INTRODUCTION
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease primarily affecting the joints. The disease hinders a patient’s ability to perform daily activities, negatively affects patient quality-of-life (QoL), and exacerbates morbidity and mortality [
1]. In South Korea, the prevalence of RA is increasing, with a reported yearly increase in prevalence from 0.28% in 2009 to 0.32% in 2012 [
2].
The goal of RA treatment should be to reach a target of sustained remission or low disease activity [
3,
4].
Methotrexate is generally recommended as first-line conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (cDMARD) monotherapy in patients with early RA, with other cDMARDs (e.g., leflunomide or sulfasalazine) being appropriate in some patients [
3,
4]. However, many patients require the addition of other DMARDs to achieve low disease activity. In patients who have not achieved target disease activity despite taking maximally tolerated doses of methotrexate, the 2021 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) guidelines [
3] conditionally recommend adding a biological DMARD (bDMARD) or targeted synthetic DMARD (tsDMARD) instead of initiating triple therapy (i.e., adding sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine), with this recommendation being highly sensitive to the physician’s judgment and patient preference. For example, triple therapy may be preferred in lower resource settings, and in patients with specific comorbidities in whom the risk of adverse events may be significantly higher with bDMARD or tsDMARD therapy [
3]. According to the 2022 updated European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) recommendations, the choice of subsequent treatment in patients who have not achieved target disease activity with their first cDMARD strategy depends on the absence or presence of poor prognostic factors (e.g., persistent moderate or high disease activity despite cDMARD therapy; high acute phase reactant levels; high swollen-joint count; presence of rheumatoid factor and/or anticitrullinated protein antibody, especially at high levels; presence of early erosions; failure of two or more cDMARDs). If the treatment is not achieved with the first DMARD strategy, changing to or adding a second cDMARD should be considered in the absence of poor prognostic factors. When poor prognostic factors are present, a bDMARD should be added to cDMARD therapy (treatment with JAK-inhibitors may also be considered after assessing pertinent risk factors for cardiovascular events and malignancies [
5]) [
4].
Based on the current clinical evidence, it is not possible to definitively conclude that treatment with a cDMARD plus an anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agent is superior to treatment with multiple cDMARDs in RA patients. Meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) have shown that combination treatment with either a cDMARD plus an anti-TNF agent or multiple cDMARDs is more effective than cDMARD monotherapy, with the two combination regimens generally displaying comparable efficacy regardless of the outcome assessed, including the prevention of radiographic progression [
6-
8]. Conversely, in large real-world studies in RA patients in whom initial methotrexate therapy had failed, switching to cDMARD plus anti-TNF therapy was associated with several better outcomes than multiple cDMARD therapy [
9,
10], and supports the ACR’s conditional recommendation of switching to cDMARD plus bDMARD or tsDMARD [
3].
Since further evidence is still needed to establish which treatment regimen is superior in patients in whom previous cDMARD treatment has failed, this real-world study was conducted in South Korea. RA patients with moderate or high disease activity (i.e., disease activity score 28-joint count with erythrocyte sedimentation rate [DAS28-ESR] score ≥3.2 points) despite treatment with two or more cDMARDs for >3 months, could be switched to treatment with multiple cDMARDs or to a cDMARD plus an anti-TNF agent, depending on the physician's judgment and patient preference. The clinical effectiveness of the treatments over the 12-month study was assessed, with a focus on changes from baseline in disease activity (DAS28-ESR) at 6 months. This endpoint is considered clinically appropriate, as the EULAR guidelines recommend that patients be assessed for achievement of target disease activity 6 months after changes in treatment using a validated composite disease activity measure that includes joint count [
4]. The DAS28-ESR is a validated method of evaluating RA treatment efficacy [
11], with validity comparable to that of other methods, including the clinical disease activity index (CDAI), simplified disease activity index (SDAI), and the ACR core set criteria [
12].
