Abstract
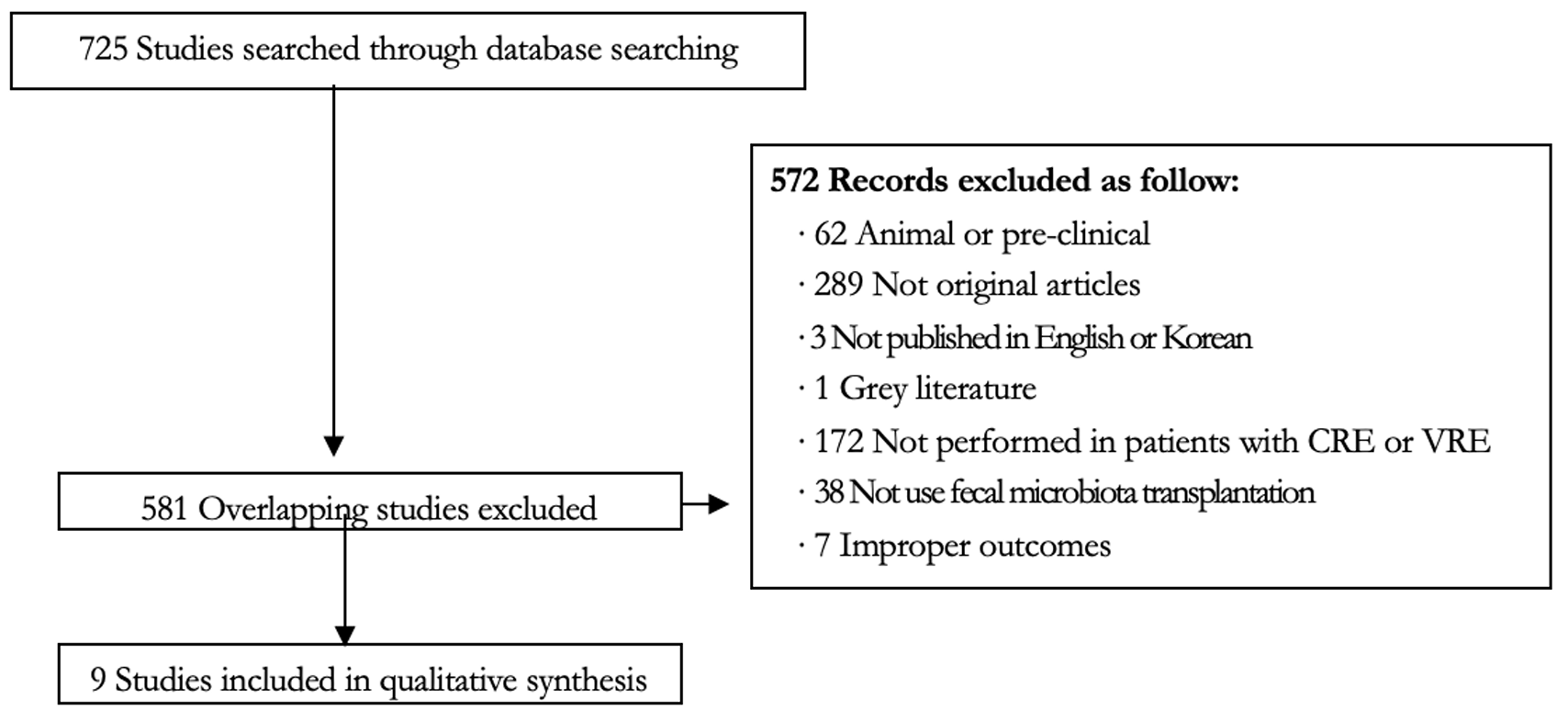
Background: Fecal microbiota transplantation against gut colonization using a multidrug-resistant organism is a technique used to treat infections through normalizing the gut microbiota via fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with confirmed colonization by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) or vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) based on a fecal culture test within the past one week. In this study, we aimed to determine the safety and effectiveness of this technique. Methods: The safety and effectiveness were assessed via a systematic review. A literature search was conducted using five Korean databases, such as KoreaMed, and international databases, including Ovid-MEDLINE, Ovid-EMBASE, and Cochrane Library. Results: Main results are described here. From the studies retrieved using the aforementioned search strategy, the remaining 581 studies were screened using the inclusion and exclusion criteria, resulting in the selection of nine studies for further consideration. In terms of safety, many studies reported deaths and adverse reactions associated with different causes. Fewer studies reported the rate of colonization; however, the effect of colony rate was inconsistent when compared to no treatment group. Additionally, none of the studies assessed the recurrence rate, a decrease in the prevalence of diseases related to infection by multidrug-resistant bacteria, and the quality of life. Conclusion: Fecal bacterial colonization for the decolonization of intestinal multidrug-resistant bacteria was evaluated using a technique that requires further research as there is insufficient literature evidence to validate its safety and efficacy in treating infections through normalizing the intestinal flora of patients with confirmed colonization by CRE or VRE.
