Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Notes
Fund/Grant Support: This study was supported by Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Program (grant number 2020GXNSFAA297130) and Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (grant number YCSW2023246) and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Health Committee Self-financing Scientific Research Project (grant number Z20200317).
References
Fig. 1
The expression of SOX11. (A) Neuroblastoma (NB) tissue and adrenal gland tissue. (B) Receiver operating characteristics of SOX11. (C–F) Different age groups (C), risk groups (D), MYCN status groups (E), and histology groups (F) in NB tissue. SOX11, SRY-box transcription factor 11; mRNA, messenger RNA; TARGET, Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments database (https://ocg.cancer.gov/programs/target); TPR, true positive rate; FPR, false positive rate; AUC, area under the curve; CI, confidence interval. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
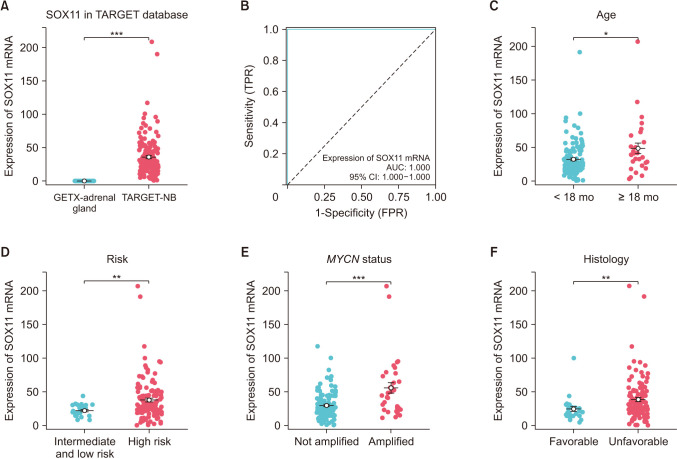
Fig. 2
Prognostic value of SOX11 in neuroblastoma. Hazard ratio, 1.719; 95 confidence interval, 0.798–1.963. SOX11, SRY-box transcription factor 11.
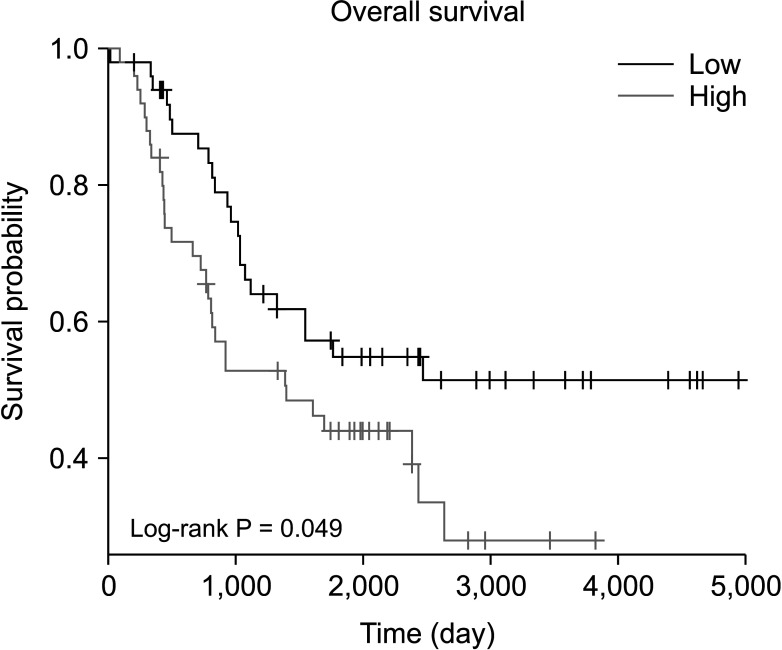
Fig. 3
Silencing SOX11 inhibited the migration of SK-N-SH. (A) Western blot confirmed the efficiency of the silencing. (B) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction confirmed the efficiency of the silencing. (C–E) Effect of silencing SOX11 on SK-N-SH migatory capability (C), SK-N-SH invasion capability (D), and the proliferative capacity of SK-N-SH (E). SOX11, SRY-box transcription factor 11; si, small interfering; NC, negative control; mRNA, messenger RNA; NS, no statistically significant difference. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
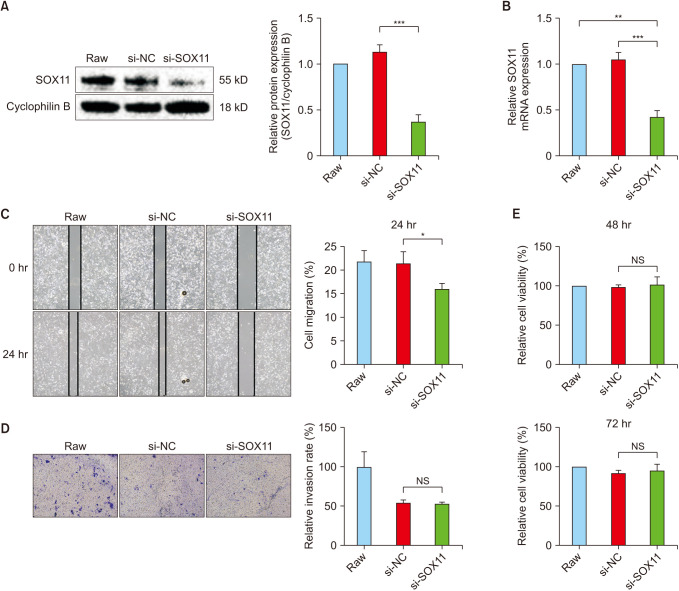
Fig. 4
Enrichment analysis of SOX11 co-expressed genes in neuroblastoma (NB). (A) Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of NB. (B) Intersection Venn diagram of DEGs of NB and all transcription factors (TFs) of humans. (C) Biological processes. (D) Cellular components. (E) Molecular function. (F) Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway. SOX11, SRY-box transcription factor 11; NS, not significant.