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design and patients
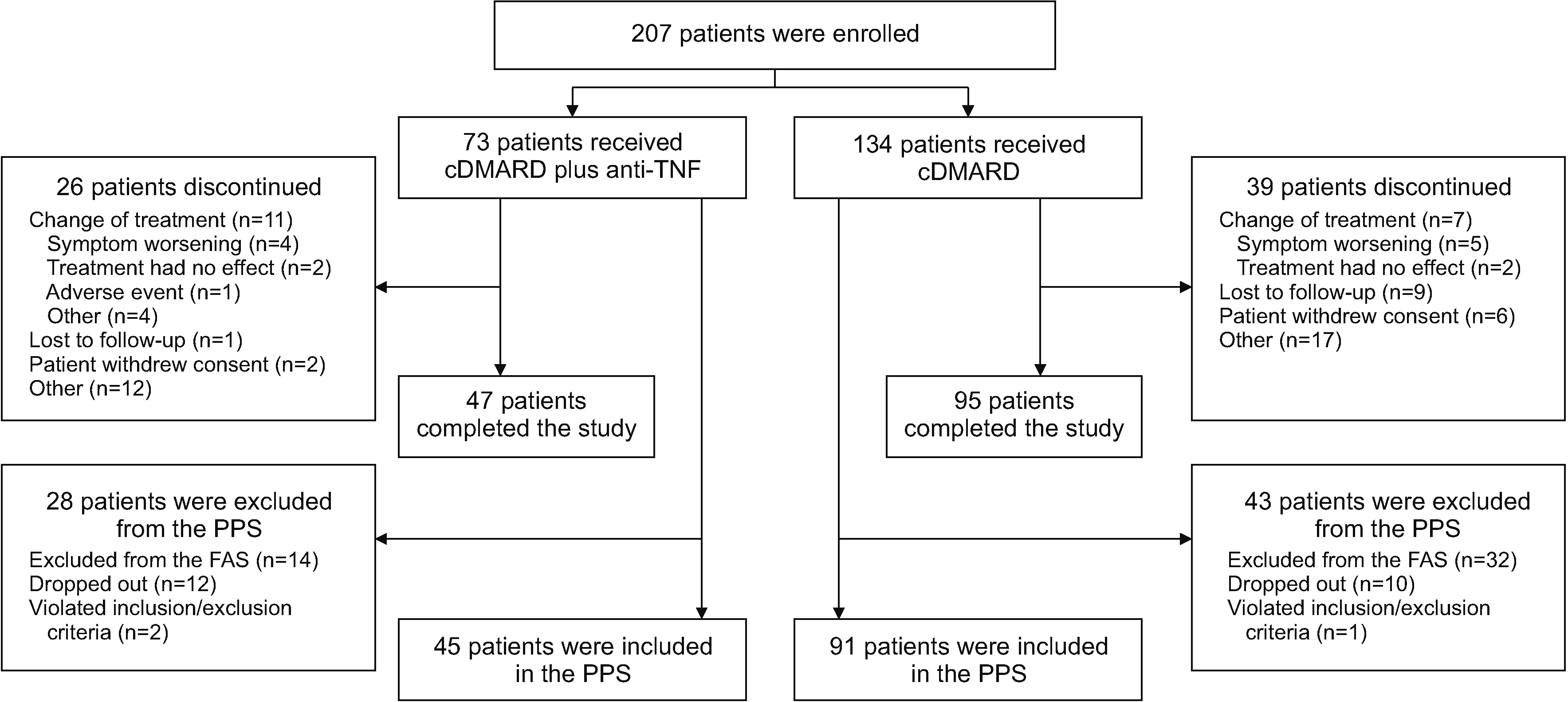
This prospective, observational study was conducted at multiple centers in South Korea. For inclusion in the study, patients were required to have received previous multiple cDMARD treatment (i.e., stable doses of two or more cDMARDs for at least 3 months prior to consent) that had failed, moderate to severe disease activity as shown by a DAS28-ESR score of ≥3.2 points at the time of consent, and to have agreed to have their current treatment regimen changed to either a single cDMARD plus an anti-TNF agent or multiple (two or more) cDMARDs based on the discernment of their treating physician. Eligible patients were also required to be aged ≥19 years with a diagnosis of RA according to the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria within the past 3 years. Exclusion criteria included the previous use of a bDMARD for the treatment of RA, being pregnant or breastfeeding, participating in or planning to participate in other interventional studies, and having contraindications to study therapy. The study was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, with the identifier NCT03264703.