REFERENCES
1. Crouzet L, Rigottier-Gois L, Serror P. Potential use of probiotic and commensal bacteria as non-antibiotic strategies against vancomycin-resistant enterococci. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2015;362:fnv012.
2. Ghani R, Mullish BH, McDonal JAK, Ghazy A, Williams HRT, Brannigan ET, et al. Disease prevention not decolonization: a model for fecal microbiota transplantation in patients colonized with multidrug-resistant organisms. Clin Infect Dis 2021;72:1444-7.
3. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 2009;6:e1000097.
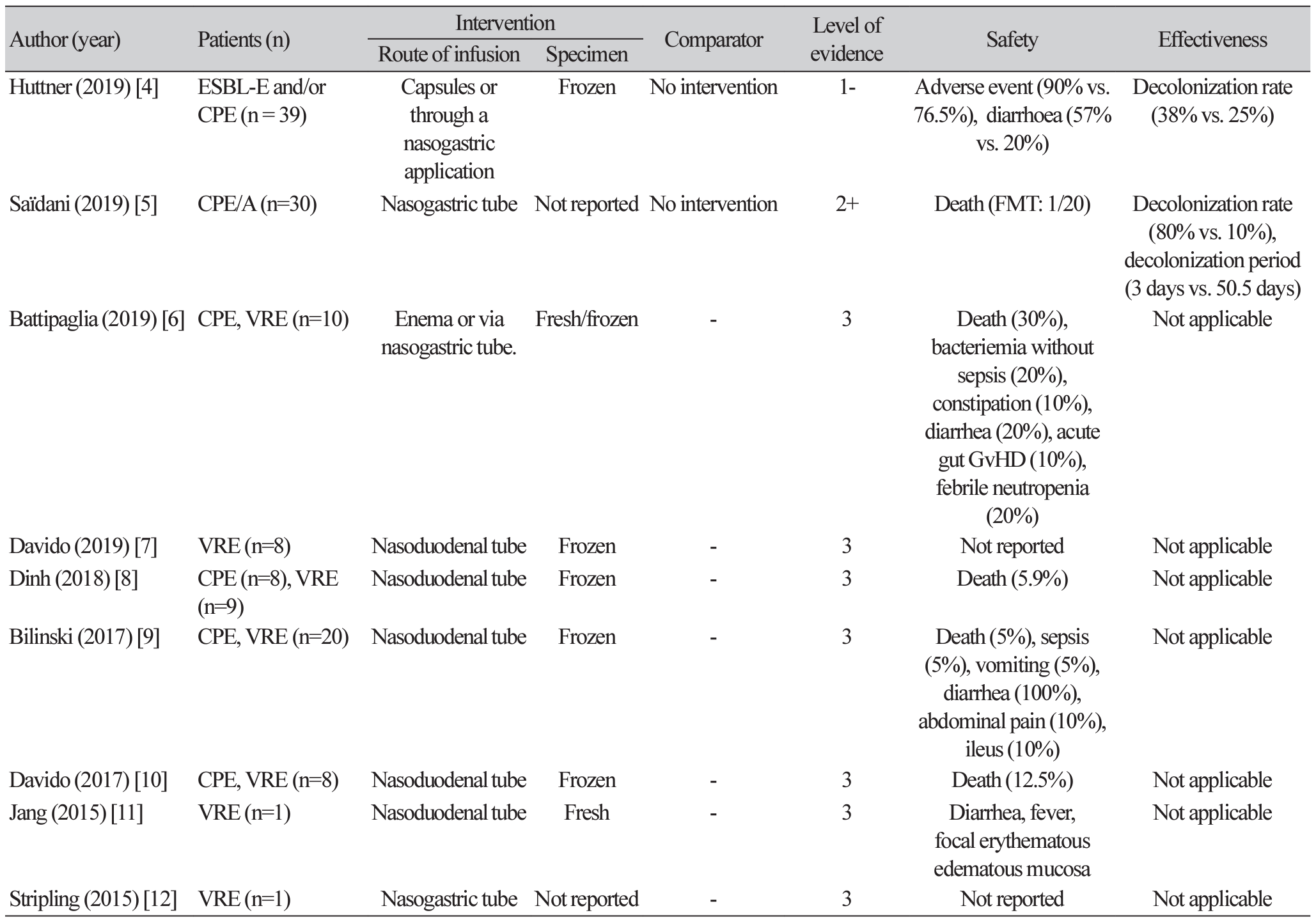
4. Huttner BD, de Lastours V, Wassenberg M, Maharshak N, Mauris A, Galperine T, et al. A 5-day course of oral antibiotics followed by faecal transplantation to eradicate carriage of multidrugresistant Enterobacteriaceae: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Microbiol Infect 2019;25:830-8.
