Abstract
Our society is aging rapidly, and the number of elderly people who are in charge of purchasing and preparing foods at home is increasing. However, most the elderly have difficulty managing nutrition and food safety by themselves. The purpose of this study was to develop the necessary knowledge, through focus group interview and Delphi technique to establish a food safety and nutrition education program. The diet and educational needs of the elderly were surveyed through FGI. The education topics were decided by the Delphi technique. The education program consisted of a five week program, and the topics taught were 'Dietary Change for Healthy Life', 'Prevention of Food Poisoning in Everyday Life', 'Safe Food Handling for my Health', 'Healthy Dietary Life to Prevent Chronic Disease', and 'Safety! Nutrition! Healthy Dietary Life'. This education program was designed to decrease the perceived barriers, and to increase the perceived interests and the sense of self-efficacy. Education program materials, lesson plans, slides, handouts, videos, leaflets, and booklets were developed. Based on the results, the contents of the food safety guideline leaflets for the elderly were decided as the following: (1) wash your hands in the correct way; (2) select safe food; (3) cook foods safely; (4) keep foods safely; (5) keep kitchen utensils clean. In conclusion, if advanced education programs are implemented and delivered continuously in locations such as health centers and community welfare centers, those will contribute significantly to enhance the perception of food safety and to change the desirable dietary behavior of the elderly.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
A food safety guideline leaflet developed for the elderly (http://www.kfda.go.kr/index.kfda?mid=56&seq=16013&cmd=v)

Table 3
Appropriateness of contents on food safety and nutrition education for the elderly rated by delphi expert group
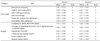
Table 4
Importance of topics and sub-theme on food safety education for the elderly rated by delphi expert group

Table 5
Importance of topics and sub-theme on nutrition education for the elderly rated by delphi expert group

References
1. Ahn Y, Kim KA, Kang HJ, Kim KW. Development of nutrition education materials for healthy aging. Korean J Community Nutr. 2006. 11(6):740–749.
2. Altekruse SF, Yang S, Timbo BB, Angulo FJ. A multi-state survey of consumer food-handling and food-consumption practices. Am J Prev Med. 1999. 16(3):216–221.
3. Bryan FL. Risks of practices, procedures and processes that lead to outbreaks of foodborne diseases. J Food Prot. 1988. 51(8):663–673.
4. Buzby JC. Older adults at risk of complications from microbial foodborne illness. Food Review. 2002. 25(2):30–35.
5. Cho YH, Park MH, Shon SH. A study on the direction of consumer education program for food safety and the production of case programs. Korean J Human Ecology. 2011. 20(6):1167–1184.
6. Choi BS, Kwon SY, Seo JY, Lee IS, Lee HJ. Comparison of nutrient intake and meal service satisfaction of elderly at the local community centers: free and reduced meal service charge. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005. 10(3):303–310.
7. Contento IR, Michela JL, Williams SS. Adolescent food choice criteria: role of weight and dieting status. Appetite. 1995. 25(1):51–76.
8. Darmton-Hill I. Psychological aspects of nutrition and aging. Nutr Rev. 1992. 50(12):476–479.
9. De Luis D, Guzman AL. Nutritional status of adult patients admitted to internal medicine departments in public hospitals in Castilla y Leon, Spain-A multi-center study. Eur J Intern Med. 2006. 17(8):556–560.
10. Gettings MA, Kiernan NE. Practices and perceptions of food safety among seniors who prepare meals at home. J Nutr Educ. 2001. 33(3):148–154.
11. Han HK, Choi SS, Kim MW, Lee SD. Food habits and nutritional status of the long-lived elderly people in Ganghwa-gun area. Korean J Community Nutr. 2005. 10(1):101–110.
12. Hanson JA, Benedict JA. Use of the health belief model to examine older adult's food-handling behavior. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2002. 34:Suppl 1. S25–S30.
13. Hong WS, Choi YS, Yim JM. The sanitary performance and sanitary education of elementary and middle school food service employees in the Seoul area. Korean J Food Cookery Sci. 2010. 26(3):252–262.
14. Hong WS, Yim JM. Evaluation of foodservice employees' sanitary performance and sanitary education in middle and high schools in Seoul. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2009. 15(2):113–127.
15. Hong WS, Yim JM, Choi YS. Sanitary performance and knowledge of elementary school foodservice employees in Seoul. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2008. 14(4):382–395.
16. Hudson PK, Hartwell HJ. Food safety awareness of older people at home: a pilot study. J R Soc Promot Health. 2002. 122(3):165–169.
17. Long-term care, health and welfare services for the elderly. Japan Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. 2010. cited 2012 Jan 30. Available from http://www.mhlw.go.jp.
