Abstract
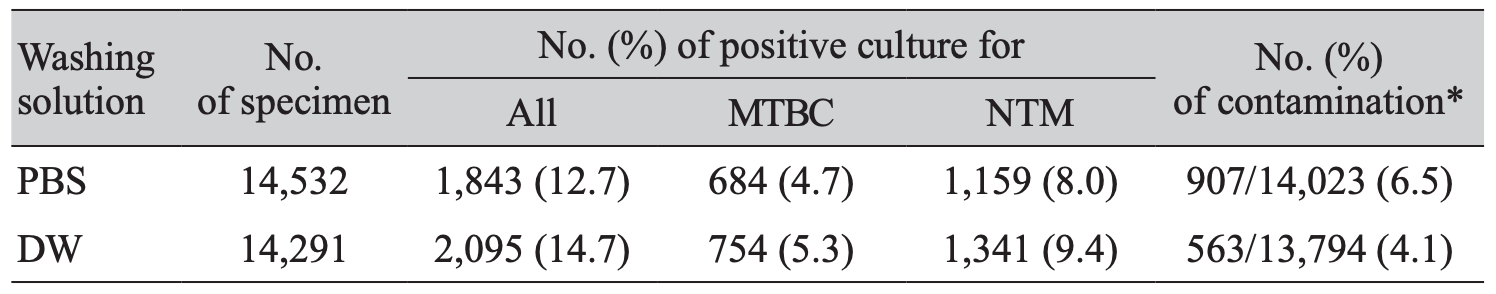
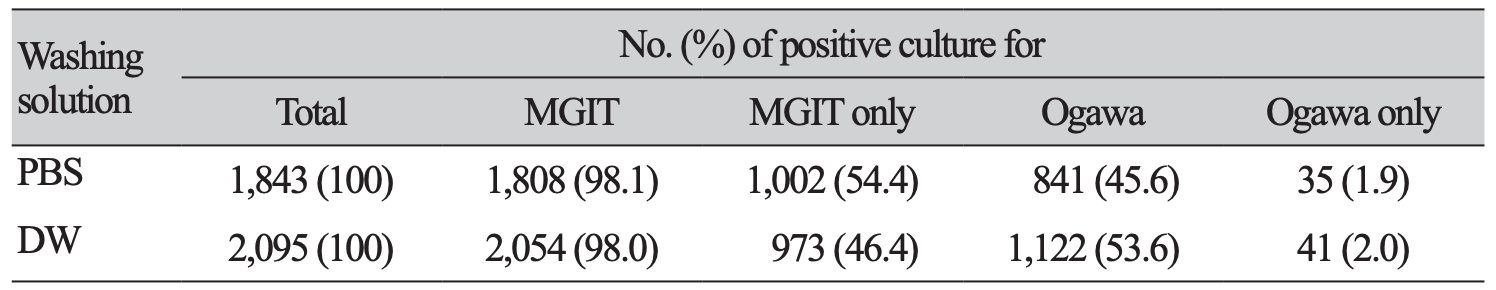
Background: Respiratory specimens subjected to mycobacterial detection were initially pre-treated with N-acetyl-L-cysteine-sodium hydroxide (NALC-NaOH) to remove the mucus and normal flora. Next, they were washed and neutralized with phosphate-buffered solution (PBS). The effectiveness of distilled water (DW) compared to PBS as a washing neutralizer during identification of mycobacteria was evaluated in this study. Methods: We analyzed the results of mycobacterial test conducted at a general hospital in Gwangju from October 2016 to September 2018. PBS and DW were used as a respiratory sample washing agent for one year each. Results: The positive culture rate for the culture of mycobacteria was 12.7% (1,843/14,532) and 14.7% (2,095/14,291), when PBS and DW were used, respectively. The recovery rate of the mycobacteria growth indicator tubes (MGIT) and the separation rates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) showed no significant change. However, in 2% Ogawa medium, as the NTM culture increased from 47.4% (399/841) to 56.1% (630/1,122), the recovery rate increased from 45.6% (841/1,843) to 53.6% (1,122/2,095). The MGIT contamination rate decreased from 6.5% to 4.1%. Conclusion: DW as a washing agent for NALC-NaOH increased the recovery rate of Ogawa media and reduced the contamination rate of MGIT. Therefore, use of DW instead of PBS as a washing neutralizer during identification of mycobacteria might be useful.
Go to : 
ACKNOWLEGEMENTS
In this study, Woon-Seok Yeo, the medical information office of Gwangju Christian Hospital, helped collect data.
REFERENCES
1. Hwang SS, Oh KJ, Jang IH, Uh Y, Yoon KJ, Kim HY, et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic performance of the AdvanSure TB/NTM real-time PCR kit for detection of mycobacteria. Korean J Clin Microbiol 2011;14:55-9.
