1. Alhazmi A, Gianoli C, Neppl S, Martins J, Veloza S, Podesta M, et al. 2018; A novel approach to EPID-based 3D volumetric dosimetry for IMRT and VMAT QA. Phys Med Biol. 63:115002. DOI:
10.1088/1361-6560/aac1a6. PMID:
29714714.

3. Farhood B, Ghorbani M, Abdi Goushbolagh N, Najafi M, Geraily G. 2020; Different methods of measuring neutron dose/fluence generated during radiation therapy with megavoltage beams. Health Phys. 118:65–74. DOI:
10.1097/HP.0000000000001130. PMID:
31764421.

4. Israngkul-Na-Ayuthaya I, Suriyapee S, Pengvanich P. 2015; Evaluation of equivalent dose from neutrons and activation products from a 15-MV X-ray LINAC. J Radiat Res. 56:919–926. DOI:
10.1093/jrr/rrv045. PMID:
26265661. PMCID:
PMC4628218.

5. Trang LTN, Chuong HD, Thanh TT. 2021; Optimization of p-type HPGe detector model using Monte Carlo simulation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 327:287–297. DOI:
10.1007/s10967-020-07473-2.

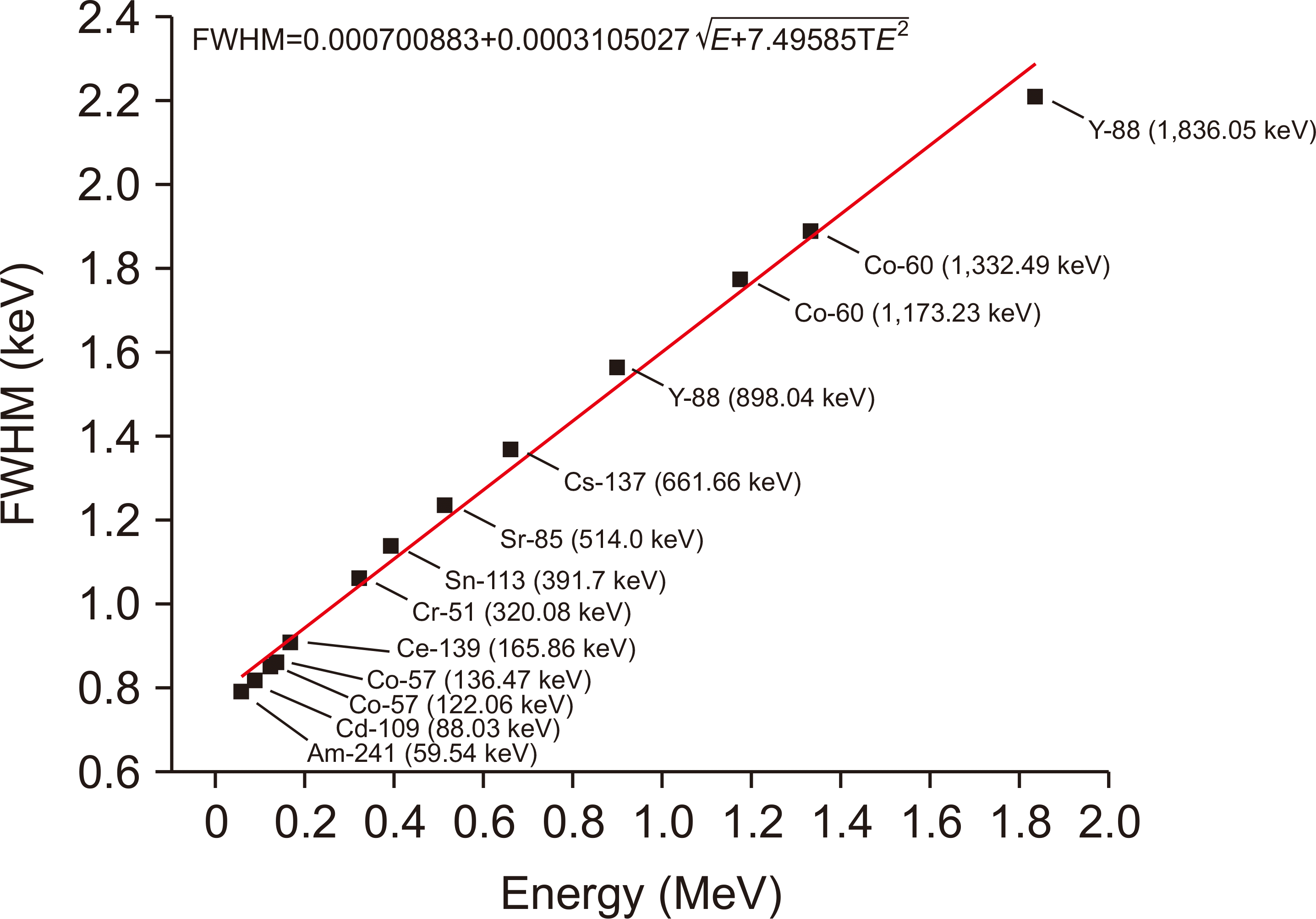
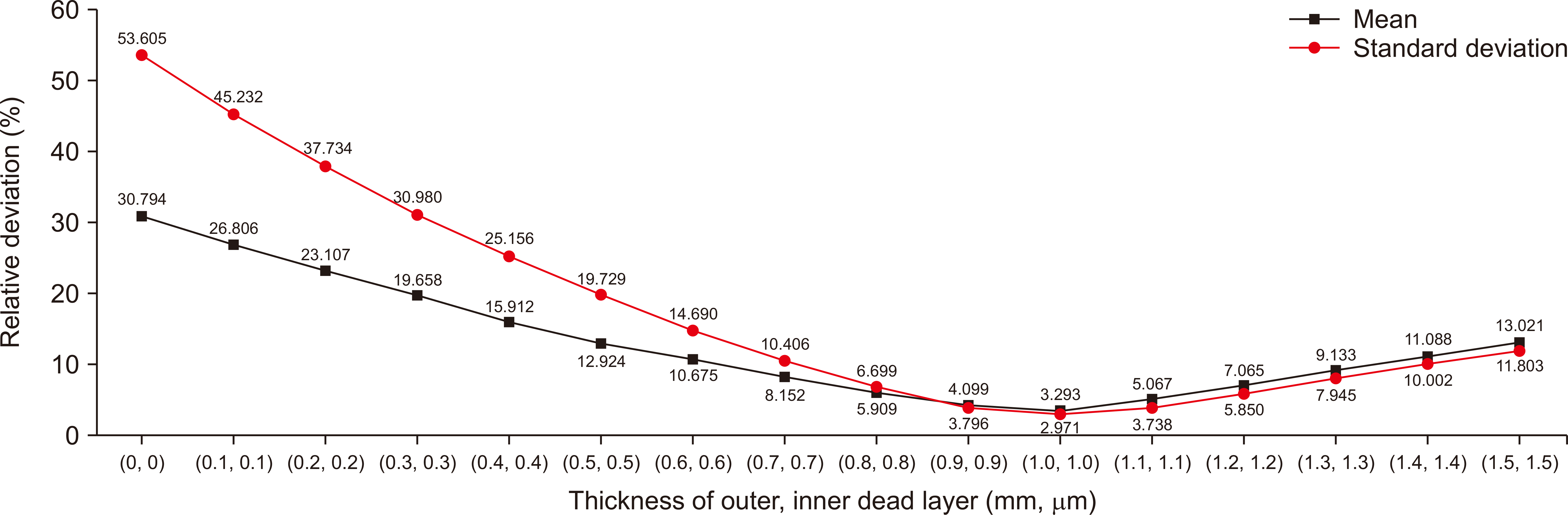
6. Kaya S, Çelik N, Bayram T. 2022; Effect of front, lateral and back dead layer thicknesses of a HPGe detector on full energy peak efficiency. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res. 1029:166401. DOI:
10.1016/j.nima.2022.166401.

