Abstract
Clinical case reports and research regarding the mental spines and their associated structures create a detailed picture of the floor of the mouth for assessment during clinical treatment. This compilation of information covers the mental spines, the attached geniohyoid and genioglossus muscles, the lingual foramina, and the veins and arteries of the jaw and floor of the mouth. It is important to consider the variations in the mental spines for oral and maxillofacial treatment involving the mandible. Differences in anatomy of the mental spine, including their number, location, and size, can impact diagnosis and treatment approaches.
The mental spines (genial tubercles) and the lingual foramina are part of the mandibular symphysis, located along the anterior mandible’s midline and lower lingual position [1, 2]. Generally, the human mandible consists of four mental spines split into pairs, which serve as muscle attachment sites. The superior pair attaches to the genioglossus muscle, while the inferior pair attaches to the geniohyoid muscle [1].
While it has been widely accepted that the standard mandible features four mental spines, recent research has revealed that one or two distinct mental spines are possible but may also be more common than the presence of four (Fig. 1) [3]. Variations in the anatomy of the mental spines contribute to changes in the lingual foramina and the attachment of muscles to the anterior mandible [1, 3-6]. These changes help determine how the arteries that supply blood to the submandibular region enter the mandible through the lingual foramina [7-19].
The mental spines are generally of small size but can develop into larger prominences due to calcification of the geniohyoid and genioglossus muscle tendons and severe atrophy of the mandible. This condition is referred to as the “elongated mental spine” (Fig. 2) [2, 20]. The more eminent tubercles become prone to fracturing spontaneously or due to ill-fitting dentures [9, 21-23]. To begin treatment, several radiographic techniques in differing combinations are used in oral and maxillofacial diagnoses to acquire clear images of affected regions [21, 24-31]. Next, clinical treatment of fractured mental spines is accomplished through conservative or surgical means, typically leading to successful recovery of the damaged mandible and attached muscles [31].
The mental spines of the mandible are also known as genial spines, genial tubercles, genial apophysis, and spinae mentalis [32]. The terms tubercle, spine, and apophysis describe bone projections that remain attached to the larger bone structure they originate from. In this case, the larger bone is the anterior mandible [33]. These terms are typically used interchangeably, but their situational use varies depending on the size of the protuberance [2]. “Mental” originates from the Latin word mentum, and “genial” derives from the Greek word genion, both referring to the chin [33].