As this was an observational study, study participants did not undergo treatment randomization, and there were no mandated therapeutic interventions or rescue treatment options. Instead, patients were included in one of the two treatment groups based on whether their failed treatment with multiple cDMARDs was changed to either a single cDMARD plus an anti-TNF agent or multiple (two or more) cDMARDs. Treatment changes were made at the discretion of the treating physician.
To collect clinical data, patients were followed for 12 months. Clinical study visits were conducted at baseline, 3 months (±3 weeks), 6 months (±1 month), and 12 months (±1 month); evaluations included measurement of vital signs and weight, laboratory tests, 28-tender joint count, 28-swollen joint count, patient global assessment, Korean Health Assessment Questionnaire (KHAQ-20) scores, and corticosteroid dosage and discontinuation. Demographic information, medical history, and previous medications for the treatment of RA were collected at the baseline visit. The DAS28-ESR was calculated on a visual analog scale of swollen joint count, tender joint count, ESR, and patient global assessment of 28 joints. No testing or confirmation of drug-related safety was planned. Adverse reactions during the clinical study period were treated according to routine practice.
To avoid the confounding effects of changes in treatment on the study results, patients who changed treatments during the study period were dropped from the per-protocol set (PPS).
Efficacy endpoints
The primary efficacy endpoint was the least square mean (LSM) change from baseline in disease activity as measured by the DAS28-ESR at 6 months; changes from baseline in this endpoint at 3 and 12 months were secondary endpoints. Other secondary efficacy endpoints (all assessed at 3, 6, and 12 months) were the rate of clinical remission (defined as the proportion of patients with a DAS28-ESR score of ≤2.6), changes from baseline in disease activity and disease improvement criteria (both classified using the EULAR definitions [
11,
13]), the rate of corticosteroid reduction/discontinuation (defined as the proportion of patients achieving a >50% reduction from baseline in total daily corticosteroid dose), and LSM changes from baseline in QoL as measured by the KHAQ-20 (decrease in score indicates improved QoL). Efficacy analyses were performed in the PPS.
Statistical methods
Based on the calculated sample size, 138 patients were required in the PPS of each treatment group to achieve an effect size of 0.5 with a 0.05 significance level and 80% power. Given the inherent nature of observational studies, ≈40% of patients may potentially be lost from the PPS during the 12-month study period due to a variety of reasons (e.g., discontinuation of study treatment, loss to follow-up, withdrawal of consent, violation of inclusion criteria, etc.). To account for this potential 40% loss, it was calculated that 230 patients per group were initially needed to provide a PPS sample of 138 patients. The PPS of each treatment group were used for all reported analyses.
Continuous endpoints were summarized using descriptive statistics (e.g., means±standard deviation), and categorical endpoints were summarized as frequency and percentage. Continuous endpoints were analyzed using the two-sample t-test or Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test, and categorical endpoints were analyzed using Pearson’s chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. To account for between-group differences (BGDs) in baseline scores, the BGDs in LSM changes from baseline in DAS28-ESR and KHAQ-20 scores were calculated by performing analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), with patient age, duration of RA, and the relevant baseline scores as covariates. A p-value of <0.05 was considered significant. Missing values were not imputed for endpoint analyses and no adjustments were made for multiplicity. Statistical analyses were conducted using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
Ethics
Ethical approval was obtained from the institutional review boards of each participating institution (
Supplementary Table 1). The study was conducted in accordance with the International Council for Harmonization-Good Clinical Practice guidelines, the Declaration of Helsinki, and all applicable national regulations. All patients provided written informed consent prior to study participation.
DISCUSSION
This prospective, observational real-world study found that switching to single cDMARD plus anti-TNF therapy may have some benefits in patients with moderate-to-severe RA in whom previous cDMARDs had failed. Treatment with a cDMARD plus anti-TNF therapy significantly improved QoL scores and reduced corticosteroid use, but did not significantly reduce disease activity, relative to treatment with multiple cDMARDs.
