in the females. Smoking (p < 0.001) was significantly higher in the males. Type of beverages consumed (p < 0.001) was significantly different between males and females. Nutrition knowledge score (11.8 vs 12.9, p < 0.05) was significantly higher in the females. Scores on 'Iron deficiency is leading to anemia (p < 0.01)' and 'carbonated beverages, such as coke, have no calorie (p < 0.05)' were significantly higher in the females. Food habits score (56.4 vs 53.7, p < 0.01) was significantly higher in the males. Scores on 'I have three meals a day (p < 0.01)', 'I have breakfast regularly (p < 0.001)', 'I have meals on time (p < 0.001)', 'I do exercise every day (p < 0.001)', 'I don't eat junk food often (p < 0.05)', 'I don't eat sweet food often (p < 0.05)', and 'I don't eat out often (p < 0.05)' were significantly higher in the males.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Abood DA, Black DR, Birnbaum RD. Nutrition education intervention for college female athletes. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2004; 36(3):135–139.
2. Brown LB, Dresen RK, Eggett DL. College students can benefit by participating in a prepaid meal plan. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005; 105(3):445–448.
3. Chang HS, Kim MR. A study on the anthropometry and healh-related lifestyle habits of women college students in Kunsan. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003; 8(4):526–537.
4. Cheong SH, Chang KJ. Anthropometric measurement, dietary behavior and nutrient intake of the nation-wide college students attending a nutrition education via internet. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2006; 35(5):565–571.
5. Cheong SH, Kwon WJ, Chang KJ. A comparative study on the dietary attitudes, dietary behaviors and diet qualities of food and nutrition major and non-major female university students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2002; 7(3):293–303.
6. Chung HA. Effects of nutrition related courses on nutrition knowledge and dietary attitudes of university students in Gyeongnam. Kyungnam University;2009. 4–50. MS thesis.
7. Guo JL, Kim SK, Kim JW, Kim MH, Kim SN, Kim SB. Effects of nutrition education for Chinese college students in Korea - Focused on personalized daily energy requirement and food exchange units -. Korean J Community Nutr. 2013; 18(6):565–576.
8. Ha EJ, Caine-Bish N. Effect of nutrition intervention using a general nutrition course for promoting fruit and vegetable consumption among college students. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2009; 41(2):103–109.
9. Hwang JH, Lee HM. A study on lifestyles, dietary habits, nutrition knowledge and dietary behaviors of male university students according to residence type. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007; 12(4):381–395.
10. Jin YH, You KH. A study on the eating habit and eating out behavior of the university students in the Gyeonggi area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2010; 15(5):687–693.
11. Kang HJ, Byun KW. Effect of two-year course of food and nutrition on improving nutrition knowledge, dietary attitudes and food habits of junior college female students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2010; 15(6):750–759.
12. Kim BR. A study on nutrition knowledge, dietary habits, health-related life style and health condition of college students in Chuncheon. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2006; 35(9):1215–1223.
13. Kim HK, Kim JH, Jung HK. A comparison of health related habits, nutrition knowledge, dietary habits, and blood composition according to gender and weight status of college students in Ulsan. Korean J Nutr. 2012; 45(4):336–346.
14. Kim KH. A Study of the dietary habits, the nutritional knowledge and the consumption patterns of convenience foods of university students in the Gwangju area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003; 8(2):181–191.
15. Kim IS, Yu HH, Han HS. Effects of nutrition knowledge, dietary attitude, dietary habits and life style on the health of college students in the Chungnam area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2002; 7(1):45–57.
16. Kim MH, Jeong ES, Kim EJ, Chol HK, Bae YJ, Choi MK. Night eating status of university students in partial area of Chungnam. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2011; 21(4):563–576.
17. Kim YR. The relationship among types of leisure activity, subjective health status and the happy life. Korean J Sport Sci. 2009; 20(3):553–566.
18. Ko MS. The comparison in daily intake of nutrients and dietary habits of college students in Busan. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007; 12(3):259–271.
19. Healthy drinking club. Korea Public Health Associantion;2015. cited March 20, 2015. Available from http://kpha.intzvill.co.kr/club/sub/intro.php?p_mbs=02-01-01.
20. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Guideline for treatment of obesity. Cheongun, Seoul: 2012. p. 17–21.
21. Kwak HK, Lee MY, Kim MJ. Comparisons of body image perception, health related lifestyle and dietary behavior based on the self-rated health of university students in Seoul. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16(6):672–682.
22. Lee JS, Kim GS. Factors on the seafood preference and eating frequency of the elementary school children. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2000; 29(6):1162–1168.
23. Lee MS, Kwak CS. The comparison in daily intake of nutrients, quality of diets and dietary habits between male and female college students in Daejeon. Korean J Community Nutr. 2006; 11(1):39–51.
24. Lee SL. Effect of nutrition education on improving dietary attitudes, food habits and food frequency - Female in twenties shift work in Gyeonggi area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2013; 18(1):55–64.
25. Lee Y, Cho WK, Oh YJ. Comparison of eating behavior between commensality and solo-eating of university students by BMI. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17(3):280–289.
26. Park HO, Hyun HJ, Song KH. The nutrition knowledge, attitudes, and dietary habits of physical education majors and non-majors of male college students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009; 14(4):363–373.
27. Park MS, Kim SA. Effect of nutrition education on improving diet behavior of university students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005; 10(2):189–195.
28. Guidelines for applicants. Republic of Korea army headquarters;2015. cited April 18, 2015. Available from http://www.goarmy.mil.kr/sub_noncom/sub_recruit3_5.jsp.
29. Seo EH. A study on food habits and nutrient intakes according to BMI in food and nutrition major and non-major female students in Kyungnam university. Korean J Community Nutr. 2014; 19(4):297–316.
30. Korea's society index, 2014. Statistics Korea;2015. cited March 19, 2015. Available from http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/6/1/index.board?bmode=read&bSeq=217&aSeq=334501&pageNo=1&rowNum=10&navCount=10&currPg=&sTarget=title&sTxt=.
31. The Ministry of Health and Welfare [MOHW]. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [KCDCP]. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VI-1). Seoul: The Ministry of Health and Welfare Division of Health Policy;2014. p. 2–113.
32. Winkleby MA, Cubbin C. Changing patterns in health behaviors and risk factors related to chronic diseases, 1990-2000. Am J Health Promot. 2004; 19(1):19–27.
33. Yeon JY, Hong SH, Bae YJ. A study on nutritional status and dietary quality of university students by body image. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17(5):543–554.
34. You JS, Chin JH, Kim MJ, Chang KJ. College students' dietary behavior, health-related lifestyles and nutrient intake status by physical activity levels using International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) in Incheon area. Korean J Nutr. 2008; 41(8):818–831.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print








 XML Download
XML Download