18. Jeong HY, Yang IS, Chae IS, Lee HY. Analyzing the operational differences of foodservice center for homebound elderly by the presence of the dietitian. Korean J Community Nutr. 2004. 10(2):197–204.
19. Johnson AE, Donkin AJ, Morgan K, Lilley JM, Neale RJ, Page RM, Silburn R. Food safety knowledge and practice among elderly people living at home. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1998. 52(11):745–748.
20. Jung JI, Kang EJ, Choi MY, Choi GS, Hong YP, Seo KJ, Kim GH. Development and evaluation of consumer educational contents on safety management of imported foods for female college students in Seoul. J Food Hyg Saf. 2009. 24(4):291–298.
21. Kang NE, Lee JY. The analysis of effect on nutrition education program for the elderly in Sung-nam area. Korean J Food Nutr. 2005. 18(4):357–366.
22. Keller HH, Gibbs A, Wong S, Vanderkooy P, Hedley M. Men can cook! development, implementation, and evaluation of a senior men's cooking group. J Nutr Elder. 2004. 24(1):71–87.
23. Kendall P, Medeiros LC, Hillers V, Chen G, Dimascola S. Food handling behaviors of special importance for pregnant women, infants and young children, the elderly, and immunecompromised people. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003. 103(12):1646–1649.
24. Kendall PA, Hillers VV, Medeiros LC. Food safety guidance for older adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 42(9):1298–1304.
25. Kim JG. Equity in the delivery of health care in Korea: focused on analysis by age groups. Korean Soc Secur Stud. 2011. 27(3):91–122.
26. Kim KA, Lee YK. The effect of nutrition education using animations on the nutrition knowledge, eating habits and food preferences of elementary school students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2010. 15(1):50–60.
27. Kim SJ, Yi NY, Chang HJ, Kwak TK. Current status of sanitation management performance in Korean-food restaurants and development of the sanitary training posters based on their risk factors. Korean J Food Cult. 2008. 23(5):582–594.
28. Kim YK, Lee HO, Chang R, Choue RW. A study on the food habits, nutrient intake and the disease distribution in the elderly (aged over 65 Years)(1). Korean J Community Nutr. 2002. 7(4):516–526.
29. Kohl KS, Rietberg K, Wilson S, Farley TA. Relationship between home food-handling practices and sporadic salmonellosis in adults in Louisiana, United States. Epidemiol Infect. 2002. 129(2):267–276.
30. Korean Society of Community Nutrition. Nutrition program for the elderly. 2009.
31. Kwak KS, Bae YJ, Kim MH. Nutritional status and dietary quality in the low-income elderly residing at home or in health dare facilities. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2008. 14(4):337–350.
32. Kwon BA, Kwon SH. A comparative study on influence of nutrition's teaching diet and nutrition to elementary school students: influences on nutrition knowledge, food habits, dietary behaviors. J Korea Sport Res. 2011. 22(2):15–25.
33. Ledermana LC. Assessing educational effectiveness: the focus group interview as a technique for data collection. Commun Educ. 1990. 39(2):117–127.
34. Lee HJ, Lee HS, Lee Y, Jang YA, Moon JJ, Kim CI. Nutritional environment influences hypertension in the middle aged Korean adults - based on 1998 & 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007. 12(3):272–283.
35. Lee HJ, Park SJ, Kim JH, Kim CI, Chang KJ, Yin KS, Kim KW, Choi HM. Evaluating nutrient intakes of Korean elderly using semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003. 8(3):311–318.
36. Lee KE, Yi NY, Park JY. Food safety knowledge and home food safety practices of home-delivered meal service recipients. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2009. 38(5):529–656.
37. Lee OH. A comparison of nutritional status and muscle strength of elderly women in a social welfare center and those residing at home. Korean J Community Nutr. 2002. 7(5):603–614.
38. Linestone HA, Turoff M. The delphi method: technique and applications. 1975. MA: Addison-Wesley, Reading;277.
39. Medeiros LC, Hillers VN, Chen G, Bergmann V, Kendall P, Schroeder M. Design and development of food safety knowledge and attitude scales for consumer food safety education. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004. 104(11):1671–1677.
40. Medeiros LC, Hillers VN, Kendall PA, Mason A. Food safety education: what should we be teaching to consumers? J Nutr Educ. 2001. 33(2):108–113.
41. Mitroff II, Turoff M. Technological forecasting and assessment: science and/or mythology? Technol Forecast Soc Change. 1973. 5(2):113–134.
42. Morley JE. Anorexia of aging: physiologic and pathologic. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997. 66(4):760–773.
43. Healthy eating after 50. National Institute on Aging. 2010. cited 2012 Jan 30. Available from http://www.nia.nih.gov.
44. Owen AL, Splett PL, Owen GM. Nutrition in the community: the art and science of delivering services. 1999. New York: WCB McGraw-Hill;310–338.