The superior and inferior pairs of mental spines are typically accompanied by lingual foramina in varying numbers, forms, and positions [1]. The lingual foramina are entrances to canals that run from the cortical bone surface to the intraosseous region on the lingual surface of the mandible [4, 6]. These foramina can be categorized by their location in relation to the mental spines [1, 3]. Supra-spinosum describes when the foramen is above the mental spines, inter-spinosum refers to when the foramen is between or at the same level as the superior and inferior mental spines, and infra-spinosum pertains to when the foramen is below the inferior mental spines [1, 3, 5, 6].
The sublingual artery branches into several vessels to reach different parts of the floor of the mouth. Its branches enter the lingual foramina near the mental spines as an anastomosis of vessels from the left and right lingual arteries [15].
The submental artery, the largest cervical branch of the facial artery, follows various paths. Its branches often perforate the mylohyoid muscle to enter the median lingual foramina near the mental spine or the lateral lingual foramina into the mandible, where it can anastomose with branches of the sublingual artery and eventually reach the skin of the chin [34].
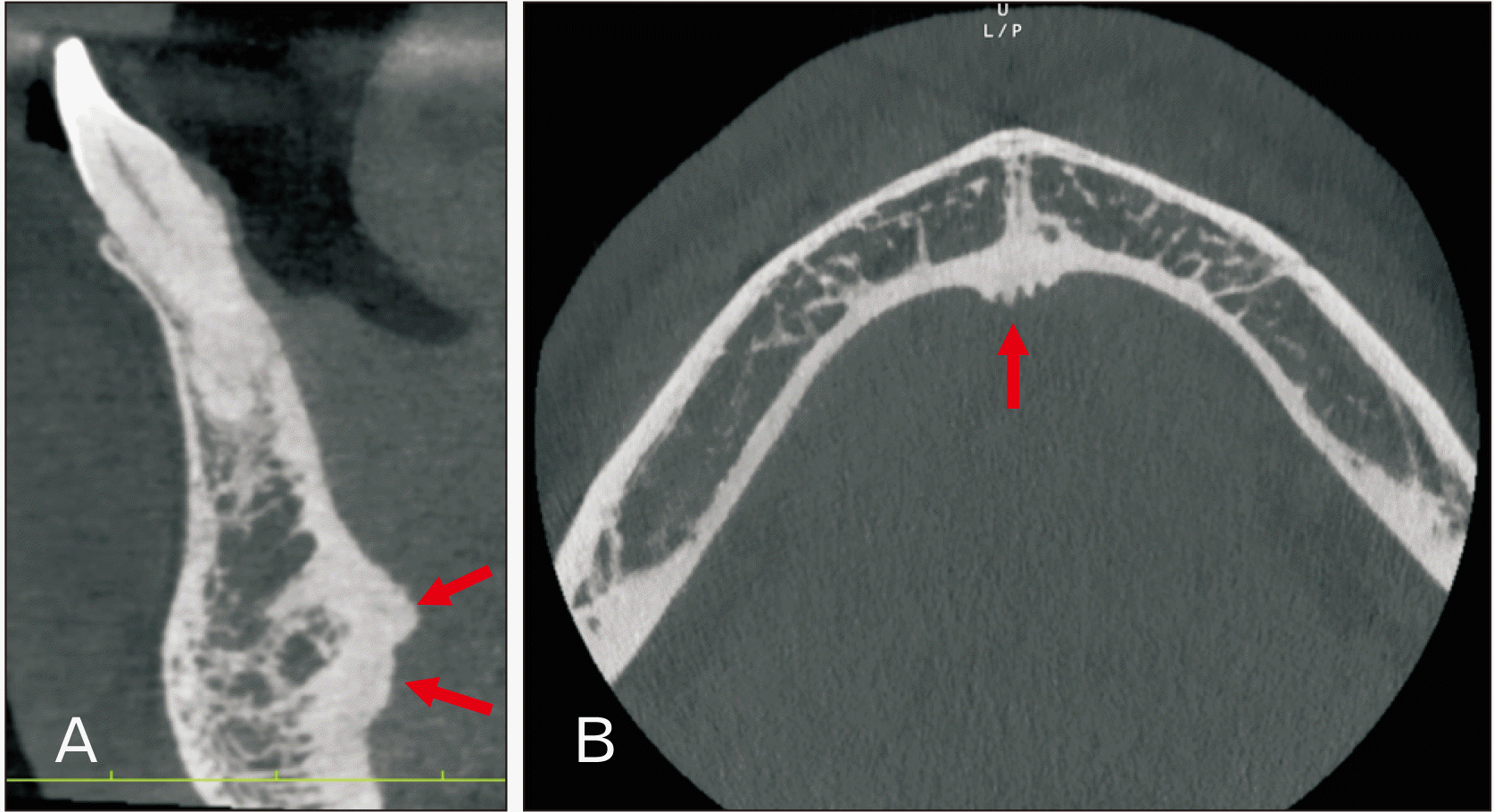
The mental spines are usually shown as a prominence of the lingual cortical plate at the inferior mandible on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) (Fig. 3). Conventional CT and CBCT scans can confirm a diagnosis and determine the extent of the fracture damage [21, 31]. Lateral oblique and posteroanterior X-rays can be used in conjunction with other radiographs for a clinician to investigate the affected area [31].
Most anatomical textbooks describe the mental spines as four protuberances on the internal surface of the mandibular symphysis, arranged in two pairs placed one above the other [3, 35-41]. However, it has been discovered that human mandibles can have between one and four spines with varying positionings [3, 40, 41].
Studies have found that the most common mental spine anatomy consists of two superior spines [3, 40-42]. These spines form due to the consistent use of attached muscles pulling on the bone [3]. The genioglossus muscle attaches to the mandible via the superior pair of mental spines [2, 3]. The genioglossus muscle runs along the entire ventral surface of the tongue, so when the muscle is contracted, the tongue is drawn forward and out of the mouth [3]. The constant protrusion and depression of the tongue during deglutition leads to the greater prominence of the superior mental spines [3]. The geniohyoid muscle, attached to the mandible via the inferior mental spines (Fig. 4), runs along the anterior surface of the hyoid bone to either draw it forward when the mandible is fixed or depress the mandible when the hyoid is fixed [3]. The less prominent inferior mental spines result from this muscle’s weaker contraction and pulling force [3].
When the geniohyoid muscle originates from a linear attachment on the mandibular symphysis, a median vertical spine can replace the two inferior mental spines [43]. However, a rough impression may result when the muscle’s origin is weakly attached [3].
Rarely the genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles originate from the same point of attachment on the mandible, causing the formation of a single large eminence instead of superior and inferior mental spines [39]. This single prominent eminence may sometimes form, and in some cases, no spine, ridge, or notable prominence is possible [3].
