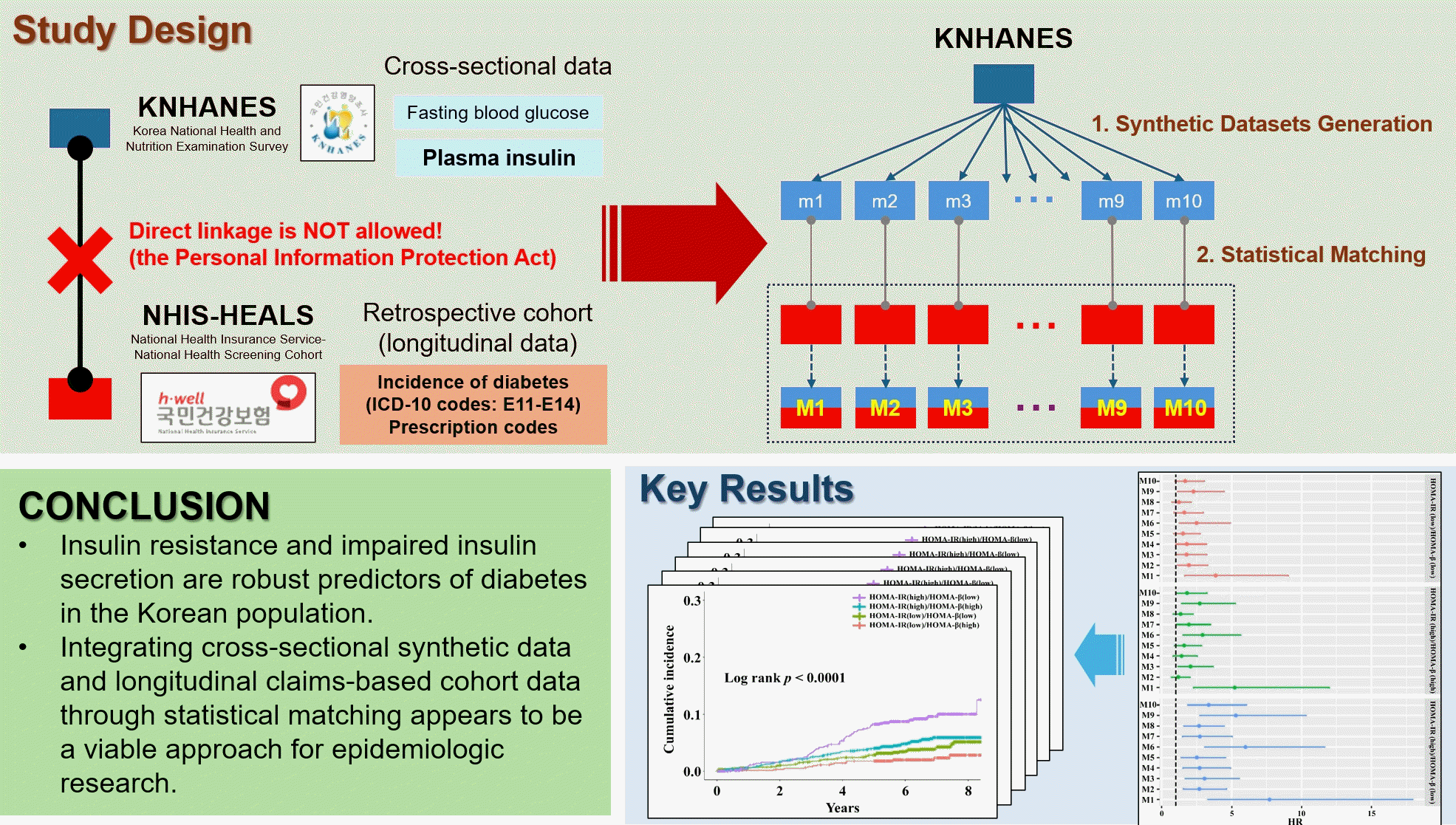
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Conclusion
Supplementary Material
Supplemental Table S1.
Supplemental Table S2.
Supplemental Table S3.
Supplemental Table S4.
Supplemental Fig. S1.
Supplemental Fig. S2.
Supplemental Fig. S3.
