INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents
Sample preparation
Animals and experimental protocols
T-maze test
Novel object recognition test
Morris water maze test
Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation
Measurement of lipid peroxidation
Measurement of nitric oxide (NO) production
Western blot analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Effects of PE on space perceptive ability in T-maze test
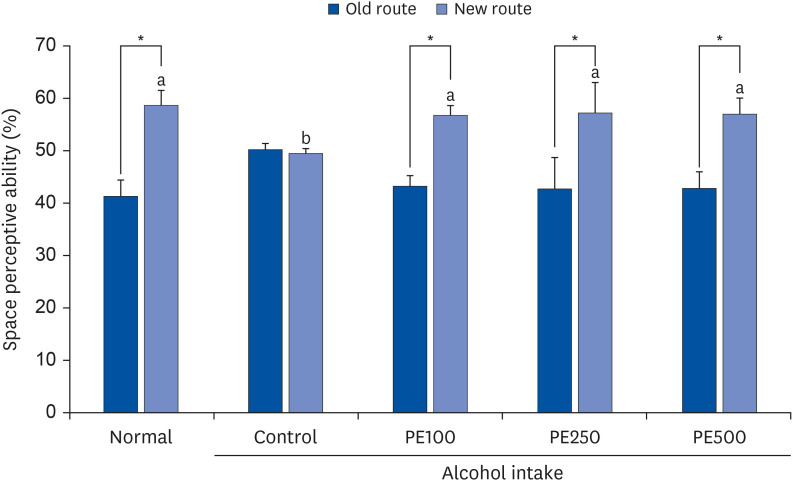 | Fig. 2Effect of PE on the T-maze test in alcohol-induced mouse.Values are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz.
*Space perceptive abilities for old and new routes were significantly different, as determined by Student’s t-test (P < 0.05).
a,bMeans with different letters are significantly different (P < 0.05), according to Duncan’s multiple range test.
|
Effects of PE on object cognitive ability in novel object recognition test
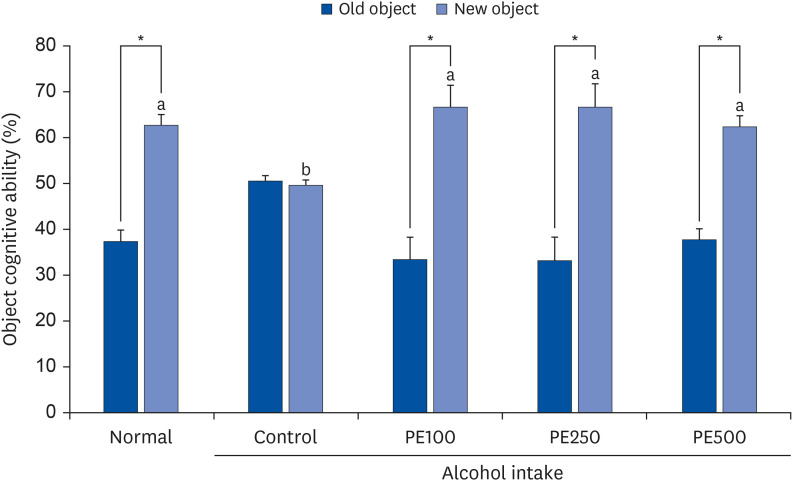 | Fig. 3Effect of PE on novel object recognition test in alcohol-induced mouse.Values are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz.
*Significant differences in cognitive ability between familiar and novel objects were determined using the Student’s t-test (P < 0.05).
a,bMeans with different letters on the bars are significantly different, according to Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
|
Effects of PE on Morris water maze test
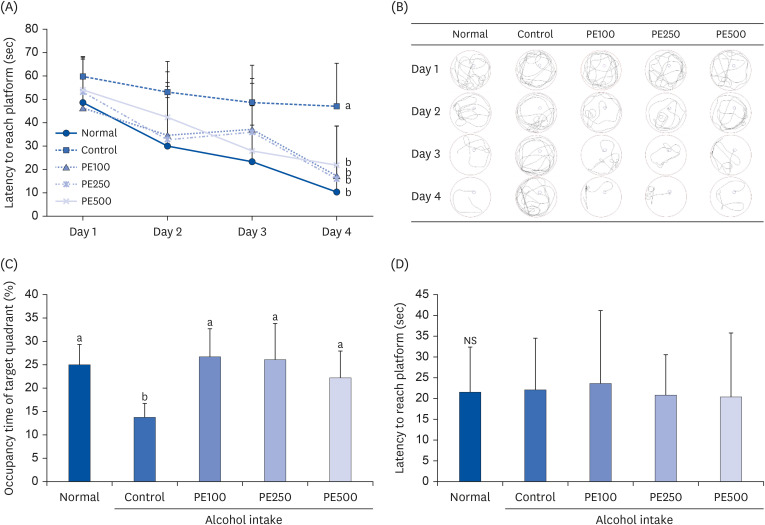 | Fig. 4Effect of PE on Morris water maze test in alcohol-induced mouse.(A) Escape latency to the hidden platform, (B) path tracing of each group to reach the hidden platform, (C) occupancy time of target quadrant, and (D) latency to exposed platform.