These morphological patterns of the mental spine have been investigated in some studies [3, 40, 41]. Singh et al. [3] examined 1,200 dry adult mandibles and classified them into five morphological groups. Araby et al. [40] adopted same classification for CBCT of 155 subjects. However, Hu et al. [41] investigated superior and inferior mental spines of 102 mandibles respectively and made seven groups in total for mental spine classification. The frequency of these different morphologies in the studies are summarized in the Table 1.
The mental spines play an important role in the success or failure of a patient’s ability to support dentures. For patients with resorbed mandibles, the mental spines serve as a solid foundation for withstanding the vertical forces of dentures since the attachment of the genioglossus muscles allows the spines to resist resorption [44]. However, the mucosa covering the protuberances tends to restrict the tubercles’ ability to be primary stress-bearing regions [44]. If the skin has been grafted over the mental spines and the tissue overlying the muscle attachment zones becomes keratinized, this can serve as a primary support area [44].
Severe mandibular atrophy, particularly around the alveolar ridge, can leave the mental spines as hard, prominent projections, leading to fracture of the tubercles, either spontaneously or due to an ill-fitting denture [9, 21-23]. The pressure from lower dentures causes micro-fractures in the tubercles. Following this, the contraction of attached muscles leads to their spontaneous separation from the mandible [31, 45]. Clinicians have two approaches for treating fractured mental spines. The first is a conservative method, which involves pain relief and allowing the body to heal naturally. The second approach involves surgical removal of the fractured tubercle, followed by replacement or repositioning of the associated muscles [31, 46].
The mental spines’ role as attachment sites for the genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles underscores their significant implications for the broader oral and facial structure. Careful attention to these mental spines and associated muscles, arteries, and bone is crucial to delivering effective and efficient care. Ongoing clinical studies enhance the methods, speed, and effectiveness of diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank those who donated their bodies to science so that anatomical research could be performed. Results from such research can potentially increase mankind’s overall knowledge that can then improve patient care. Therefore, these donors and their families deserve our highest gratitude [47].
Notes
References
1. von Arx T, Lozanoff S. Clinical oral anatomy: a comprehensive review for dental practitioners and researchers. Springer International Publishing;2017. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-41993-0.
2. Wong TL, Iwanaga J, Anand MK, Tubbs RS. 2019; An elongated mental spine: case report. Natl J Clin Anat. 8:130–1. DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-1698603.