7. Novotny SJ, To D. 2015; Characterization of a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector through Monte Carlo simulation and nonlinear least squares estimation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 304:751–761. DOI:
10.1007/s10967-014-3902-7.

8. Konstantinova M, Germanas D, Gudelis A, Plukis A. 2021; Efficiency calibration of high-purity germanium detector using Monte Carlo simulations including coincidence-summing corrections: volume source case. Lith J Phys. 61:66–73. DOI:
10.3952/physics.v61i1.4408.

9. Subercaze A, Sauzedde T, Domergue C, Destouches C, Philibert H, Fausser C, et al. 2022; Effect of the geometrical parameters of an HPGe detector on efficiency calculations using Monte Carlo methods. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res. 1039:167096. DOI:
10.1016/j.nima.2022.167096.

10. Aviv O, Elia P. 2020; Monte-Carlo simulations of the full-energy-peak efficiency for a broad-energy germanium detector-a comparison between GEANT4 and FLUKA. J Inst. 15:P05016. DOI:
10.1088/1748-0221/15/05/P05016.

11. Andreotti E, Hult M, Marissens G, Lutter G, Garfagnini A, Hemmer S, et al. 2014; Determination of dead-layer variation in HPGe detectors. Appl Radiat Isot. 87:331–335. DOI:
10.1016/j.apradiso.2013.11.046. PMID:
24331853.

12. Bölükdemir MH, Uyar E, Aksoy G, Ünlü H, Dikmen H, Özgür M. 2021; Investigation of shape effects and dead layer thicknesses of a coaxial HPGe crystal on detector efficiency by using PHITS Monte Carlo simulation. Radiat Phys Chem. 189:109746. DOI:
10.1016/j.radphyschem.2021.109746.

13. Liye L, Jizeng M, Franck D, Carlan LD, Binquan Z. 2006; Monte Carlo efficiency transfer method for full energy peak efficiency calibration of three type HPGe detectors: a coaxial N-type, a coaxial P-type and four BEGe detectors. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res. 564:608–613. DOI:
10.1016/j.nima.2006.03.013.

14. Boson J, Ågren G, Johansson L. 2008; A detailed investigation of HPGe detector response for improved Monte Carlo efficiency calculations. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res. 587:304–314. DOI:
10.1016/j.nima.2008.01.062.

15. Loan TTH, Ba VN, Thy THN, Hong HTY, Huy NQ. 2018; Determination of the dead-layer thickness for both p- and n-type HPGe detectors using the two-line method. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 315:95–101. DOI:
10.1007/s10967-017-5637-8.

16. Huy NQ. 2011; Dead-layer thickness effect for gamma spectra measured in an HPGe p-type detector. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res. 641:101–104. DOI:
10.1016/j.nima.2011.02.097.

17. Elanique A, Marzocchi O, Leone D, Hegenbart L, Breustedt B, Oufni L. 2012; Dead layer thickness characterization of an HPGe detector by measurements and Monte Carlo simulations. Appl Radiat Isotopes. 70:538–542. DOI:
10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.11.014. PMID:
22115878.

18. Kwon NH, Jang YJ, Kim J, Kim KB, Yoo J, Ahn SH, et al. 2021; Measurements of neutron activation and dose rate induced by high-energy medical linear accelerator. Prog Med Phys. 32:145–152. DOI:
10.14316/pmp.2021.32.4.145.






 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download