Abstract
Objective
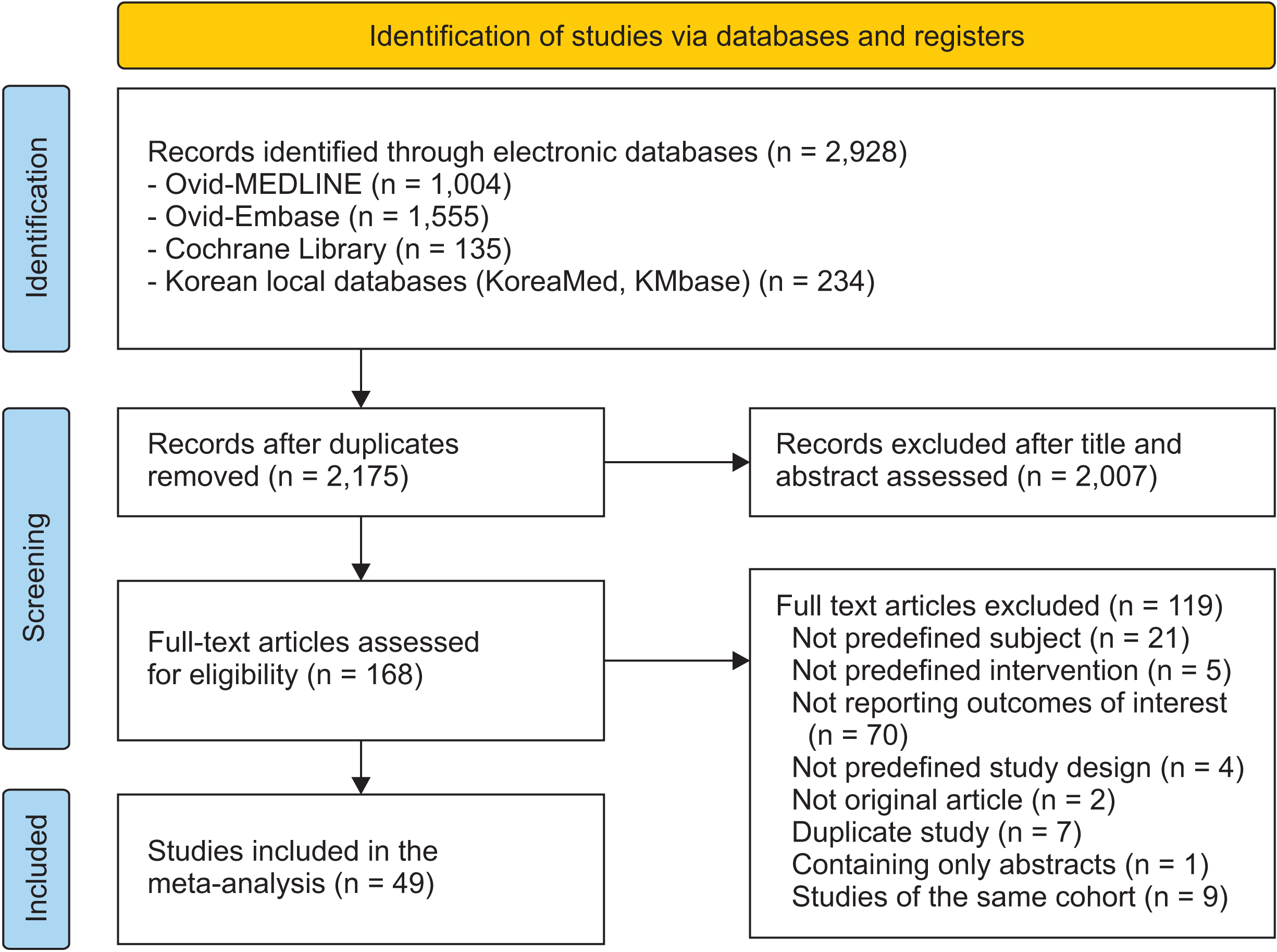
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: MJK, SHJ. Data curation: YJK, MYK, NJ, HGS. Formal analysis: MJK. Funding acquisition: HGS, MJK, SHJ. Investigation: YJK, MYK, HGS. Methodology: YDK, MHJ. Project administration: HGS, MJK. Resources: HGS, MJK. Software: MJK. Supervision: YDK, SHJ. Validation: MHJ, MJK. Visualization: YJK, NJ, MJK. Writing–original draft: YJK, MYK, MHJ. Writing–review & editing: YJK, NJ, SHJ.