3. Singh V, Anand MK, Dinesh K. 2000; Variations in the pattern of mental spines and spinous mental foramina in dry adult human mandibles. Surg Radiol Anat. 22:169–73. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-000-0169-1. PMID: 11143309.

4. He P, Truong MK, Adeeb N, Tubbs RS, Iwanaga J. 2017; Clinical anatomy and surgical significance of the lingual foramina and their canals. Clin Anat. 30:194–204. DOI: 10.1002/ca.22824. PMID: 28033685.

5. Sanomiya Ikuta CR, Paes da Silva Ramos Fernandes LM, Poleti ML, Alvares Capelozza AL, Fischer Rubira-Bullen IR. 2016; Anatomical study of the posterior mandible: lateral lingual foramina in cone beam computed tomography. Implant Dent. 25:247–51. DOI: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000387. PMID: 26910183.
6. Tagaya A, Matsuda Y, Nakajima K, Seki K, Okano T. 2009; Assessment of the blood supply to the lingual surface of the mandible for reduction of bleeding during implant surgery. Clin Oral Implants Res. 20:351–5. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2008.01668.x. PMID: 19298289.

7. Bavitz JB, Harn SD, Homze EJ. 1994; Arterial supply to the floor of the mouth and lingual gingiva. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 77:232–5. DOI: 10.1016/0030-4220(94)90290-9. PMID: 8170652.

8. Beer JI, Sieber DA, Scheuer JF 3rd, Greco TM. 2016; Three-dimensional facial anatomy: structure and function as it relates to injectable neuromodulators and soft tissue fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 4(12 Suppl):e1175. DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000001175. PMID: 28018776. PMCID: PMC5172484.

9. Hayakawa I. Principles and practices of complete dentures: creating the mental image of a denture. Quintessence Pub. Co.;1999.
10. Hofschneider U, Tepper G, Gahleitner A, Ulm C. 1999; Assessment of the blood supply to the mental region for reduction of bleeding complications during implant surgery in the interforaminal region. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 14:379–83. PMID: 10379111.
11. Hollinshead WH. Textbook of anatomy. 3rd ed. Harper & Row;1974.
12. Kalpidis CD, Setayesh RM. 2004; Hemorrhaging associated with endosseous implant placement in the anterior mandible: a review of the literature. J Periodontol. 75:631–45. DOI: 10.1902/jop.2004.75.5.631. PMID: 15212344.

13. Laboda G. 1990; Life-threatening hemorrhage after placement of an endosseous implant: report of case. J Am Dent Assoc. 121:599–600. DOI: 10.14219/jada.archive.1990.0231. PMID: 2229738.

14. Lee HJ, Won SY, O J, Hu KS, Mun SY, Yang HM, Kim HJ. 2018; The facial artery: a comprehensive anatomical review. Clin Anat. 31:99–108. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23007. PMID: 29086435.
15. McDonnell D, Reza Nouri M, Todd ME. 1994; The mandibular lingual foramen: a consistent arterial foramen in the middle of the mandible. J Anat. 184(Pt 2):363–9. PMID: 8014127. PMCID: PMC1259996.
16. Meegalla N, Sood G, Nessel TA, Downs BW. Anatomy, head and neck: facial arteries. StatPearls Publishing;2022.
17. Seki S, Sumida K, Yamashita K, Baba O, Kitamura S. 2017; Gross anatomical classification of the courses of the human lingual artery. Surg Radiol Anat. 39:195–203. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-016-1696-8. PMID: 27189234.

18. Sicher H, Brul ELD. Sicher's oral anatomy. 7th ed. Mosby;1980.
19. Williams PL, Warwick R, Dyson M, Bannister LH. Gray's anatomy. 37th ed. Churchill Livingstone;1989.
20. van Leeuwen AC, van der Meij EH, de Visscher JG. 2014; Fracture of the genial tubercles of the mandible: case report and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 72:1994.e1–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2014.05.001. PMID: 25234536.