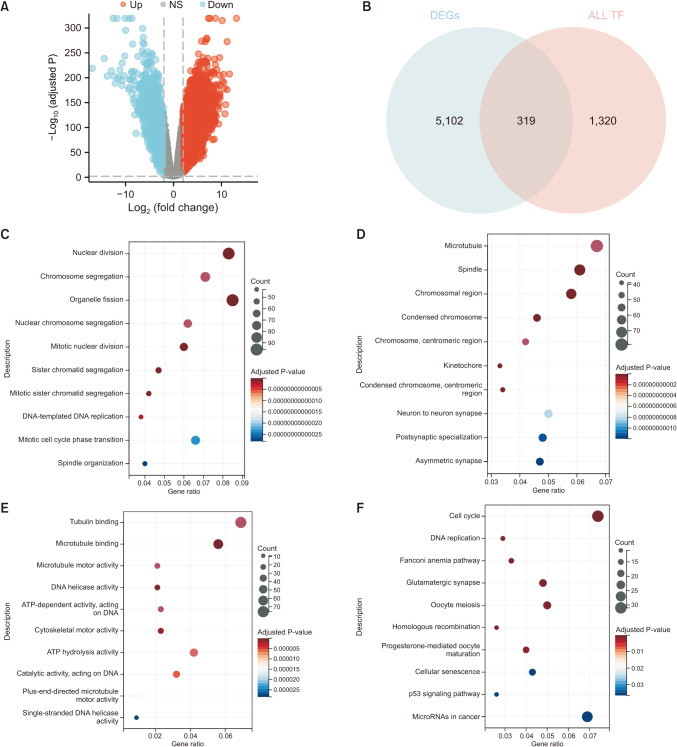
Fig. 5
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) analysis. (A) GSEA analysis overall view. (B) Neuronal system. (C) Nervous system development. (D) Developmental biology. KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; NABA, network for analysis of biomedical acceleration matrisome; NES, normalized enrichment score; FDR, false discovery rate.
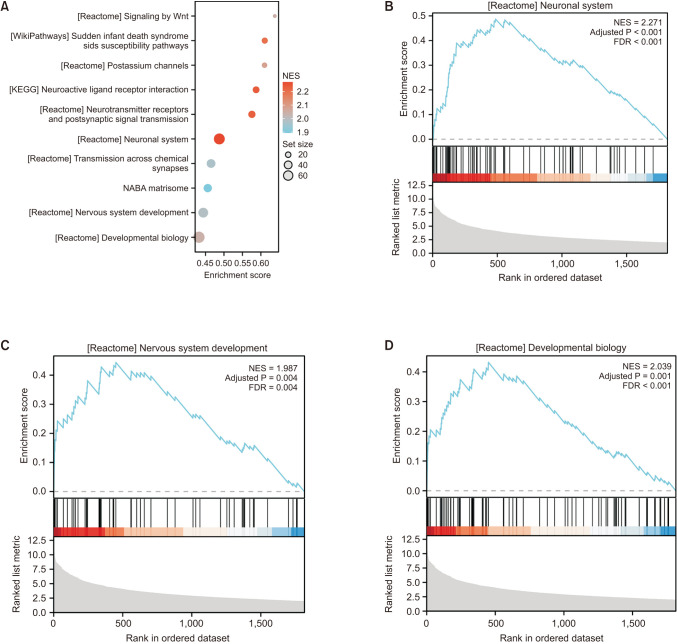
Fig. 6
SOX11 activates the expression of EZH2. (A) Intersection of target genes predicted by CHEA Transcription Factor Targets and Cistrome Data Browser (DB) with up-regulated differential genes (DEGs). (B) Binding peak of SOX11 and EZH2. (C) Expression of EZH2 in adrenal gland and neuroblastoma (NB). (D) Receiver operating characteristics of EZH2. (E) Correlation between SOX11 and EZH2 expression. SOX11, SRY-box transcription factor 11; EZH2, enhancer of zeste homolog 2; TARGET, Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments database; GTEx, Gene-Tissue Expression Project; TPR, true positive rate; FPR, false positive rate; AUC, area under the curve.