REFERENCES
Figure 2
Figure 3
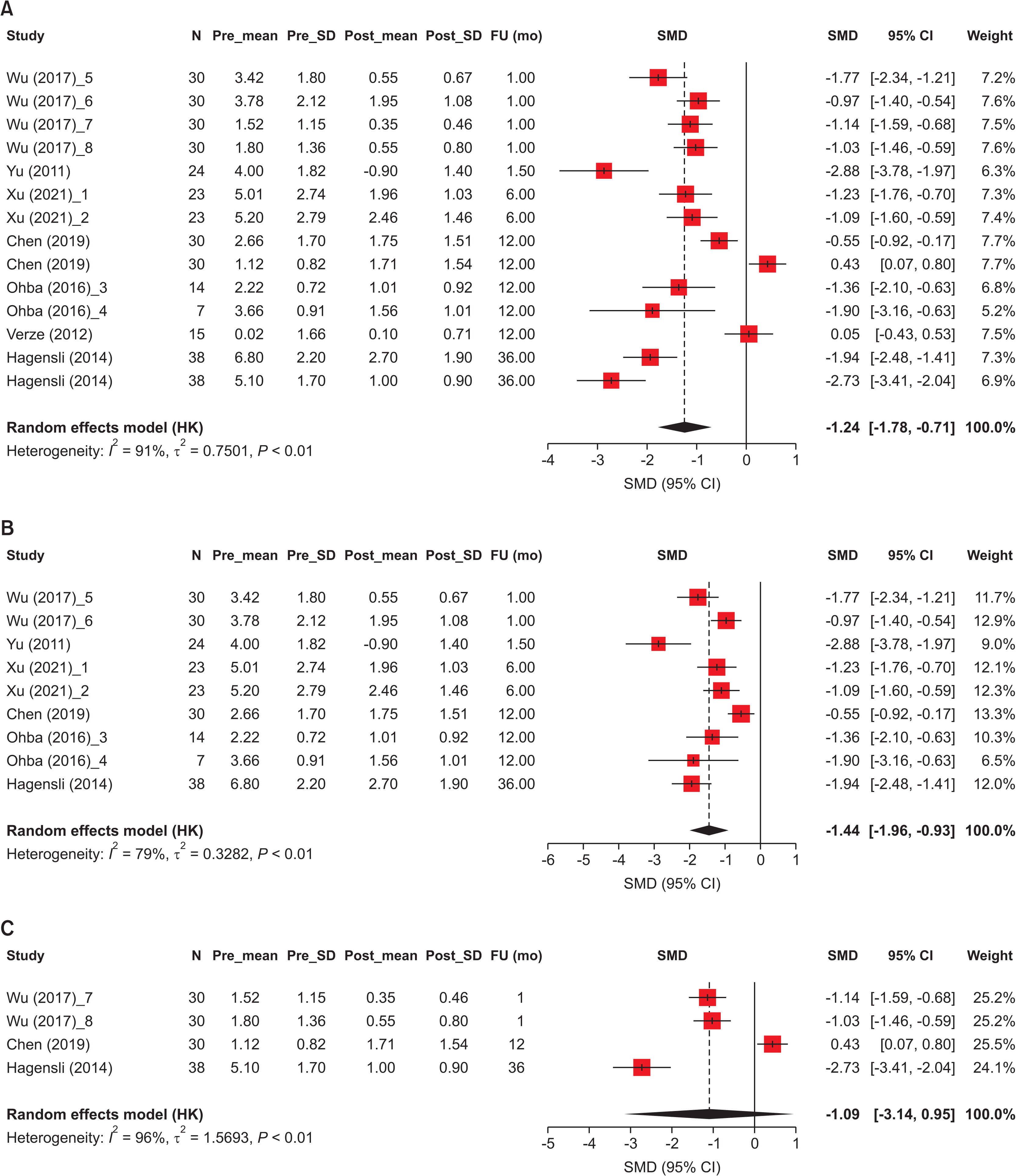
Figure 4
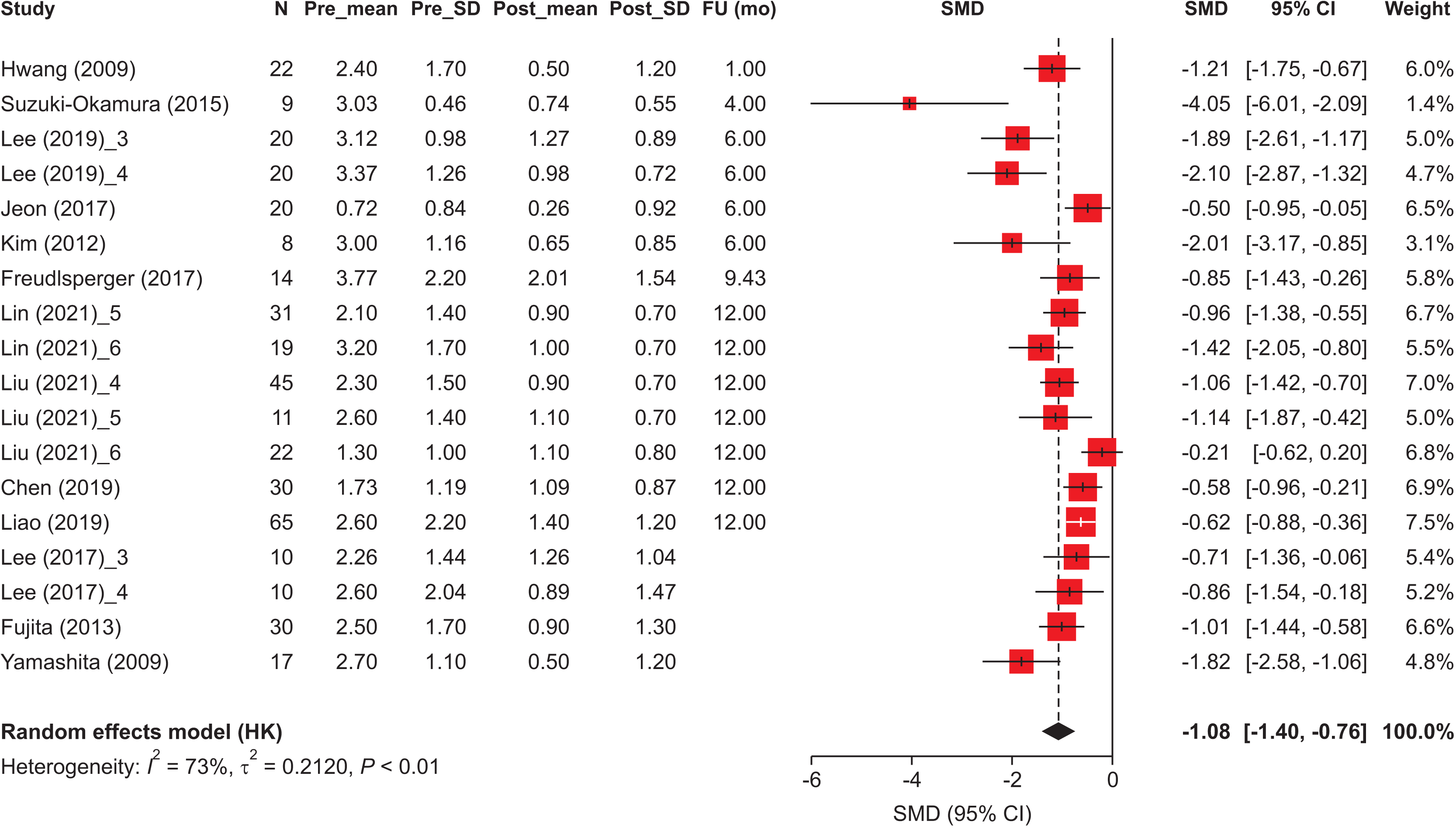
Figure 5
Table 1
Table 2
| Outcome variables | Definition |
|---|---|
| Skeletal symmetry | Linear and angular measurements of the anatomic landmarks of the facial skeleton using radiographs for assessment of facial asymmetry |
| Menton deviation | Distance from the menton of the mandible to the midsagittal reference plane |
| Maxillary canting | Angle between the maxillary plane and the horizontal reference plane |
| Frontal ramal inclination* | Angle between the midsagittal reference line and the line connecting the most lateral point of the condylar head and gonion in the frontal plane |
| Ramus height* | Distance from the condylion to gonion |
| Body length* | Distance from the gonion to menton |
| Midline discrepancies | Deviation of upper and lower dental midline from the midsagittal reference line; midline discrepancy between the upper and the lower dentition |
| Lip canting | The angle between the line where the upper and lower lips meet and the horizontal reference line |
| TMD | Signs and symptoms related to TMD |
| Quality of life | Quality of life related to surgical treatment of facial asymmetry |
| Relapse | Change of more than 1 mm in the menton deviation after surgery |
Table 3
| Study (year) | Outcome | Surgical technique (mandible) | Computer simulation | 1-jaw vs. 2-jaw | SFA | Imaging | Subgroup for meta-analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aoyama et al.42 (2018) | Me, MC | SSRO | No | 2-jaw + genioplasty | No | 2D | 1: Me, 2: MC |
| Chen et al.51 (2016) | Me | SSRO | No | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | No | 3D | 1: Group I*, 2: Group II†, 3: Group III‡ |
| Chen et al.36 (2019) | U1, L1, LC, Me | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | Yes | 3D | |
