INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study design
Device
 | Fig. 1.Nasal positive airway pressure mask used in this study during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. SuperNO2VA Nasal Positive Airway Pressure Ventilation System (Vyaire). (A) Positioning and attachment of the device. (B) Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with the nasal positive airway pressure mask in place. |
Statistics
Ethical statements
RESULTS
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Nasal cannula | Nasal PAP mask | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 51 (100.0) | 51 (100.0) | |
| Female | 20 (39.2) | 20 (39.2) | |
| Male | 31 (60.8) | 31 (60.8) | >0.99 |
| Age (yr) | |||
| Mean | 67.7 | 66.2 | 0.53 |
| Median (range) | 67 (40–92) | 69 (37–94) | 0.63 |
| Inpatient | 31 (60.8) | 32 (62.7) | |
| Outpatient | 20 (39.2) | 19 (37.3) | >0.99 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||
| Mean | 31.5 | 33.3 | 0.13 |
| Median (range) | 31 (25.2–41.2) | 31.5 (25.1–61.0) | 0.34 |
| BMI >30 | 29 (56.9) | 34 (66.7) | 0.42 |
| BMI >40 | 2 (3.9) | 7 (13.7) | 0.16 |
| Known respiratory diseasesa) | 0.08 | ||
| Yes | 3 (5.9) | 10 (19.6) | |
| No | 48 (94.1) | 41 (80.4) | |
| O2 supplementation before endoscopy | 0.48 | ||
| Yes | 0 (0) | 2 (3.9) | |
| No | 51 (100.0) | 49 (96.1) | |
| EGD | 31 (60.8) | 25 (49.0) | 0.32 |
| EGD+intervention | 5 (9.8) | 5 (9.8) | >0.99 |
| ERCP | 6 (11.8) | 7 (13.7) | >0.99 |
| EUS | 8 (15.7) | 5 (9.8) | 0.55 |
| Combination | 1 (2.0) | 9 (17.6) | 0.02 |
| Procedure duration (min) | |||
| Mean | 16 | 19 | 0.25 |
| Median (range) | 12 (5–85) | 13 (5–66) | 0.08 |
Values are presented as number (%) unless otherwise indicated.
PAP, positive airway pressure; BMI, body mass index; EGD, esophagogastroduodenoscopy; ERCP, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; EUS, endoscopic ultrasound.
a) Respiratory diseases recorded in the nasal cannula group was asthma (2 cases) and in the nasal PAP mask group were obstructive sleep apnea (OSAS) (3), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (2), both OSAO and COPD (1), recent pneumonia (2), recent pulmonary embolism (1), and sarcoid disease (1).
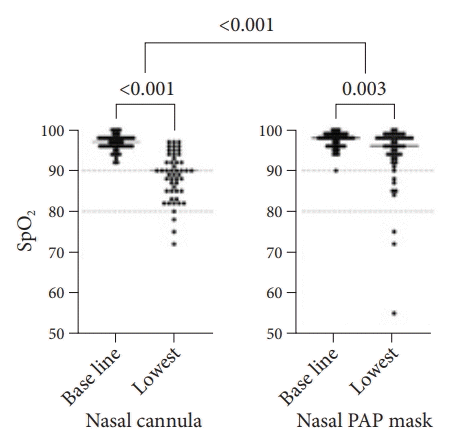 | Fig. 2.Oxygen saturation before and during sedation. Oxygen saturation (SpO2) before sedation (baseline) and lowest value during sedation (lowest) in patients with nasal cannula compared to those in the nasal positive airway pressure (PAP) mask cohort. Within each group, differences were tested for statistical significance using Wilcoxon signed ranks test; the difference in delta-SpO2 between the groups was tested using two-sided Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download