Combination treatment with a cDMARD plus an anti-TNF agent is significantly more effective than cDMARD monotherapy in treating RA [
14,
15]. In RCTs, adalimumab plus methotrexate significantly improved mean DAS28-CRP scores at week 26 [
14], and golimumab plus methotrexate significantly improved DAS28-ESR scores at 16 weeks [
16], relative to methotrexate monotherapy. Furthermore, according to a meta-analysis of 15 RCTs in patients with active early RA, treatment with either a cDMARD plus an anti-TNF agent or multiple cDMARDs increased ACR response rates, and delayed disability and erosive radiographic progression to a significantly greater extent than methotrexate monotherapy [
6]. However, it was not clear which combination regimen was more effective, as both displayed comparable efficacy [
6]. Likewise, a meta-analysis of 8 RCTs in patients with RA found that treatment with methotrexate plus an anti-TNF agent was not superior to treatment with two to three cDMARDs in preventing radiographic progression at 12 and 24 months, despite a greater improvement in DAS28 scores with cDMARD plus anti-TNF therapy at 6 months [
7]. Similarly, a network meta-analysis of 39 RCTs concluded that bDMARDs plus methotrexate may not be superior to treatment with multiple cDMARDs or one or two cDMARDs plus low-dose corticosteroids in preventing radiographic progression [
8].
In contrast, large real-world studies [
10,
11] support the ACR’s conditional recommendation to switch to cDMARD plus bDMARD or tsDMARD therapy when initial methotrexate therapy had failed [
3]. As shown in our study, bDMARD-containing regimens were associated with several better outcomes than multiple cDMARD therapy in these studies [
9,
10]. In one study, treatment with anti-TNF agent plus methotrexate was associated with significantly higher rates of attaining low disease activity, greater improvements in CDAI scores, and lower rates of mediation discontinuation at 6 months than triple cDMARD therapy in patients who had not previously been exposed to a bDMARD [
9]. In the other study, DAS responses at 6 and 12 months were significantly better when patients were switched to a regimen containing a bDMARD than when they were switched to a regimen containing cDMARD(s) with or without corticosteroids [
10].
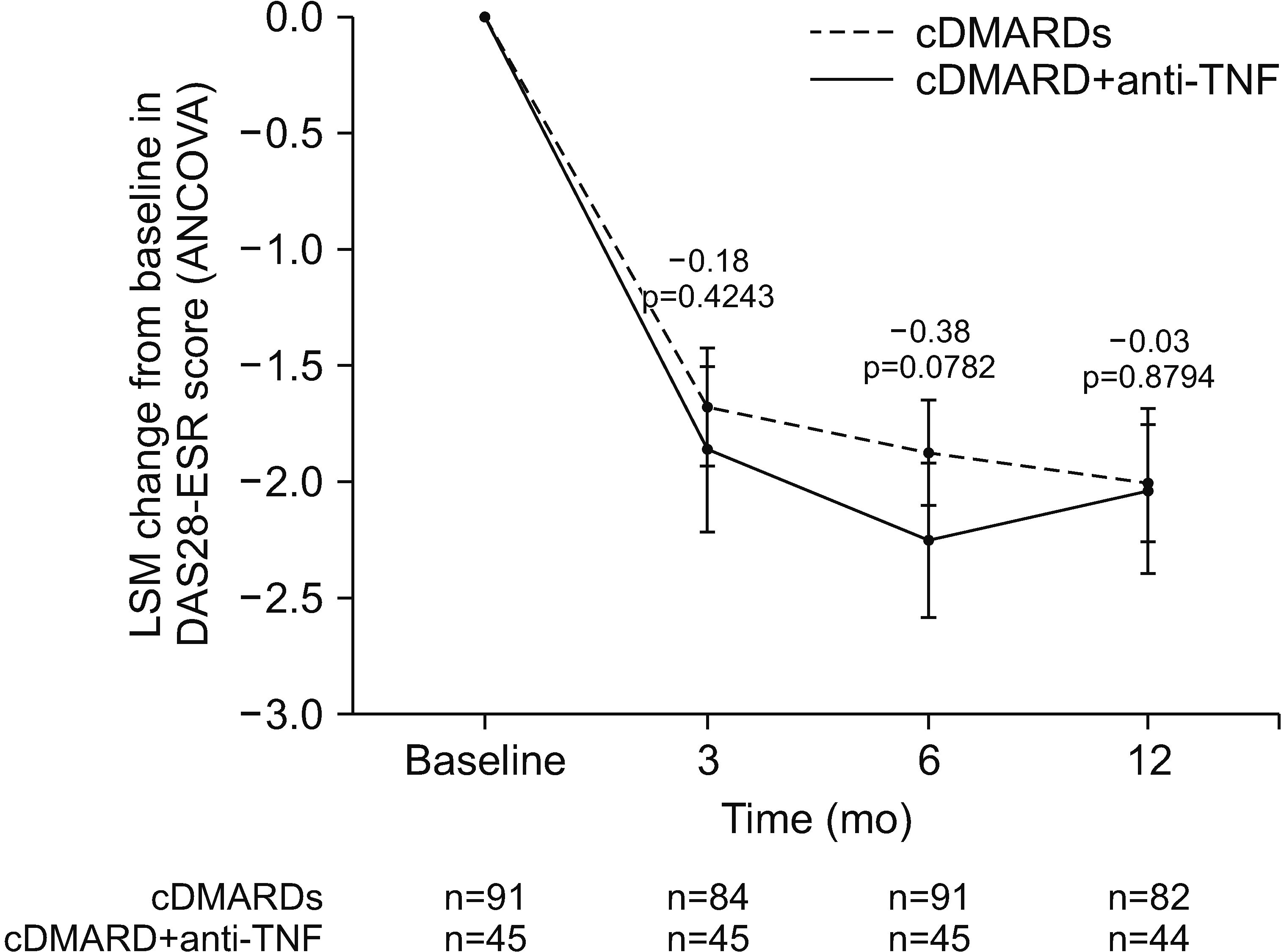
The present study directly compared the effectiveness of cDMARD plus anti-TNF therapy with that of multiple cDMARDs treatment in the real-world setting. DAS28-ESR scores improved from baseline in both treatment groups, with no statistically significant BGDs at 3, 6, or 12 months. Nevertheless, there was a tendency for cDMARD plus anti-TNF therapy to reduce disease activity at a faster rate than multiple-cDMARD treatment. Several studies have reported that anti-TNF treatment responses may vary according to the reaction of individual patients to these drugs as a result of genetic pleomorphism, bioavailability, anti-TNF product stability, and anti-TNF antibody formation [