21. Gallego L, Junquera L, Villarreal P, de Vicente JC. 2007; Spontaneous fracture of the mandibular genial tubercles. A case report. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 12:E599–601. PMID: 18059247.
22. Păuna MR, Babiuc I, Farcaşiu AT. 2015; Prosthodontic management of an extreme atrophy of the mandible correlated with a prominent genial tubercle - a clinical report. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 56(2 Suppl):867–70. PMID: 26429188.
23. Shohat I, Shoshani Y, Taicher S. 2003; Fracture of the genial tubercles associated with a mandibular denture: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 89:232–3. DOI: 10.1067/mpr.2003.46. PMID: 12644795.

24. Choi YJ, Jun SH, Song YD, Chang MW, Kwon JJ. Subburaj K, editor. CT scanning and dental implant. CT Scanning - Techniques and Applications. InTech;2011. p. 229–50. DOI: 10.5772/19250.

25. Cosson J. 2020; Interpreting an orthopantomogram. Aust J Gen Pract. 49:550–5. DOI: 10.31128/AJGP-07-20-5536. PMID: 32864665.

26. Easley J. A new look at dental radiology. Paper presented at: Proceedings of the 48th Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners Annual Convention. 2002 Dec 4-8; Orlando (FL), USA. p. 412–20.
27. Gupta A, Devi P, Srivastava R, Jyoti B. 2014; Intra oral periapical radiography - basics yet intrigue: a review. Bangladesh J Dent Res Educ. 4:83–7. DOI: 10.3329/bjdre.v4i2.20255.

28. Kim JH, Aoki EM, Cortes AR, Abdala-Júnior R, Asaumi J, Arita ES. 2016; Comparison of the diagnostic performance of panoramic and occlusal radiographs in detecting submandibular sialoliths. Imaging Sci Dent. 46:87–92. DOI: 10.5624/isd.2016.46.2.87. PMID: 27358815. PMCID: PMC4925655.

29. Schüler IM, Hennig CL, Buschek R, Scherbaum R, Jacobs C, Scheithauer M, Mentzel HJ. 2023; Radiation exposure and frequency of dental, bitewing and occlusal radiographs in children and adolescents. J Pers Med. 13:692. DOI: 10.3390/jpm13040692. PMID: 37109079. PMCID: PMC10141634.

30. Sukovic P. 2003; Cone beam computed tomography in craniofacial imaging. Orthod Craniofac Res. 6 Suppl 1:31–6. discussion 179–82. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-0544.2003.259.x. PMID: 14606532.

31. Wan C, Bowe C, Madhavarajan S. 2017; Spontaneous fracture of the genial tubercles of the mandible: a case report and review of the literature. Gerodontology. 34:493–7. DOI: 10.1111/ger.12286. PMID: 29094437.

32. Selvamuthukumar SC, Aswath N, Karthika B. 2010; An incidental finding of enlarged genial tubercles in a case of oral carcinoma. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 22:99–101. DOI: 10.4103/0972-1363.166925.

33. Dorland WAN. The American illustrated medical dictionary. 2nd ed. Saunders;1901.
34. Katsumi Y, Tanaka R, Hayashi T, Koga T, Takagi R, Ohshima H. 2013; Variation in arterial supply to the floor of the mouth and assessment of relative hemorrhage risk in implant surgery. Clin Oral Implants Res. 24:434–40. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02348.x. PMID: 22092873.

35. Carter RB, Keen EN. 1971; The intramandibular course of the inferior alveolar nerve. J Anat. 108(Pt 3):433–40. PMID: 5575310. PMCID: PMC1234179.
36. Romanes GJ. Cunningham's manual of practical anatomy. 15th ed. Oxford University Press;1986.
37. Last RJ, McMinn RMH. Last's anatomy, regional and applied. 8th ed. Churchill Livingstone;1990.
38. Morris H, Anson BJ. Morris' human anatomy: a complete systematic treatise. 12th ed. McGraw-Hill Book Company;1966.
39. Williams PL. Gray's anatomy. 38th ed. Churchill Livingstone;1995.
40. Araby YA, Alhirabi AA, Santawy AH. 2019; Genial tubercles: morphological study of the controversial anatomical landmark using cone beam computed tomography. World J Radiol. 11:94–101. DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v11.i7.94. PMID: 31396372. PMCID: PMC6682497.