Values are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz.
a,bMeans with different letters on the bars are significantly different according to Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05). NS indicates that there is no significant difference (P < 0.05) among groups by Duncan’s multiple range test.
|
Effects of PE on ROS generation
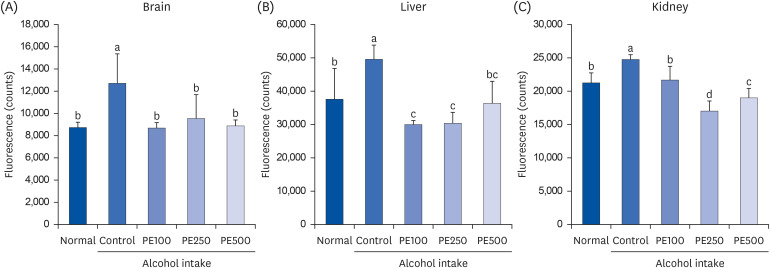 | Fig. 5Effect of PE on ROS in (A) brain, (B) liver, and (C) kidney in alcohol-induced mouse.Values are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
a-dMeans with different letters on the bars are significantly different, according to Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
|
Effects of PE on lipid peroxidation
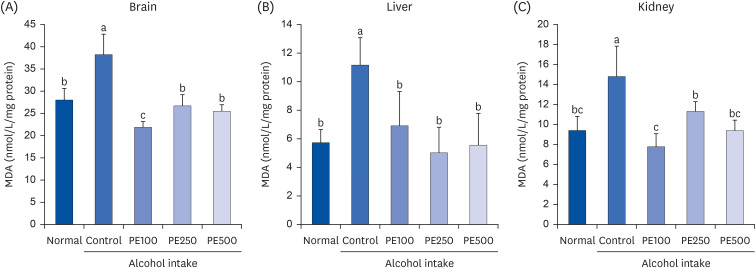 | Fig. 6Effect of PE on lipid peroxidation in (A) brain, (B) liver, and (C) kidney in alcohol-induced mouseValues are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz; MDA, malondialdehyde.
a-cMeans with different letters on the bars are significantly different, according to Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
|
Effects of PE on NO production
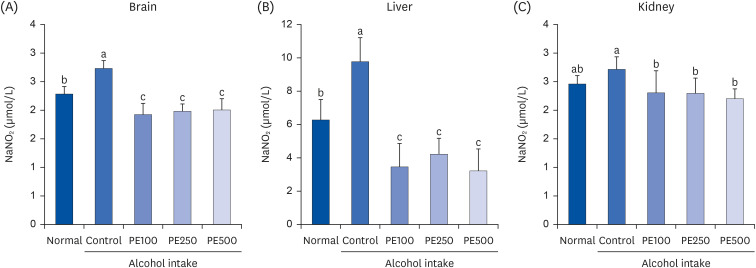 | Fig. 7Effect of PE on NO production in (A) brain, (B) liver, and (C) kidney in alcohol-induced mouse.Values are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz; NO, nitric oxide.