16-
18]. The positive effect of an anti-TNF agent on disease activity slightly decreased between months 6 and 12 in our study, which may reflect the development of anti-TNF neutralizing antibodies to monoclonal anti-TNF agents. Due to the small number of patients, it is not possible to observe any differences in effectiveness between individual anti-TNF therapies or between various combinations of cDMARDs. Because of this, the DAS28-ESR results should be interpreted with caution.
A rapid improvement in disease activity was also shown by the changes from baseline in EULAR disease activity status at 3 months. Most patients in the cDMARD plus anti-TNF group who were classified as having moderate disease activity at baseline were reclassified as low, and most of those classified as having high disease activity at baseline were reclassified as moderate or ‘low’ at 3 months, with improvements generally being maintained throughout the 12-month study. Overall, outcomes were comparable in the multiple cDMARD group, with no statistically significant BGDs. Similar results were shown in the open-label, non-inferiority TACIT RCT in RA patients with high baseline disease activity: improvements in disease activity were initially greater in patients treated with an anti-TNF agent than in those treated with multiple cDMARDs, but these differences did not persist beyond 6 months [
19].
Significantly more patients in the cDMARD plus anti-TNF group than in the multiple cDMARD group experienced a >50% reduction in corticosteroid dose. Corticosteroids are often used as short-term adjunct treatment with cDMARDs, as they rapidly and effectively suppress inflammation, and slow radiographic progression in patients with RA [
3,
4,
20,
21]. However, they have well-known toxicities and adverse effects (infections, osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, etc.), which detrimentally affect patient QoL and increase overall healthcare costs. It is, therefore, important that treatment with corticosteroids is limited to the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. In South Korea, it is generally recommended to slowly reduce and discontinue even very small amounts of corticosteroids. Likewise, the EULAR guidelines recommend that corticosteroids are tapered and discontinued as rapidly as clinically feasible [
4], and the ACR guidelines strongly recommend against the long-term (≥3 month) use of corticosteroids [
3].
