Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this systematic review was to assess the effects of family support programs on caregiving burden, depression, and stress in family caregivers of people with dementia.
Methods
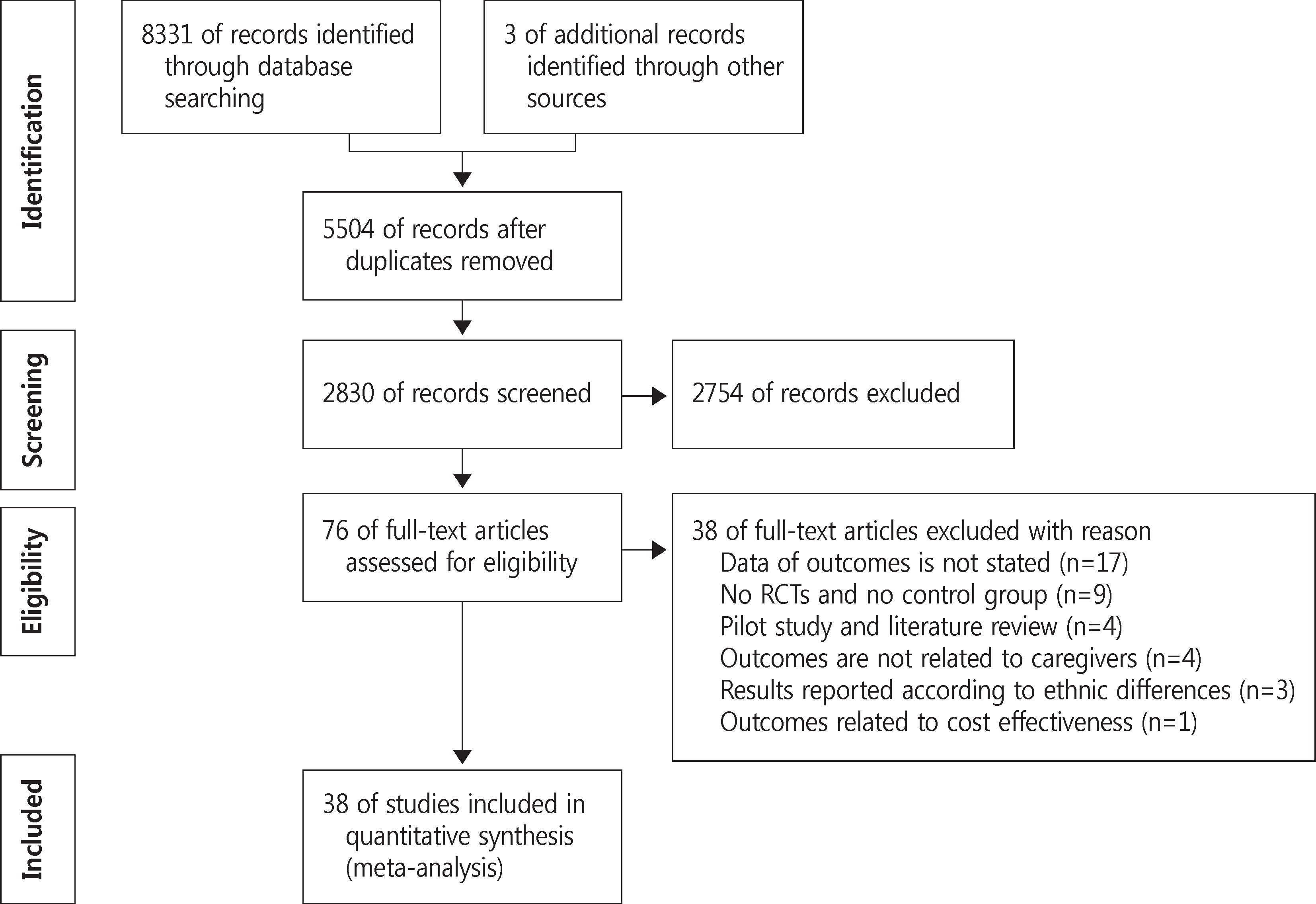
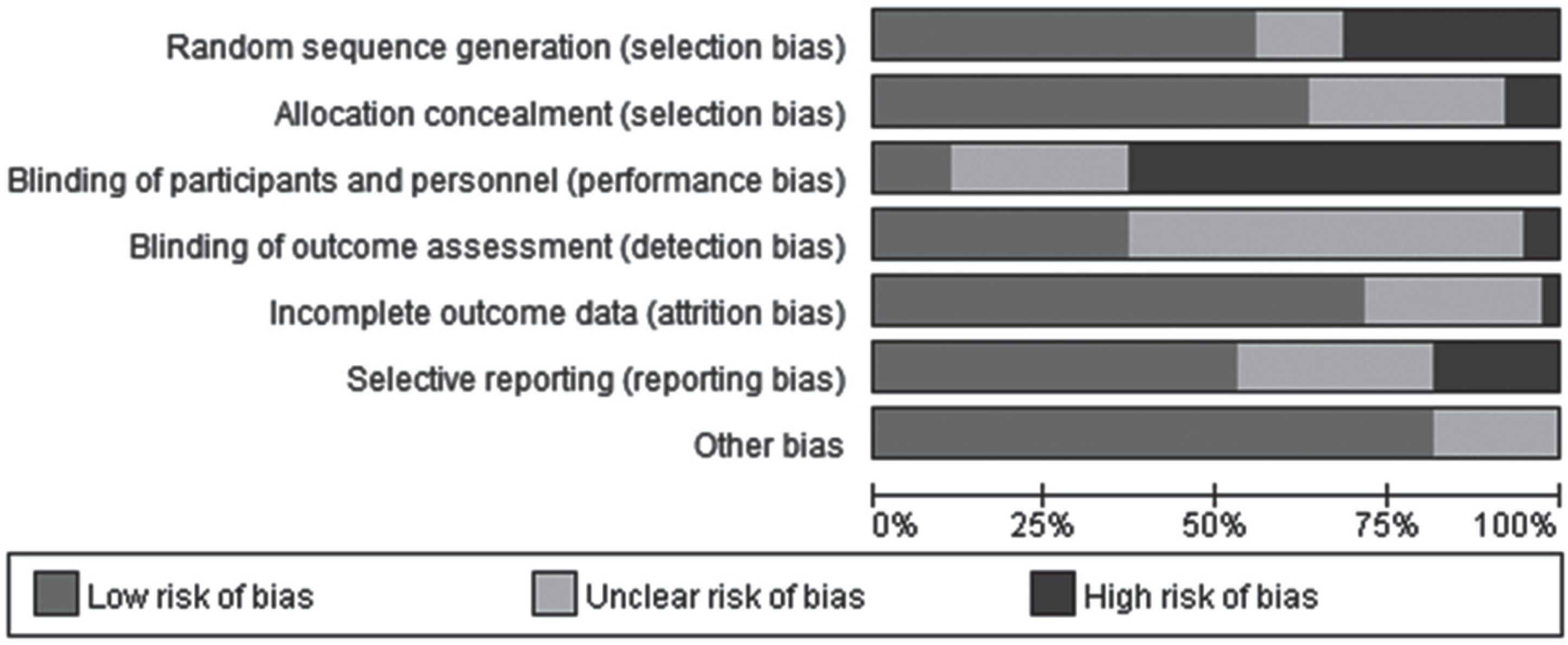
A literature search was conducted of electronic databases to identify randomized controlled studies with family support programs done between 2000 and 2014. Studies published in English and/or Korean were included for the analysis with search strategies adapted from the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group. Studies were rated for quality assessment by two independent reviewers using the appraisal checklist developed by Cochrane Reviews and Dissemination. Of 8,334 articles identified in the literature search, full texts of 76 articles that met the inclusion criteria were reviewed and 38 were found to include relevant outcomes.
Results
Results from selected studies were pooled in statistical meta-analysis using Review Manager Software and heterogeneity between combined studies was assessed using the Chi-square test. Meta-analysis showed that the effect sizes of family caregiver support programs were small to medium for categories of caregiving burden (Hedge's g= - 0.17, 95% CI= - 0.30~ - 0.04), depression (Hedge's g= - 0.30, 95% CI= - 0.40~ - 0.20), and stress (Hedge's g= - 0.39, 95% CI= - 0.52~ - 0.25).
References
1. Korea National Statistical Office. The causes of death statistics in 2005. Daejeon: Author;2006.
2. George LK, Gwyther LP. Caregiver well-being: A multidimen- sional examination of family caregivers of demented adults. The Gerontologist. 1986; 26(3):253–259. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geront/26.3.253.
3. Gaugler JE, Jarrott SE, Zarit SH, Stephens MA, Townsend A, Greene R. Adult day service use and reductions in caregiving hours: Effects on stress and psychological well-being for dementia caregivers. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2003; 18(1):55–62. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/gps.772.