2. Kim YS, Jo YH, Lee HJ, Suh JT, Lee YJ. Comparison of the MGIT (mycobacteria growth indicator tube) with Ogawa media for recovery of mycobacteria. Korean J Clin Microbiol 2001;4:58-61.
3. Go UY, Park MS, Kim UN, Lee SD, Han SM, Lee JY, et al. Tuberculosis prevention and care in Korea: evolution of policyand practice. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis 2018;11:28-36.
4. Schlossberg D. Tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. 6th ed. Washington, DC; ASM Press, 2011.
5. Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, Catanzaro A , Daley C , Gordin F, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007;175:367-416.
6. Kang H, Sung N, Lee S, Kim D, Jeon D, Hwang S, et al. Comparison of smear and culture positivity using NaOH method and NALC-NaOH method for sputum treatment. Tuberc Respir Dis 2008;65:379-84.
7. Beran V, Havelkova M, Kaustova J, Dvorska L, Pavlik I. Cell wall deficient forms of mycobacteria: a review. Vet Med 2006;7:365–89.
8. Yi JY, Kim JP, Shin JH, Suh SP, Ryang DW. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using BACTEC mycobacteria growth indicator tube (MGIT) 960 system: comparison with BACTEC 460 TB system and Ogawa media. Korean J Clin Pathol 2000;20:384-91.
9. Subramanyam B, Sivaramakrishnan G, Sangamithrai D, Ravi R, Thiruvengadam K, Vijayaragavan V, et al. Reprocessing of contaminated MGIT 960 cultures to improve availablility of valid results for mycobacteria. Int J Microbiol 2020;1721020:1-3.
10. Jung H, Bang HI, Choi TY. Evaluation of the effectiveness of a re-decontaminating process with bacterial contaminated specimens showing a positive MGIT signal for the detection of mycobacteria. Korean J Clin Lab Sci 2019;51:171-6.