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: S.A., J.H.O., C.M.S. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: S.A., C.M.S., E.J., D.K., S.J.J. Drafting the work or revising: H.J., S.A., J.H.O., C.M.S., E.J., J.L. Final approval of the manuscript: H.J., S.A., J.H.O., C.M.S., E.J., D.K., S.J.J., J.L.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
REFERENCES
Fig. 1.
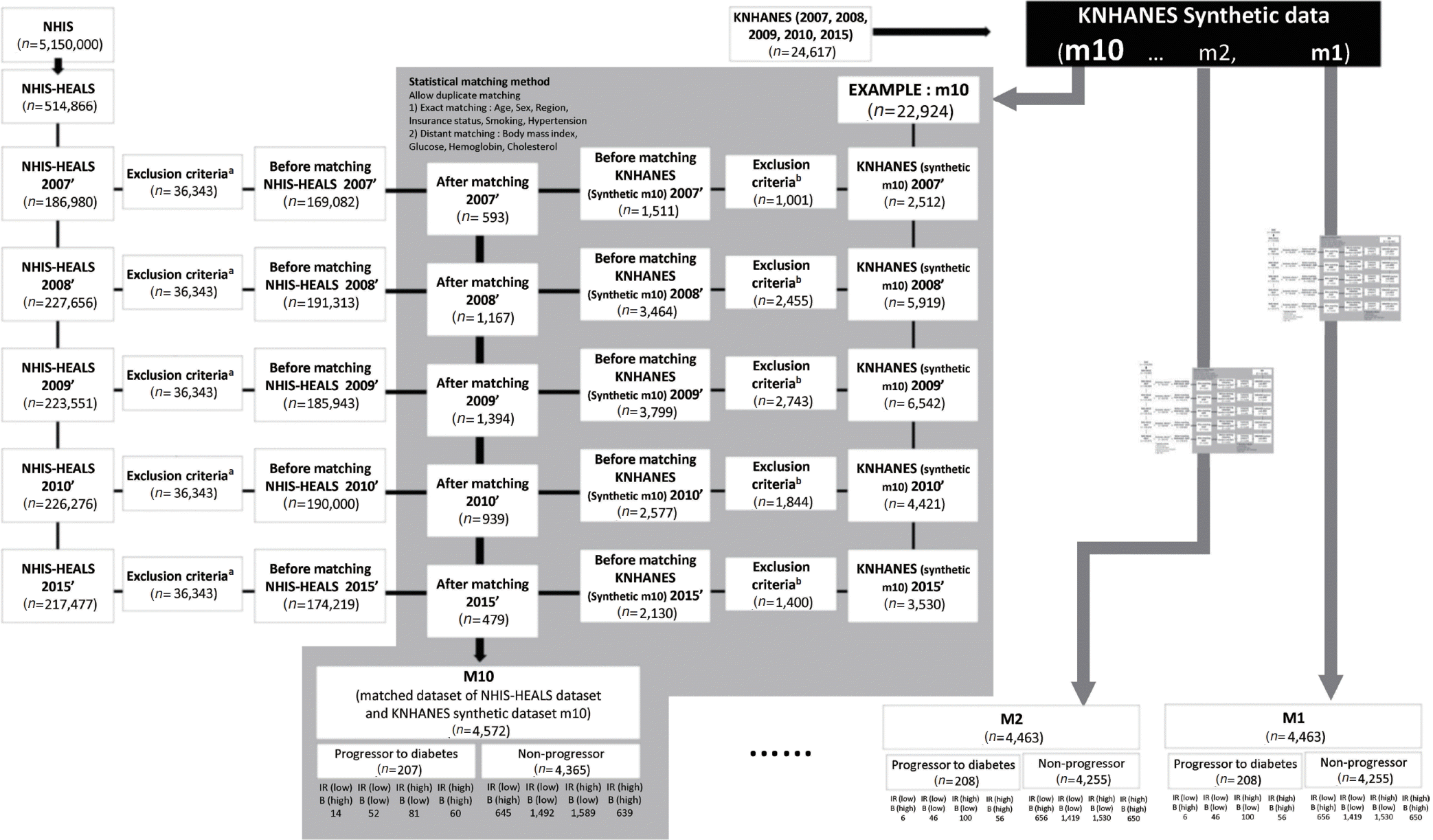
Fig. 2.
