Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to develop web-based self-nutrition management u-Health program for diabetic patients (DMDMG: Diabetes Mellitus Dietary Management Guide) for achieving systematic self-management of diet.
Methods
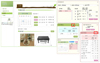
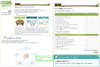
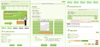
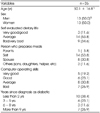
The program consisted of five parts with different contents according to the results of needs assessment. Five major parts were 1) meal management part which contains calorie prescription, meals recording and dietary assessment, 2) prevention of disease part with information of diabetes and assessment of dietary behavior, 3) dietary behavior modification part with an education on dietary behavior modification plan and dietary behavior plan, 4) meal plan containing a training section for meal plan and self constructing part for meal planning by making tables, and 5) information about myself which composed with general and physical information. The system proposed in this study provides nutrients intake results right after input of diet intake, which is possible with simultaneous calculation of input data in the server with 3,495 food and 1,821 meal data base. The nutrients analysis program was evaluated with 26 diabetic patients with two-day 24 hr recall.
Results
The differences of nutrients intakes between DMDMG and CANPRO 3.0 ranged from 13.5-16.5%, which was caused by the differences of databases of the two programs. The characteristics of DMDMG were; 1) it can provide an interactive tailored nutrition management, 2) it is a practical tool of diabetes nutritional management, 3) the program gives motivation for the dietary behavior modification.
Figures and Tables
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education and Technology (MEST) (2010-0017210) and partially supported by Soonchunhyang University Research Funds.
References
1. Ahn Y, Kim JH, Youn JE, Kim HS. Needs assessment for development of u-Health self-nutrition management program for diabetic patients: by using focus group interview. In : Proceedings of the KSCN Conference (Oct); 2009. p. 196.
2. Ahn Y, Bae J, Youn JE, Kim HS. Needs assessment for web-based self-management program by the nutrition knowledge levels of diabetic patients. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16(1):155–168.
3. Han JS, Jeong JH. A web-based internet program for nutritional counseling and diet management of patient with diabetes mellitus. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2004; 33(1):114–122.
4. Her ES, Lee KH. Development of computer-aided nutritional education program for the school children. Korean J Nutr. 2002; 35(7):791–799.
5. Hyun T, Yon M, Kim SH, Kim NH, An SM, Lee SM, Chi HJ, Sun MH, Oh CH, Wang SH, Hong MK. Development of a nutrition education website for children. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003; 8(3):259–269.
6. Kim JM, Choi SK, Seo JS. Development of program based on the website for individual meal planning. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009; 14(1):31–42.
7. Kim HW, Lee KA, Cho EJ, Chae JC, Kim YK, Lee S, Lee KH. Development of an educational web site and e-Learning system for elementary school students to reduce sugar, natrium and fat intakes. Korean J Community Nutr. 2010; 15(1):36–49.
8. Kwon JS, Kim K, Kim HK. A study on application of food photographs for estimating individuals' dietary intake. Korean J Community Nutr. 2010; 15(6):760–775.
9. Kim H, Kim S. Effects of an integrated self-management program on self-management, glycemic control, and maternal identity in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2013; 43(1):69–80.
10. Kim H, Ryu EK, Lee SW. Security considerations on cognitive radio based on body area networks for u-Healthcare. J Secur Eng. 2013; 10(1):9–20.
11. Klesges RC, Eck LH, Ray JW. Who underreports dietary intake in a dietary recall? Evidence from the Second National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1995; 63(3):438–444.
12. Korean Diabetes Association. Korean food exchange lists for diabetes. 3rd ed. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;2010.
13. Korean Food & Drug Administration. KFDA nutrition information. 2007. cited July 12, 2014. Available from http://www.mfds.go.kr/nutrition/foodlife/index.htm.
14. Kwon SY, Kwon MJ, Park KS, Cha EJ, Chun MG. Development of personal hypertension management system using PDA. J Fuzzy Log Intell Syst. 2007; 17(5):718–723.
15. Lee HS, Kim YH, Cho GC, Chough BK. Software system development for supporting nutritional management. Korean J Nutr. 1989; 22(4):290–299.
16. Lee KH, Her ES. A study on the development of a computer-assisted program for elementary school foodservice (II): based on foodservice management. Korean J Community Nutr. 2000; 5(2):217–224.
17. Lee YH, Kim JH, Kim JK, Min KP, Jung EY, Park DK. Smart phone based personalized menu management system for diabetes patient. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2010; 10(12):1–9.
18. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2010: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-1). Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2011.
19. Nam SZ. Application status for mobile education. In : Proceedings of the JKCA Conference; 2013. p. 19–20.
20. Park JC, Hwang DG, Park KS, Kim KA, Cha EJ, Jun BM. Design and implementation of diabetes management system based on PDA in the wireless internet environment. J Korean Acad Ind Soc. 2007; 8(6):1513–1518.
21. Park C, Yoo KH. The status and forecasts of rich internet application technology for next generation web. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2008; 6(4):10–14.
22. Park DK, Kim JH, Kim JK, Jung EY, Lee YH. U-health service model for managing health of chronic patients in multiplatform environment. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2011; 11(8):23–32.
23. Park JH, Hwangbo TK. IT convergence healthcare technology. Inf Commun Mag. 2011; 28(5):21–27.
24. Park SY, Yang YJ, Kim Y. Effects of nutrition education using a ubiquitous healthcare (u-Health) service on metabolic syndrome in male workers. Korean J Nutr. 2011; 44(3):231–242.
25. Samaras K, Kelly PJ, Campbell LV. Dietary underreporting is prevalent in middle-aged British women and is not related to adiposity (percentage body fat). Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999; 23(8):881–888.
26. Yon M, Park C, Yoo KH, Hyun T. Development and evaluation of a nutrition education website for the prevention and management of childhood obesity. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17(4):390–406.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print








 XML Download
XML Download