| Choi et al.28 (2021) | Me | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | Yes | 2D | 1: SFA, 2: Conventional approach |
| Eo et al.52 (2022) | Me | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Freudlsperger et al.25 (2017) | LC | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Fujita et al.40 (2013) | LC, Me | SSRO, IVRO | No | 1-jaw | No | 2D | |
| Guo et al.22 (2018) | FRI, RH, BL | SSRO | No | 2-jaw + genioplasty | Yes | 3D | 1: FRI, 2: RH, 3: BL |
| Ha et al.18 (2023) | FRI | SSRO | Yes | 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Hågensli et al.39 (2014) | U1, L1, Me | SSRO | No | 1-jaw | No | 2D | |
| Hu et al.31 (2019) | Me | SSRO | Yes | 2-jaw + genioplasty | Yes | 3D | 1: Group A§, 2: Group B∥ |
| Huang et al.19 (2021) | Me | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Hwang et al.13 (2009) | LC, MC | NR | No | 1-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Jeon et al.23 (2017) | Me, LC | SSRO | No | 1-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Jeon et al.30 (2020) | Me | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Ji et al.38 (2019) | BL, MC, RH | SSRO | Yes | 2-jaw + genioplasty | No | 3D | 1: BL, 2: MC, 3: RH |
| Kim et al.24 (2012) | LC, MC | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | No | ||
| Ko et al.26 (2009) | Me | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | No | 2D | |
| Kwon et al.32 (2019) | Me, FRI, RH, BL | IVRO | No | 2-jaw + genioplasty | No | 3D | 1: Me, contralateral type, 2: Me, ipsilateral type, 3: FRI, contralateral type, 4: FRI, ipsilateral type, 5: RH, contralateral type, 6: RH, ipsilateral type, 7: BL, contralateral type, 8: BL, ipsilateral type |
| Kwon et al.33 (2019) | BL, RH | IVRO | Yes | 2-jaw + genioplasty | No | 3D | 1: RH, 2: BL |
| Lee et al.60 (2017) | Me, LC | SSRO | Yes | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | Yes | 3D | 1: Me, 1-jaw, 2: Me, 2-jaw, 3: LC, 1-jaw, 4: LC, 2-jaw |