11. Krasnow I and Wayne LG. Sputum digestion. I. The mortality rate of tubercle bacilli in various digestion systems. Am J Clin Pathol 1966;45:352-5.
12. Bae E, Im JH, Kim SW, Yoon NS, Sung H, Kim MN, et al. Evaluation of combination of BACTEC mycobacteria growth indicator tube 960 system and Ogawa media for mycobacterial culture. Korean J Lab Med 2008;28:299-306.
13. Joung US, Jeong J, Lee SH, Kim SR. Comparision of mycobacterial culture by mycobacterium growth indicator tube and Ogawa media. Korean J Clin Microbiol 2004;7:135-8.
14. Kim YS, Jo YH, Lee HJ, Suh JT, Lee YJ. Comparison of the MGIT (mycobacteriia growth indicator tube) with Ogawa media for recovery of mycobacteria. Korean J Clin Microbiol 2001;4:58-61.
Go to : 
| undefined | Fig. 1.The number of Mycobacterium tuberculosis compiex (MTBC) and nontuberculous mycobacterium (NTM) cultured in Ogawa (A) and MGIT (B) medium. MGIT, mycobacterium growth indicator tube; PBS, phosphate buffered solution; DW, distilled water.
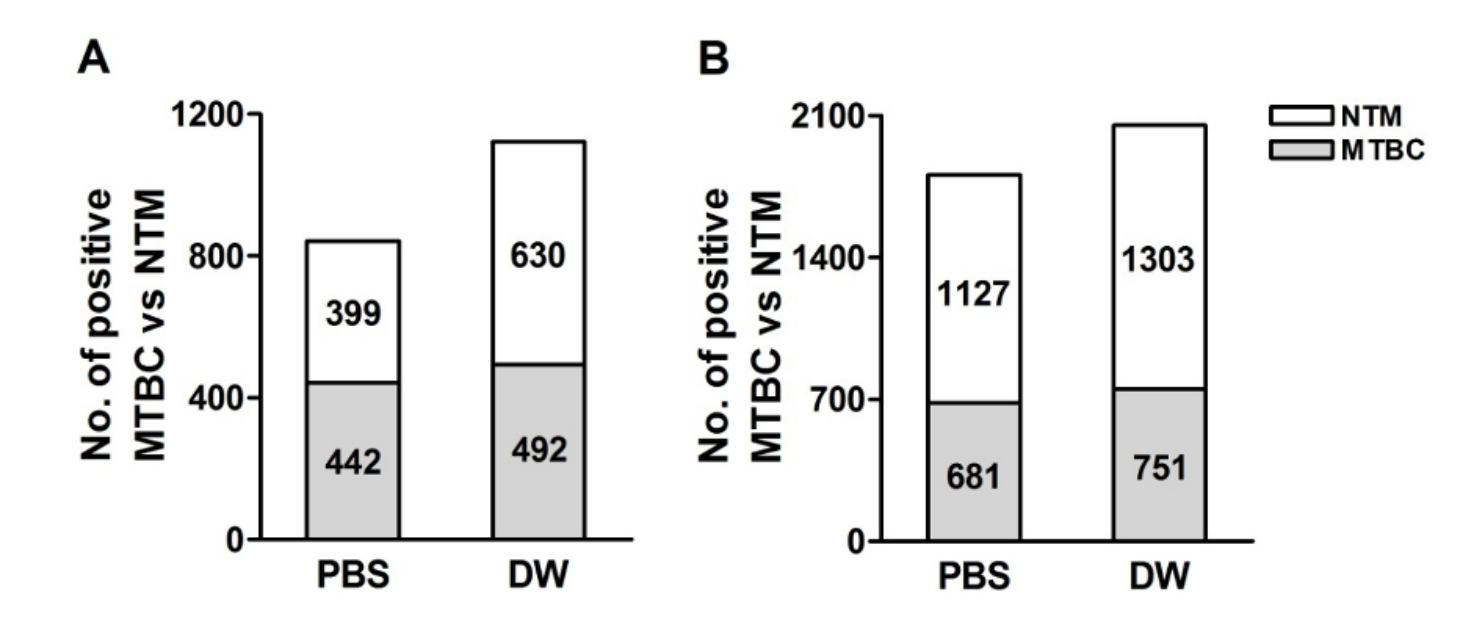
|
| undefined | Fig. 2.Annual change in the proportion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis compiex (MTBC) vs non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) isolated in patients.
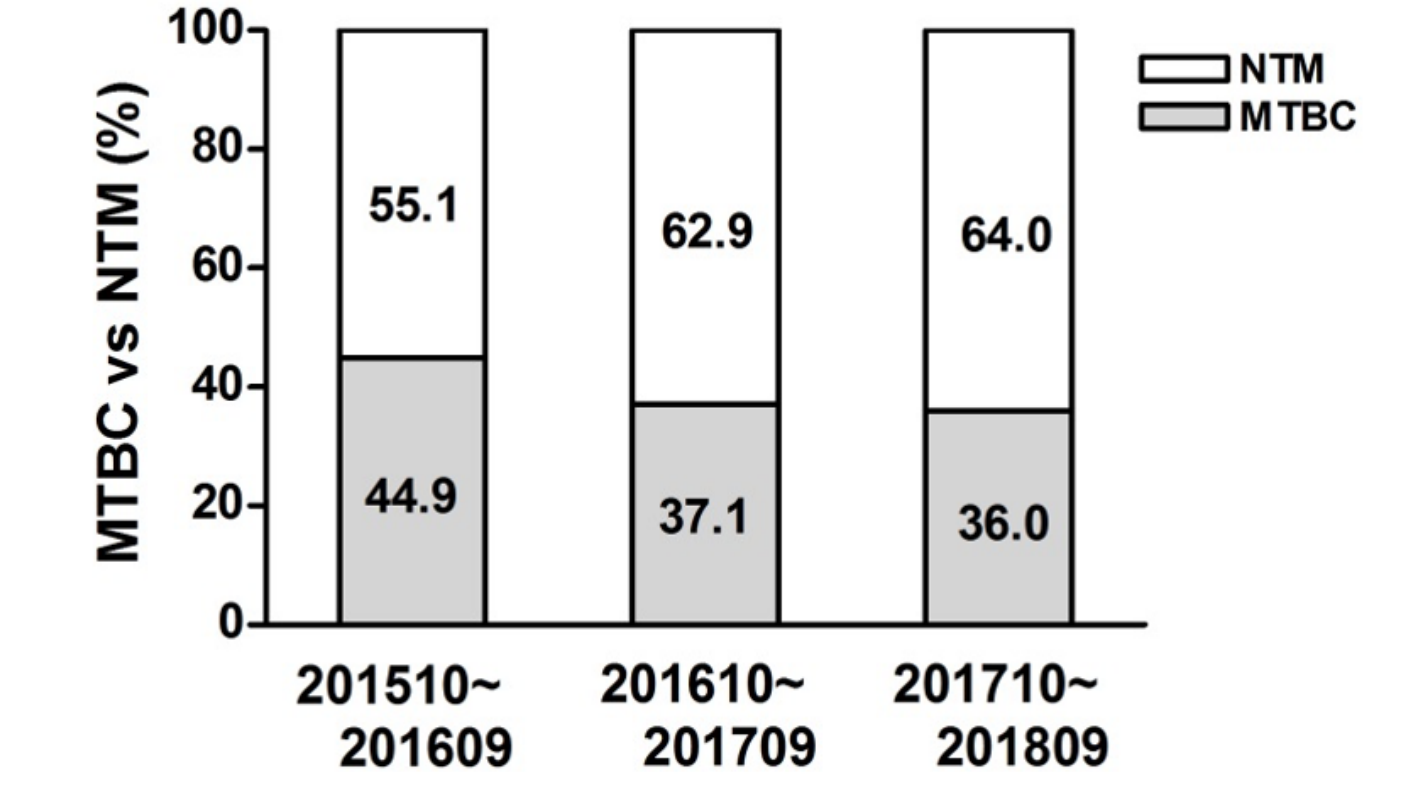
|
| undefined | Fig. 3.Changes of pH after washing pretreatment agent with PBS or DW and after inoculation of the specimenin MGIT. (A) pH of PBS and DW, (B) pH of the specimen after pretreatment and washing, (C) pH of the MGIT after inoculation of the specimen. MGIT, mycobacterium growth indicator tube; PBS, phosphate buffered solution; DW, distilled water.