5. Saïdani N, Lagier JC, Cassir N, Million M, Baron S, Dubourg G, et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation shortens the colonisation period and allows re-entry of patients carrying carbapenamase-producing bacteria into medical care facilities. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2019;53:355-61.
6. Battipaglia G, Malard F, Rubio MT, Ruggeri A, Mamez AC, Brissot E, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation before or after allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation in patients with hematologic malignancies carrying multidrug-resistance bacteria. Haematologica 2019;104:1682-8.
7. Davido B, Batista R, Fessi H, Michelon H, Escaut L, Lawrence C, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation to eradicate vancomycin-resistant enterococci colonization in case of an outbreak. Med Mal Infect 2019;49:214-8.
8. Dinh A, Fessi H, Duran C, Batista R, Michelon H, Bouchand F, et al. Clearance of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae vs vancomycin-resistant enterococci carriage after faecal microbiota transplant: a prospective comparative study. J Hosp Infect 2018;99:481-6.
9. Bilinski J, Grzesiowski P, Sorensen N, Madry K, Muszynski J, Robak K, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with blood disorders inhibits gut colonization with antibiotic-resistant bacteria: results of a prospective, single-center study. Clin Infect Dis 2017;65:364-70.
10. Davido B, Batista R, Michelon H, Lepainteur M, Bouchand F, Lepeule R, et al. Is faecal microbiota transplantation an option to eradicate highly drug-resistant enteric bacteria carriage? J Hosp Infect 2017;95:433-7.
11. Jang MO, An JH, Jung SI, Park KH. Refractory Clostridium difficile infection cured with fecal microbiota transplantation in vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus colonized patient. Intest Res 2015;13:80-4.
12. Stripling J, Kumar R, Baddley JW, Nellore A, Dixon P, Howard D, et al. Loss of vancomycinresistant Enterococcus fecal dominance in an organ transplant patient with Clostridium difficile colitis after fecal microbiota transplant. Open Forum Infect Dis 2015;2:ofv078.
13. Russell DL, Flood A, Zaroda TE, Acosta C, Riley MMS, Busuttil RW, et al. Outcomes of colonization with MRSA and VRE among liver transplant candidates and recipients. Am J Transplant 2008;8:1737-43.
14. FDA. FDA web site on medical product safety information. https://www.fda.gov/safety/ medical-product-safety-information/fecal-microbiota-transplantation-safety-alert-risk-seriousadverse-events-likely-due-transmission [Online] (last visited on 7 April 2020).
15. ANSM. ANSM website on points of information. Faecal microbiota transplantation and its supervision in clinical tirals. http://dev4-afssaps-marche2017.integra.fr/S-informer/Points-dinformation-Points-d-information/La-transplantation-de-microbiote-fecal-et-son-encadrementdans-les-essais-cliniques-Point-d-Information2 [Online] (last visited on 1 September 2021).
16. Keller JJ, Vehreschild MJ, Hvas CL, Jørgensen SM, Kupciskas J, Link A. Stool for fecal microbiota transplantation should be classified as a transplant product and not as a drug. United European Gastroenterol J 2019;7:1408-10.
17. Scheeler A. Where stool is a drug: international approaches to regulating the use of fecal microbiota for transplantation. J Law Med Ethics 2019;47:524-40.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download