a-cMeans with different letters on the bars are significantly different, according to Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
|
Effects of PE on BDNF protein expression
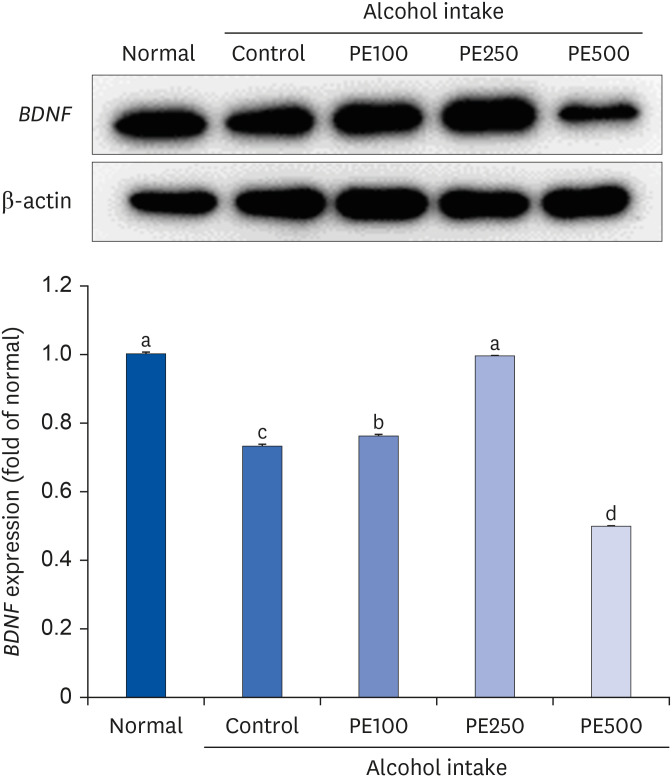 | Fig. 8Effect of PE on BDNF protein expression in alcohol-induced mouse.Values are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
a-dMeans with different letters on the bars are significantly different, according to Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
|
Effects of PE on apoptosis-related protein expression
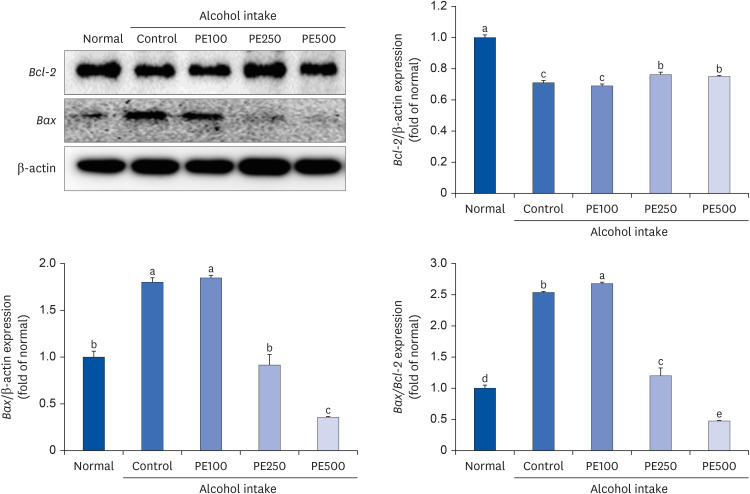 | Fig. 9Effect of PE on apoptosis-related protein expression in alcohol-induced mouse.Values are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein.
a-eMeans with different letters on the bars are significantly different, according to Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
|
Effects of PE on oxidative stress-related protein expression
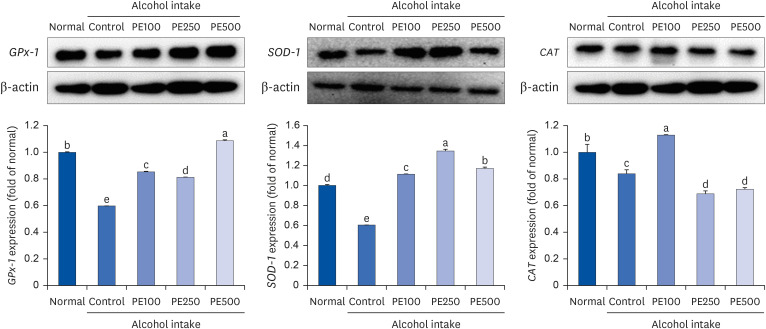 | Fig. 10Effect of PE on oxidative stress-related protein expression in alcohol-induced mouse.Values are mean ± SD.
The mice were divided into 5 groups (each group comprised 9 mice): Normal = water; Control = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day); PE100 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (100 mg/kg/day); PE250 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (250 mg/kg/day); PE500 = 16% alcohol (5 g/kg/day) + PE (500 mg/kg/day).
PE, Phyllostachys edulis (Carrière) J. Houz; GPx-1, glutathione peroxidase 1; SOD-1, superoxide dismutase 1; CAT, catalase.
a-eMeans with different letters on the bars are significantly different, according to Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download