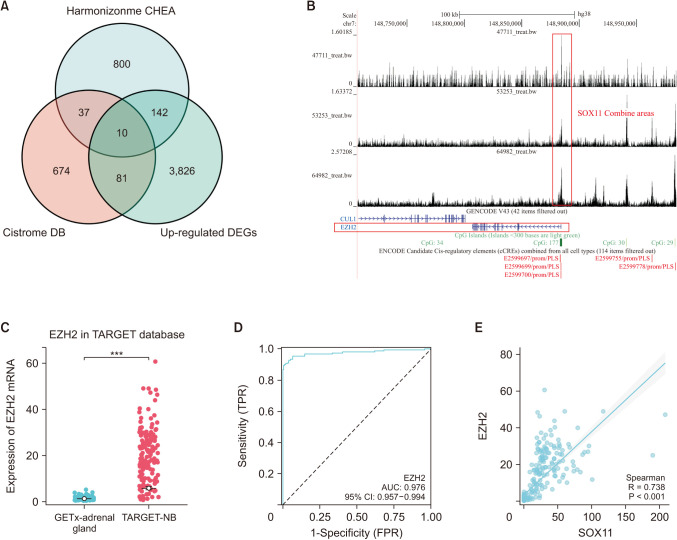
Table 2
The relationship between SOX11 expression and pathological characteristics of NB based on the TARGET database
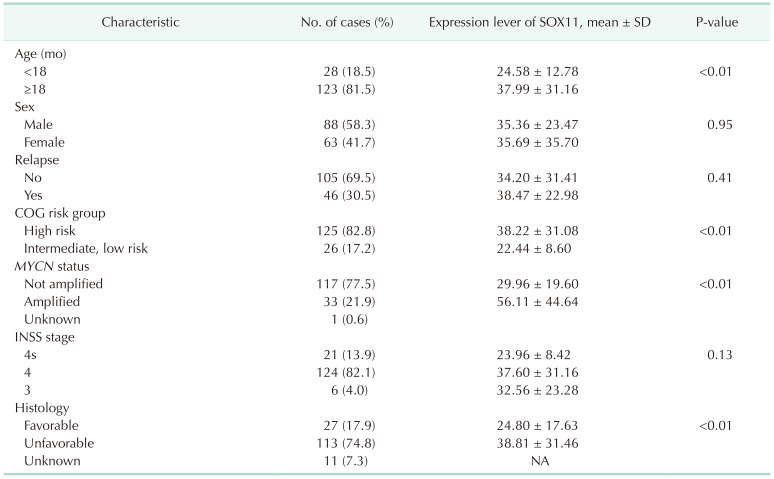
SOX11, SRY-box transcription factor 11; NB, neuroblastoma; TARGET, Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments database (https://ocg.cancer.gov/programs/target); SD, standard deviation; COG, Children’s Oncology Group; INSS, International Neuroblastoma Staging System; NA, not applicable.
Table 3
Univariate and multivariate Cox-regression results of factors related to overall survival based on TARGET
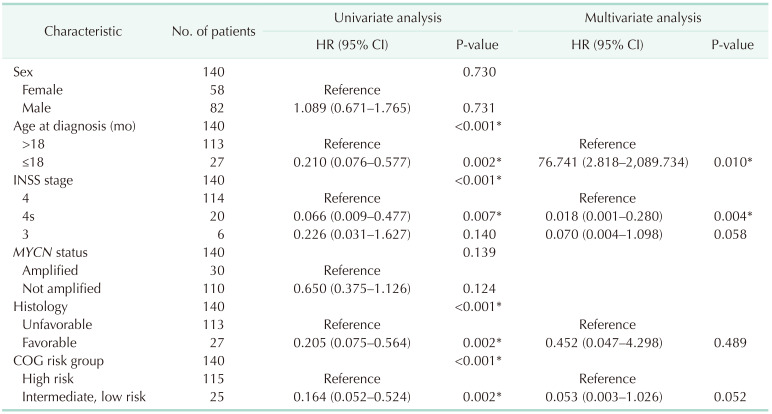
TARGET, Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments database (https://ocg.cancer.gov/programs/target); HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; INSS, International Neuroblastoma Staging System; COG, Children’s Oncology Group.
*P < 0.05, statistic significance.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download