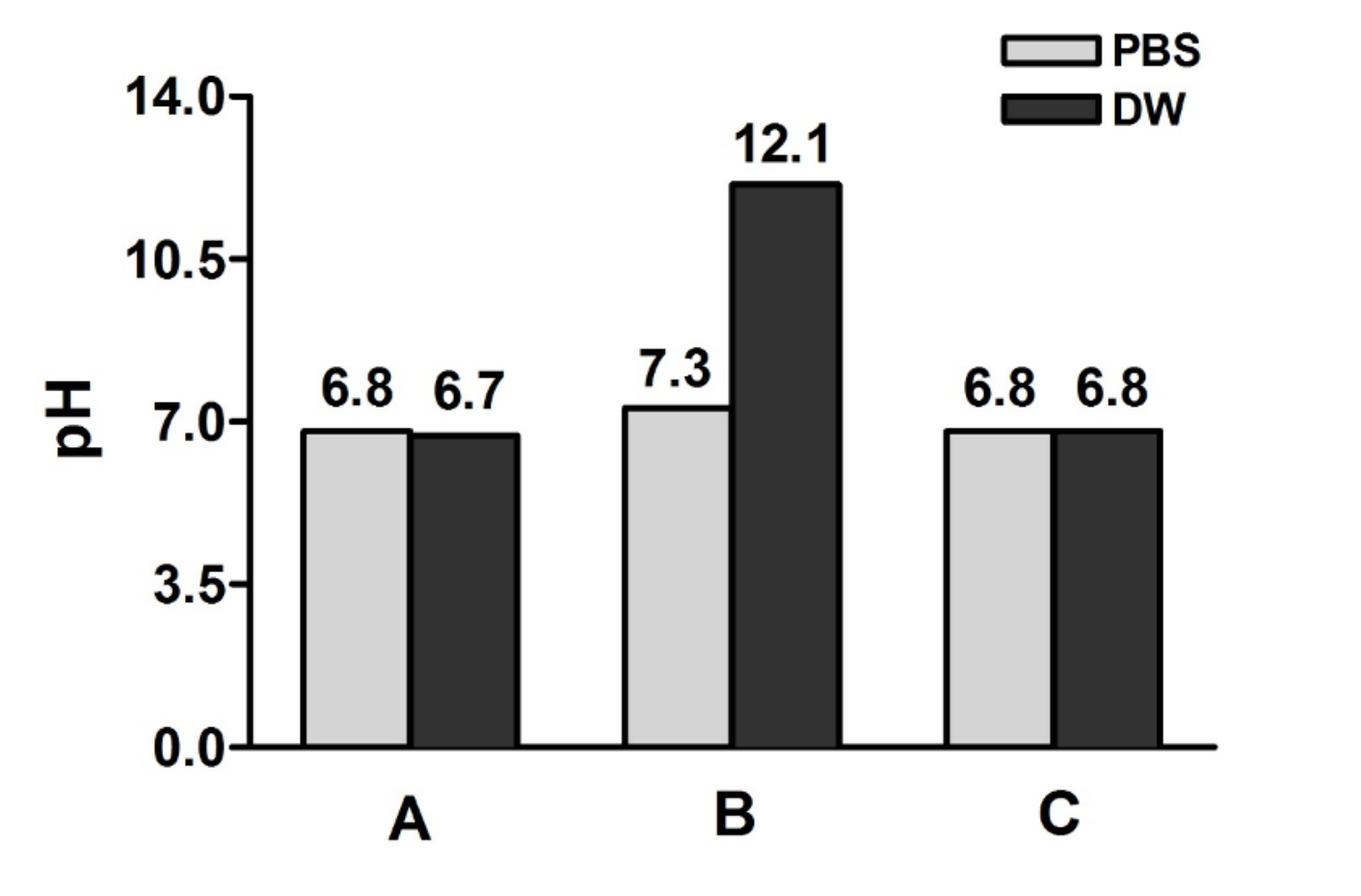
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download