45. Park JK, Son SM. The dietary behaviors, depression rates and nutrient intakes of the elderly females living alone. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003. 8(5):716–725.
46. Park JY, Choi EH, Choi JH, Shim SK, Park HS, Park KH, Moon HK, Ryu K. Assessment of consumer's food safety perceptions and practices. J Food Hyg Saf. 2009. 24(1):1–11.
47. Park PS, Chun BY, Jeong GB, Hun CH, Joo SJ, Park MY. The effect of follow-up nutrition intervention programs applied aged group of high risk undernutrition in rural area. Korean J Food Cult. 2006. 22(1):127–139.
48. Park SH, Noh JM, Chang HJ, Kang YJ, Kwak TK. Risk factor analysis for preventing foodborne illness in restaurants and the development of food safety training materials. Korean J Food Cookery Sci. 2007. 23(5):589–600.
49. Park SJ, Lee HJ, Kim WS, Lim JY, Choi HM. Food preference test of the Korean elderly menu development. Korean J Community Nutr. 2006. 11(1):98–107.
50. Pauly L, Stehle P, Volkert D. Nutritional situation of elderly nursing home residents. Zeitschrift für Gerontologie und Geriatrie. 2007. 40(1):3–12.
51. Park PS, Chun BY, Jeong GB, Hun CH, Joo SJ, Park MY. The effect of follow-up nutrition intervention programs applied aged group of high risk undernutrition in rural area. Korean J Food Cult. 2006. 22(1):127–139.
52. Putman JW, Spiegel AN, Bruininks RH. Future directions in education and inclusion of students with disabilities: a Delphi investigation. Exceptional Children. 1995. 61(6):553–576.
53. Pyun JS, Kim MJ, Lee KH. Climacteric and menopausal women's beliefs on daily meals and food supplements-a focus group interview study-. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011. 16(2):239–252.
54. Redmond EC. Consumer food handling in the home: A review of food safety studies. J Food Prot. 2003. 66(1):130–161.
55. Rowe G, Wright F, Bolger F. Delphi a re-evaluation of research and theory. Technol Forecast Soc Change. 1991. 39(3):235–251.
56. Rural Development Administration. The nutrition guideline for the elderly. 2010.
57. Seo JW, Kim HY. A study on personal hygiene education of primary school students: with elementary students in Yangjoo area. Korea J Tourism Hosp Res. 2009. 23(1):255–266.
58. Sheahan SL, Fields B. Sodium dietary restriction, knowledge, beliefs, and decision-making behavior of older females. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2008. 20(4):217–224.
59. Son SM, Kim MJ. The effect of nutrition education program for various chronic disease in elderly visiting public health center. Korean J Community Nutr. 2001. 6(4):668–667.
60. Projected population and proportion. Statistic Korea. 2003. cited 2012 Feb 13. Available from http://kostat.go.kr.
61. Projected population and proportion. Statistic Korea. 2006. cited 2012 Feb 13. Available from http://kostat.go.kr.
62. Projected population and proportion. Statistic Korea. 2011. cited 2012 Feb 13. Available from http://kostat.go.kr.
63. The Korean Dietetic Association. Milk consumption nutrition education booklet for the elderly. 2006. Seoul:
64. MyPlate for older adults. Tufts University. 2011. cited 2012 Jan 30. Available from http://now.tufts.edu.
65. Eat smart, live strong: nutrition education for older adult. United States Department of Agriculture. 2008. cited 2011 Mar 20. Available from http://snap.nal.usda.gov.
66. Food safety for older adults. United States Department of Agriculture Food Safety and Inspection Service. 2006. cited 2011 Mar 20. Available from www.fsis.usda.gov.
67. 7 Tips for cleaning fruits, vegetables. United States Food and Drug Administration. 2011a. cited 2012 Feb 15. Available from www.fda.gov/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates.
68. Using the nutrition facts label: a how-to guide for older adults. United States Food and Drug Administration. 2011b. cited 2012 Feb 13. Available from http://www.fda.gov.
69. To your health! food safety for seniors. United States Food and Drug Administration, United States Department of Agriculture. 2006. cited 2011 Mar 20. Available from http://www.fda.gov.
70. Weinrich SP, Boyd M. Education in the elderly-adapting and evaluating teaching tools. J Gerontol Nurs. 1992. 18(1):15–20.
71. White JV, Ham RJ, Lipschitz DA, Dwyer JT, Wellman NS. Consensus of the nutrition screening initiative: risk factors and indicators of poor nutritional status in older Americans. J Am Diet Assoc. 1991. 91(7):783–787.
72. Yim KS. The effects of a nutrition education program for hypertensive female elderly at the public health center. Korean J Community Nutr. 2008. 13(5):640–652.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download