2. Ministry of Health and Welfare & Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The fifth Korean national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANESV) [internet]. 2011. cited 2015 Jun 22. Available from:
http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.
3. Larsson B, Svärdsudd K, Welin L, Wilhelmsen L, Björntorp P, Tibblin G. Abdominal adipose tissue distribution, obesity, and risk of cardiovascular disease and death: 13 year follow up of participants in the study of men born in 1913. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1984; 288(6428):1401–1404.
4. Neeland IJ, Turer AT, Ayers CR, Powell-Wiley TM, Vega GL, Farzaneh-Far R. Dysfunctional adiposity and the risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in obese adults. JAMA. 2012; 308(11):1150–1159.
5. Klop B, Elte JW, Cabezas MC. Dyslipidemia in obesity: mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients. 2013; 5(4):1218–1240.
6. Jo JS, Hand DM, Park HS. The depression in the obese. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 1995; 16(4):239–245.
7. Mathias SD, Williamson CL, Colwell HH, Cisternas MG, Pasta DJ, Stolshek BS. Assessing health-related quality-of-life and health state preference in persons with obesity: a validation study. Qual Life Res. 1997; 6(4):311–322.
8. Pi-Sunyer FX. Sort-term medical benefits and adverse effects of weight loss. Ann Intern Med. 1993; 119(7 Part 2):722–726.
9. Foster GD, Wadden TA, Phelan S, Sarwer DB, Sanderson RS. Obese patients' perceptions of treatment outcomes and the factors that influence them. Arch Intern Med. 2001; 161(17):2133–2139.
10. Foster GD, Wadden TA, Vogt RA, Brewer G. What is a reasonable weight loss? Patients' expectations and evaluations of obesity treatment outcomes. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1997; 65(1):79–85.
11. Chun MY. Factors of selecting a goal weight in female obesity patient. Health Commun. 2013; 8(1):26–34.
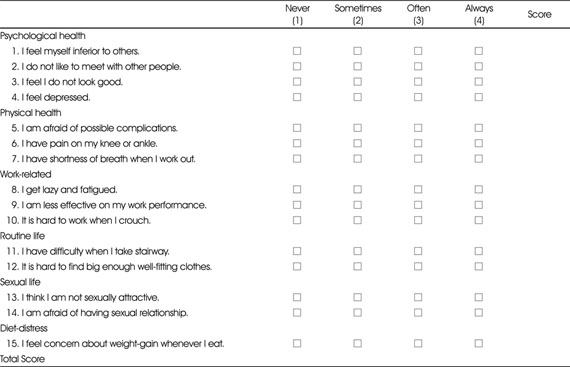
12. Park HS, Sun WS, Ou SW, Lee KY, Kim BS, Han JH, et al. Development of Korean version of obesity-related quality of life scale. J Korean Soc Study Obes. 2003; 12(4):280–293.
13. Lee JS, Shin CI, Kim BT, Lee KW, Park HS. Effect of weight reduction on obesity-specific quality of life (QOL) in obese subjects. Korean J Obes. 2006; 15(2):106–113.
14. Chaung SK, Kim CG. Obesity-related quality of life in overweight and obese female college students. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2007; 18(4):543–551.
15. Park HA, Sung EJ, Park YW, Oh SW, Park HS. Desired weight of obesity patients. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2003; 24(10):904–911.
16. Park HA, Cho JJ. Economic activities and socioeconomic status of morbidly obese Korean adults. Korean J Obes. 2011; 20(4):210–218.
17. Roehling MV. Weight-based discrimination in employment: Psychological and legal aspects. Pers Psychol. 1999; 52(4):969–1016.
18. Hall JE. Pathophysiology of obesity hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2000; 2(2):139–147.
19. Hall JE, Crook ED, Jones DW, Wofford MR, Dubbert PM. Mechanisms of obesity-associated cardiovascular and renal disease. Am J Med Sci. 2002; 324(3):127–137.
20. Frohlich ED. Clinical management of the obese hypertensive patient. Cardiol Rev. 2002; 10(3):127–138.
21. Ziegler O, Filipecki J, Girod I, Guillemin F. Development and validation of a French obesity specific quality of life questionnaire: Quality of life, obesity and dietetics(QOLOD) rating scale. Diabetes Metab. 2005; 31(3):273–283.
22. Kolotkin RL, Crosby RD. Psychometric evaluation of the impact of weight on quality of life-lite questionnaire(IWQOL-Lite) in a community sample. Qual Life Res. 2002; 11(2):157–171.
23. Bennett GA. Expectations in the treatment of obesity. Br J Clin Psychol. 1986; 25(4):311–312.







 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download