41. Hu KS, Koh KS, Han SH, Shin KJ, Kim HJ. 2006; Sex determination using nonmetric characteristics of the mandible in Koreans. J Forensic Sci. 51:1376–82. DOI: 10.1111/j.1556-4029.2006.00270.x. PMID: 17199624.
42. Oda LS, Iyomasa MM, Watanabe IS. 1977; Morphologic analysis of the "spina mentalis" in adult mandibles of Brazilian whites and negroes. Rev Bras Pesqui Med Biol. 10:357–60. PMID: 609772.
43. Frazer JES. Frazer's anatomy of the human skeleton. 6th ed. J. & A. Churchill;1965.
44. Jacobson TE, Krol AJ. 1983; A contemporary review of the factors involved in complete dentures. Part III: support. J Prosthet Dent. 49:306–13. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(83)90267-6. PMID: 6341544.

45. Yassutaka Faria Yaedú R, Regina Fisher Rubira-Bullen I, Sant'Ana E. 2006; Spontaneous fracture of genial tubercles: case report. Quintessence Int. 37:737–9. PMID: 17017637.
46. Ferreira Barbosa DA, Marinho Bezerra TM, Barros Silva PG, Menezes Pimenta AV, Kurita LM, Gurgel Costa FW. 2019; Clinical, imaging, and therapeutic aspects of genial tubercle fractures: a systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 77:1674.e1–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2019.03.030. PMID: 31028733.
47. Iwanaga J, Singh V, Ohtsuka A, Hwang Y, Kim HJ, Moryś J, Ravi KS, Ribatti D, Trainor PA, Sañudo JR, Apaydin N, Şengül G, Albertine KH, Walocha JA, Loukas M, Duparc F, Paulsen F, Del Sol M, Adds P, Hegazy A, Tubbs RS. 2021; Acknowledging the use of human cadaveric tissues in research papers: recommendations from anatomical journal editors. Clin Anat. 34:2–4. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23671. PMID: 32808702.