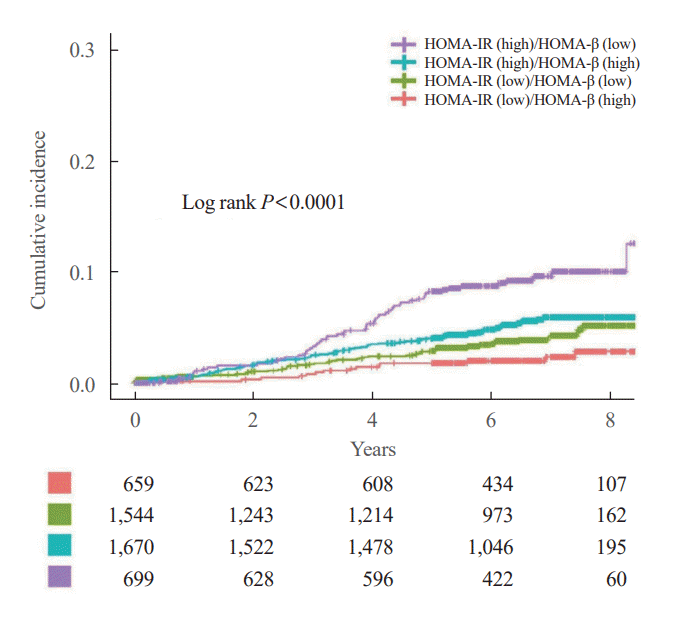
Fig. 3.
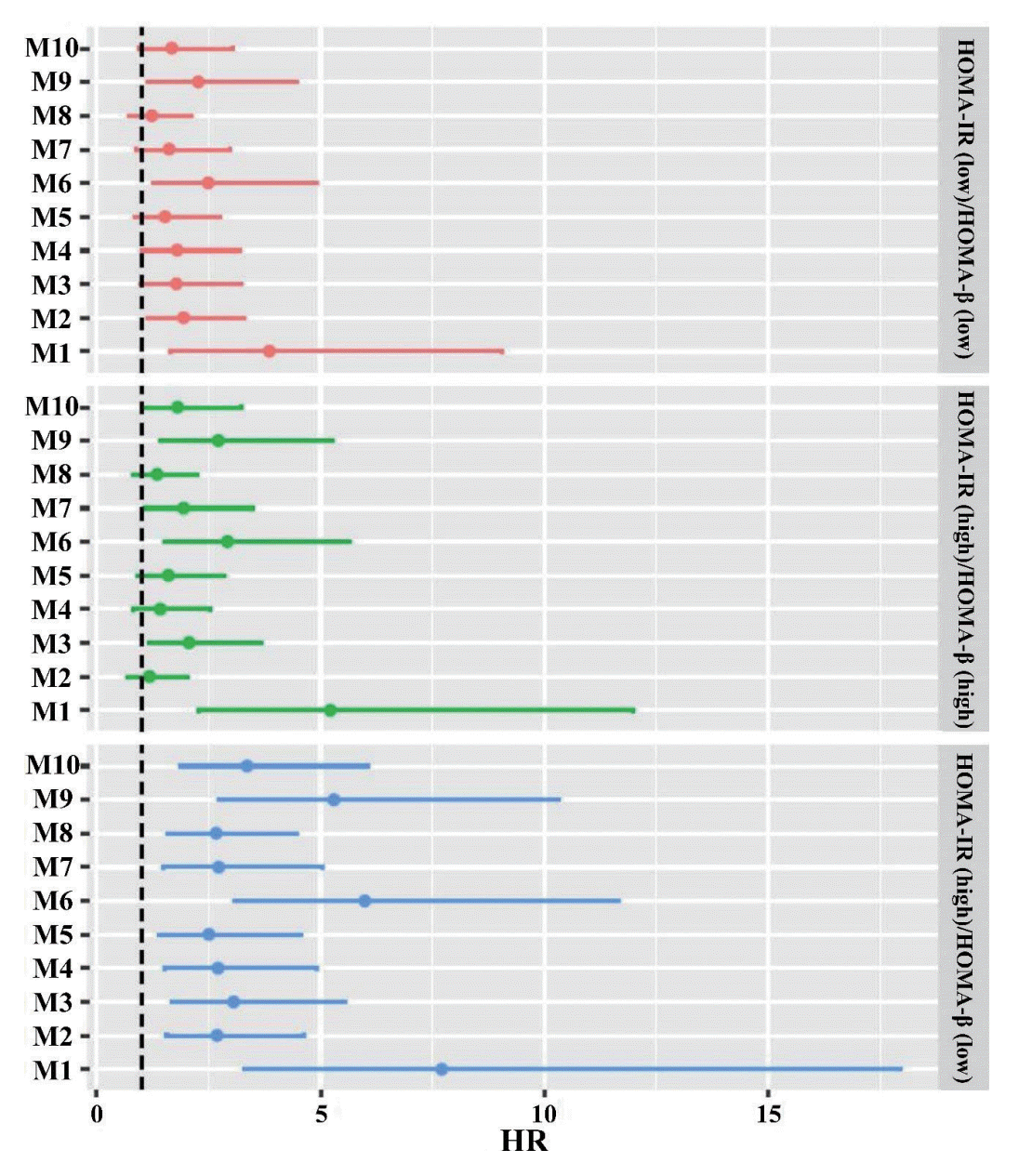
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Progressor to diabetes (n=207) | Non-progressor (n=4,365) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female sex | 121 (58.50) | 2,731 (62.60) | 0.263 |
| Age, yr | 62.39±9.48 | 59.48±9.27 | <0.001a |
| Employed insurance | 132 (63.80) | 2,639 (60.50) | 0.379 |
| Smoking | 77 (37.20) | 1,408 (32.30) | 0.159 |
| Hypertension | 90 (43.50) | 1,203 (27.06) | <0.001a |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.95±2.81 | 23.84±2.97 | <0.001a |
| Waist circumference, cm | 85.24±8.42 | 82.18±8.80 | <0.001a |
| Fasting plasma glucose, mg/dL | 102.29±11.26 | 94.63±9.40 | <0.001a |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.93±1.52 | 13.76±1.41 | 0.096 |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 118.62±18.33 | 119.13±18.16 | 0.692 |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 76.59±10.63 | 77.08±10.70 | 0.521 |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 197.17±36.18 | 194.72±35.36 | 0.330 |
| Fasting insulin, µIU/mL | 11.69±8.73 | 9.42±5.25 | <0.001a |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 48.15±10.98 | 48.79±11.39 | 0.425 |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | 134.51±91.57 | 135.29±104.54 | 0.916 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.02±2.52 | 2.23±1.39 | <0.001a |
| HOMA-β | 110.55±66.93 | 113.52±64.17 | 0.516 |
| HOMA-IR/HOMA-β status | <0.001a | ||
| HOMA-IR (low), HOMA-β (high) | 14 (6.80) | 645 (14.80) | |