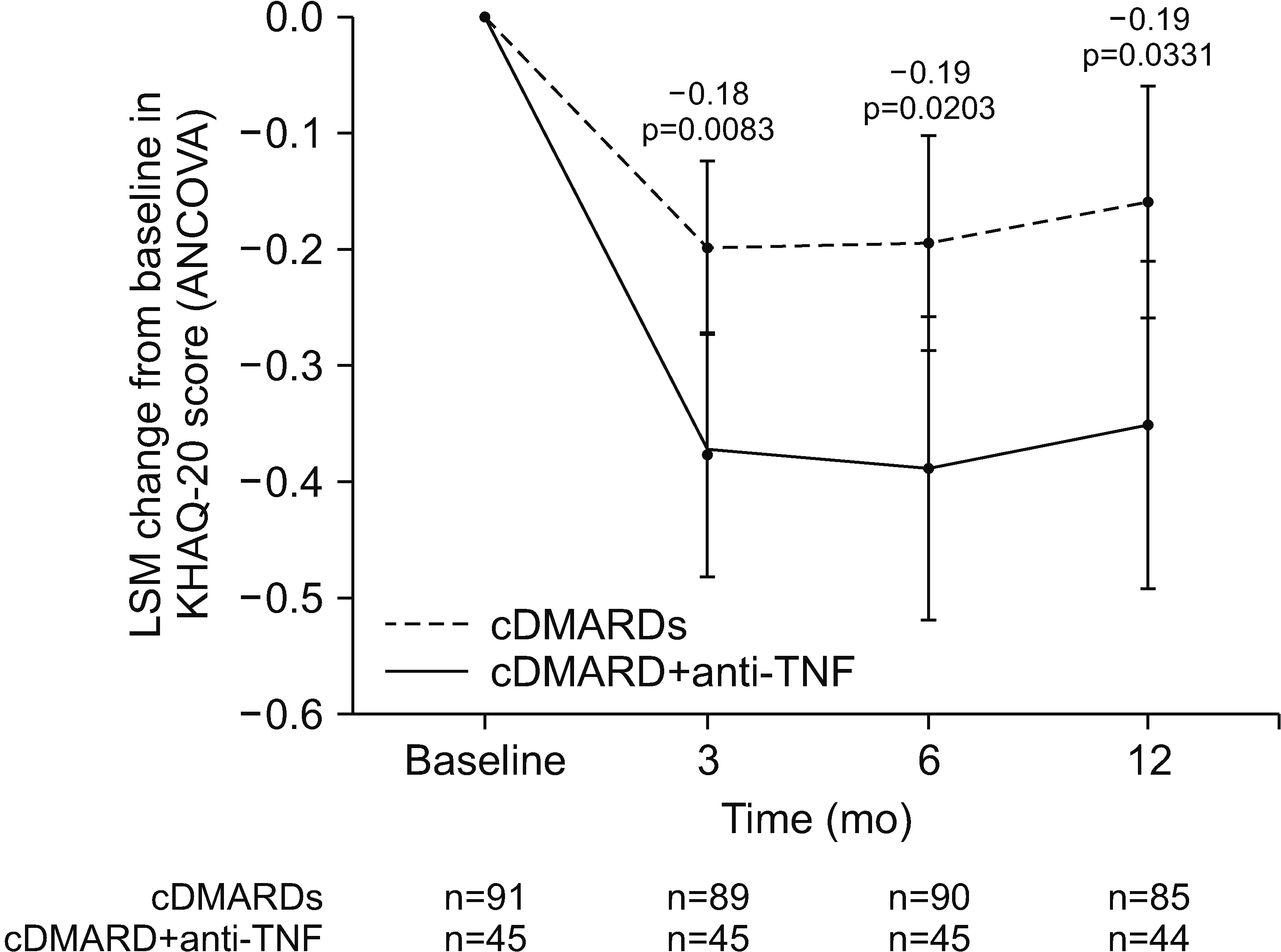
Improvements in QoL were also significantly greater in the cDMARD plus anti-TNF group than in the multiple cDMARD group. Moreover, the ANCOVA-adjusted changes from baseline in the KHAQ-20 score in the cDMARD plus anti-TNF group can be considered clinically significant at all time points (3, 6, and 12 months), as they were all greater than or equal to the minimally important differences (−0.09 for somewhat improved, −0.20 for somewhat/much better) that were previously reported for a Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) used in clinical practice to assess patients with RA [
22]. The goal of RA treatment is to reduce pain and control the disease, thereby reducing joint damage and improving QoL [
23]. The significantly greater improvement in QoL reported in the cDMARD plus anti-TNF group suggests that cDMARD plus anti-TNF treatment is a more effective treatment option for RA than multiple cDMARDs. This differs from the finding in the TACIT RCT, in which HAQ scores improved from baseline in both groups, but with multiple cDMARD treatment being favored over anti-TNF treatment (mean BGD −0.14; 95% CI −0.29 to 0.01, which was below the prespecified non-inferiority boundary of 0.22) [
19].
This study had several limitations. The target number of patients to be enrolled was not reached; this affected the statistical power of the results. Based on post-study sample size analysis, we believe that the data are sufficiently robust to allow us to draw meaningful and clinically relevant conclusions; however, such post-hoc analysis is controversial [
24,
25]. Due to the limitations of the observational study design, an equal number of patients were not enrolled in each treatment group. High acquisition costs may have contributed to the low recruitment of patients in the cDMARD plus anti-TNF group, as physicians may have hesitated to choose the more costly therapy [
19]. However, the impact of the cost of anti-TNF treatment was not addressed in our study, and well-designed pharmacoeconomic studies are required to evaluate the relative costs and benefits of various treatment options. Since the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service guideline for biological use is based on DAS28-ESR, we were only able to collect DAS28-ESR (not including DAS28-CRP or SDAI etc.), representing a limitation of this retrospective analysis. Also due to the