Fig. 1
Various number of mental spines (arrows). Note that the median lingual foramina are shown (arrowheads).
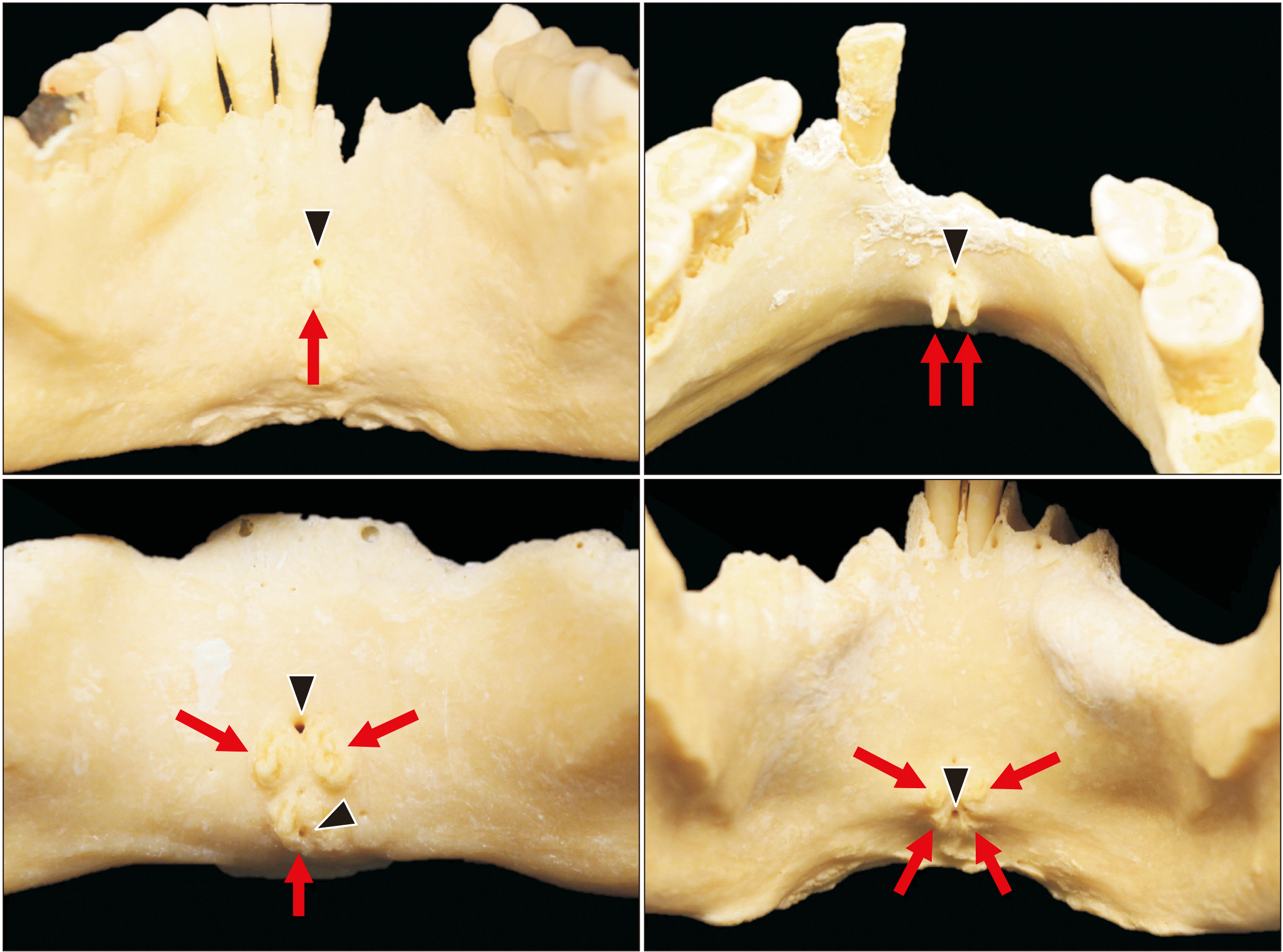
Fig. 4
Masson’s trichrome staining of the para-midsagittal mandible. Note that the tendon of the geniohyoid muscle (between arrows) attaches to the mental spines.
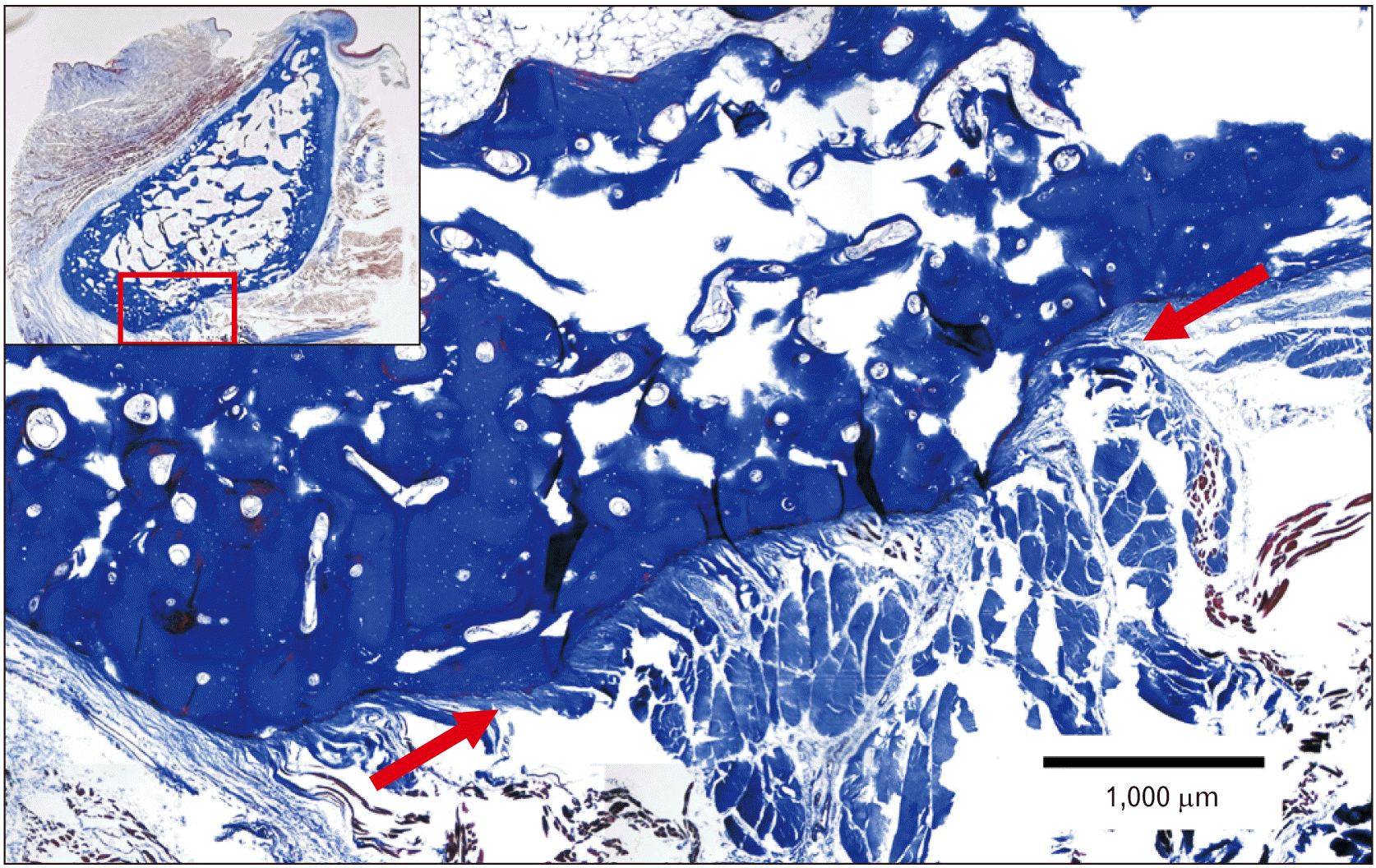
Table 1
Variation in mental spine morphology
| Type | Singh et al. [3] | Araby et al. [40] |
|---|---|---|
| Absent | 22 (1.83) | 10 (6.4) |
| Two pairs of spines placed one above the other | 231 (19.25) | 22 (14.2) |
| Two superior spines with median vertical ridge below | 562 (46.83) | 35 (22.6) |
| Two superior spines with rough impression below | 280 (23.33) | 57 (36.8) |
| Single prominence | 105 (8.75) | 31 (20) |
| Total | 1,200 (100) | 155 (100) |
| Type | Hu et al. [41] | |
| Superior mental spine | Inferior mental spine | |
| Sharp separation | 54.3 | 5.7 |
| Dull separation | 10.5 | 2.9 |
| Sharp fusion | 7.6 | 31.4 |
| Dull fusion | 3.8 | 37.1 |
| Triple separation | 0.9 | 0.0 |
| Sharp fusion (superior mental spine and inferior mental spine) | 18.1 | |
| Dull fusion (superior mental spine and inferior mental spine) | 4.8 | |
| Total | 107 (100) | |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download