| HOMA-IR (low), HOMA-β (low) | 52 (25.10) | 1,492 (34.20) | |
| HOMA-IR (high), HOMA-β (high) | 81 (39.10) | 1,589 (36.40) | |
| HOMA-IR (high), HOMA-β (low) | 60 (29.00) | 639 (14.60) |
Values are expressed as number (%) or mean±standard deviation. P values were calculated using Student’s t test or chi-square test.
KNHANES, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; NHIS, National Health Insurance Service; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function.
Table 2.
| No. | Person-year (IRR) |
Model A |
Model B |
Model C |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | |||
| HOMA-IR (low), HOMA-β (high) | 14 | 4,159.82 | 1 (Ref) | - | 1 (Ref) | - | 1 (Ref) | - |
| HOMA-IR (low), HOMA-β (low) | 52 | 8,439.04 (1.83) | 1.83 (1.02–3.31) | 0.044a | 1.70 (0.94–3.07) | 0.080 | 1.68 (0.93–3.04) | 0.085 |
| HOMA-IR (high), HOMA-β (high) | 81 | 10,021.28 (2.40) | 2.40 (1.36–4.23) | 0.003a | 2.31 (1.31–4.07) | 0.004a | 1.81 (1.01–3.22) | 0.045a |
| HOMA-IR (high), HOMA-β (low) | 60 | 4,048.49 (4.40) | 4.40 (2.46–7.86) | <0.001a | 4.07 (2.27–7.29) | <0.001a | 3.36 (1.86–6.05) | <0.001a |
Model A: unadjusted; Model B: adjusted for age and sex; Model C: adjusted for age, sex, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, and total cholesterol.
HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function; KNHANES, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; NHIS-HEALS, National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort; IRR, incidence risk ratio; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download