study’s observational design, baseline disease activity and disability were not matched in the PPS of the cDMARD plus anti-TNF and multiple cDMARD groups, resulting in significant BGDs in baseline disease activity (i.e., DAS28-ESR scores) and QoL (i.e., KHAQ-20 scores). To correct for this limitation, ANCOVA was performed using baseline DAS28-ESR and KHAQ-20 scores as covariates in the corresponding analyses, along with patient age and RA duration.
The findings of the study may have also been influenced by the number and specific combinations of cDMARDs being received in the multiple cDMARD group, as well as by the specific cDMARD and anti-TNF agent received in the other group (for example, most patients in both treatment groups received methotrexate and, in the multiple cDMARD group, patients mainly also received leflunomide or tacrolimus); however, given the small patient numbers, it would be difficult to assess the role of various drug combinations. Moreover, a high percentage of patients (31.4% overall; 35.6% in the cDMARD plus anti-TNF agent group, and 29.1% in the multiple cDMARD group) did not complete the study, which may have introduced bias to the findings. All endpoints were analyzed without replacing missing values and results were reported only in the PPS, which may profoundly affect the results and interpretation of the study.
As radiographic progression, disability endpoints, and safety outcomes were not monitored, it is difficult to conclude whether a single cDMARD plus anti-TNF agent provided greater overall benefits than multiple-cDMARD therapies. Safety-related data will be assessed in future investigations.
Moreover, this study included only treatment with cDMARDs and anti-TNF agents, while in the real-world setting there are various other treatment options including non-TNF bDMARDs and tsDMARDs. In addition, precision medicine, which takes into account individual variability in genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors [
26], has a growing role in the treatment of RA. The exclusion of these other treatment options leaves a gap between the present study and the current real-world situation. Finally, this study only included South Korean patients, limiting the generalizability of the results; however, our results are consistent with those of studies in non-South Korean patients [
14,
15].




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download