| Lee et al.50 (2019) | MC, LC | SSRO | Yes | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | Yes | 3D | 1: MC, 1-jaw, 2: MC, 2-jaw, 3: LC, 1-jaw, 4: LC, 2-jaw |
| Lee et al.27 (2022) | Me | SSRO | No | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Liao et al.54 (2020) | Me | SSRO | Yes | 2-jaw | Yes | 3D | 1: Conventional, 2: Computer simulation |
| Lin et al.37 (2018) | Me | SSRO | Yes | 2-jaw + genioplasty | No | 3D | |
| Lin et al.29 (2021) | Me, MC, LC | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | Yes | 3D | 1: Me, API¶, 2: Me, PIE**, 3: MC, API, 4: MC, PIE, 5: LC, API, 6: LC, PIE |
| Liu et al.53 (2022) | Me, LC | SSRO | Yes | 2-jaw | Yes | 3D | 1: Me, Roll-type, 2: Me, Translation-type, 3: Me, Yaw-type, 4: LC, Roll-type, 5: LC, Translation-type, 6: LC, Yaw-type |
| Liu and Li49 (2022) | BL, RH | SSRO | 1-jaw + genioplasty | No | 3D | ||
| Ming et al.21 (2020) | Me, MC | SSRO | No | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | No | 3D | 1: Me, 1-jaw, 2: Me, 2-jaw, 3: MC, 1-jaw, 4: MC, 2-jaw |
| Ohba et al.57 (2016) | Me, L1 | SSRO | No | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | No | 2D | 1: Me, Minor asymmetry, 2: Me, Severe asymmetry, 3: L1, Minor asymmetry, 4: L1, Severe asymmetry |
| Park et al.46 (2021) | FRI | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | Yes | 3D | |
| Sun and Lee56 (2019) | MC | SSRO | No | 1-jaw | Yes | 3D | |
| Suzuki-Okamura et al.17 (2015) | LC, Me | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Udomlarptham et al.12 (2018) | Me, MC | SSRO | Yes | 2-jaw | No | 3D | 1: Me (3D), 2: Me (2D), 3: MC (3D), 4: MC (2D) |
| Verzé et al.44 (2012) | U1-L1 discrepancy | Mixed | No | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Wong et al.16 (2014) | Me | SSRO | Yes | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | No | 3D | 1: Conventional, 2: Computer simulation |