4. Clipp EC, George LK. Dementia and cancer: A comparison of spouse caregivers. The Gerontologist. 1993; 33(4):534–541. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geront/33.4.534.

5. Goedendorp MM, Gielissen MF, Verhagen CA, Bleijenberg G. Psychosocial interventions for reducing fatigue during cancer treat- ment in adults. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2009; 1:CD006953. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD006953.pub2.
6. Mahoney R, Regan C, Katona C, Livingston G. Anxiety and de- pression in family caregivers of people with Alzheimer disease: The LASER-AD study. The American Journal of Geriatric Psy- chiatry. 2005; 13(9):795–801. http://dx.doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajgp.13.9.795.
7. Kong EH. The effects of dementia education program on certified geriatric caregivers in a nursing home. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2010; 19(4):349–358. http://dx.doi.org/10.12934/jkpmhn.2010.19.4.349.

8. Mittelman MS, Ferris SH, Shulman E, Steinberg G, Ambinder A, Mackell JA, et al. A comprehensive support program: Effect on depression in spouse-caregivers of AD patients. The Gerontologist. 1995; 35(6):792–802. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geront/35.6.792.

9. Mittelman MS, Roth DL, Coon DW, Haley WE. Sustained benefit of supportive intervention for depressive symptoms in caregivers of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Psychia- try. 2004; 161(5):850–856. http://dx.doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.161.5.850.

11. Etters L, Goodall D, Harrison BE. Caregiver burden among de- mentia patient caregivers: A review of the literature. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners. 2008; 20(8):423–428. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7599.2008.00342.x.
12. Nichols LO, Martindale-Adams J, Burns R, Graney MJ, Zuber J. Translation of a dementia caregiver support program in a health care system-REACH VA. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2011; 171(4):353–359. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2010.548.

13. Park YH. A study on the condition and development plan of social support: Programs for the family of old people with dementia: Fo- cused social workers in dementia facilities [master’s thesis]. Kong Ju: Kong Ju National University;2003.
14. Zarit SH, Reever KE, Bach-Peterson J. Relatives of the impaired elderly: Correlates of feelings of burden. The Gerontologist. 1980; 20(6):649–655. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geront/20.6.649.

15. Arai Y, Zarit SH. Exploring strategies to alleviate caregiver bur- den: Effects of the national long-term care insurance scheme in Japan. Psychogeriatrics. 2011; 11(3):183–189. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-8301.2011.00367.x.
16. American Psychiatric Association, editor. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. Washington, DC: Author;2013.
17. Brummett BH, Babyak MA, Siegler IC, Vitaliano PP, Ballard EL, Gwyther LP, et al. Associations among perceptions of social sup- port, negative affect, and quality of sleep in caregivers and non- caregivers. Health Psychology. 2006; 25(2):220–225. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0278-6133.25.2.220.
18. Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Version 5.1.0 [Internet]. Oxford, UK: The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. [cited 2014 November 10]. Available from: www.cochrane-handbook.org.
19. Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology(MOOSE) group. JAMA: Journal of the American Medical Association. 2000; 283(15):2008–2012.
20. Jüni P, Holenstein F, Sterne J, Bartlett C, Egger M. Direction and impact of language bias in meta-analyses of controlled trials: Em- pirical study. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2002; 31(1):115–123. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ije/31.1.115.
22. Belle SH, Burgio L, Burns R, Coon D, Czaja SJ, Gallagher- Thompson D, et al. Enhancing the quality of life of dementia care- givers from different ethnic or racial groups: A randomized, con- trolled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2006; 145(10):727–738. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-145-10-200611210-00005.
23. Gitlin LN, Belle SH, Burgio LD, Czaja SJ, Mahoney D, Gallagher- Thompson D, et al. Effect of multicomponent interventions on caregiver burden and depression: The REACH multisite initiative at 6-month follow-up. Psychology and Aging. 2003; 18(3):361–374. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0882-7974.18.3.361.

24. Acton GJ, Kang J. Interventions to reduce the burden of caregiving for an adult with dementia: A meta-analysis. Research in Nursing and Health. 2001; 24(5):349–360. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/nur.1036.

25. Parker D, Mills S, Abbey J. Effectiveness of interventions that assist caregivers to support people with dementia living in the community: A systematic review. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008; 6(2):137–172. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-1609.2008.00090.x.

26. Brodaty H, Green A, Koschera A. Meta-analysis of psychosocial interventions for caregivers of people with dementia. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2003; 51(5):657–664. http://dx.doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0579.2003.00210.x.

27. Chu H, Yang CY, Liao YH, Chang LI, Chen CH, Lin CC, et al. The effects of a support group on dementia caregivers’ burden and depression. Journal of Aging and Health. 2011; 23(2):228–241. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0898264310381522.

28. Senanarong V, Jamjumras P, Harmphadungkit K, Klubwongs M, Udomphanthurak S, Poungvarin N, et al. A counseling interven- tion for caregivers: Effect on neuropsychiatric symptoms. Interna- tional Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2004; 19(8):781–788. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/gps.1123.
Figure 3.
Forest plot of effect size by support program for family caregivers of people with dementia.

Table 1.
Descriptive Summary of Included Studies
Table 2.
Characteristics of Included Studies
RMBPC=Revised memory and behavior problem checklist; ZBI=Zarit burden interview; BDI=Beck depression inventory; MBCBS=Montgomery borgatta caregiver burden scale; CES-D=Center for epidemiological studies-depression scale; GDS=Geriatric depression scale; HADS=Hospital anxiety and depression scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg depression rating scale; PSS=Perceived stress scale; NPI=Neuropsychiatric inventory; MBPC=Memory and behavior problem checklist.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download