| Wu et al.14(2017) | Me, RH, U1, L1 | SSRO | Yes | 2-jaw | No | 1: Me (3D), 2: Me (2D), 3: RH (3D), 4: RH (2D), 5: L1 (3D), 6: L1 (2D), 7: U1 (3D), 8: U1 (2D) | |
| Xu et al.43 (2021) | L1 | SSRO | No | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | No | 3D | 1: 1-jaw, 2: 2-jaw |
| Yamashita et al.41 (2009) | LC, MC | SSRO | No | 1-jaw | No | 2D | |
| Ying et al.34 (2015) | MC | SSRO, IVRO | Yes | 2-jaw | No | 3D | |
| Yoon et al.35 (2003) | Me | SSRO | No | 1-jaw, 2-jaw | No | 2D | |
| Yu15 (2011) | FRI, L1 | SSRO | No | 2-jaw | No | 2D |
SFA, surgery-first approach; Me, menton deviation; MC, maxillary canting; SSRO, sagittal split ramus osteotomy; 2D, two-dimensional; 3D, three-dimensional; U1, upper dental midline deviation; L1, lower dental midline deviation; LC, lip canting; IVRO, intraoral vertical ramus osteotomy; FRI, frontal ramal inclination; RH, ramus height; BL, body length; NR, not reported.
Table 4
| Outcome indicator | Studies | Surgical technique | Number of patients (n) | Pre-surgery (%) | Post-surgery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sound | Fujimura et al.61 (2005) | IVSRO | 15 | 86.7 | 6.7 |
| IVRO | 15 | 80.0 | 13.3 | ||
| Park et al.46 (2021) | SSRO + IVRO | 8 | 62.5 | 37.5 | |
| SSRO | 10 | 60.0 | 50.0 | ||
| Kim and Ryu45 (2007) | Not reported | 30 | 66.7 | 23.3 | |
| Toh and Leung62 (2022) | Mixed | 64 | 37.8 | 17.8 | |
| Pain | Park et al.46 (2021) | SSRO + IVRO | 8 | 12.5 | 0 |
| SSRO | 10 | 10.0 | 0 | ||
| Kim and Ryu45 (2007) | Not reported | 30 | 53.5 | 20.0 | |
| Toh and Leung62 (2022) | Mixed | 64 | 13.3 | 6.7 | |
| Sound and pain | Park et al.46 (2021) | SSRO + IVRO | 8 | 37.5 | 0 |
| SSRO | 10 | 20.0 | 0 | ||
| Toh and Leung62 (2022) | Mixed | 64 | 15.6 | 13.3 | |
| Sound, pain, and limitation of condylar movement | Ohba et al.47 (2022) | IVRO | 14 | 17.9 | 10.7 |
| SSRO with fixation | 11 | 18.2 | 40.9 | ||
| SSRO with no fixation | 37 | 24.3 | 5.4 |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download