1. Cho SH, Bachert C, Lockey RF. Chronic rhinosinusitis phenotypes: An approach to better medical care for chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016; 4(4):639–42.

2. Akdis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, Dykewicz MS, Hellings PW, Naclerio RM, et al. Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: A PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131(6):1479–90.
3. Van Crombruggen K, Zhang N, Gevaert P, Tomassen P, Bachert C. Pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis: Inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128(4):728–32.

4. Polzehl D, Moeller P, Riechelmann H, Perner S. Distinct features of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Allergy. 2006; 61(11):1275–9.

5. Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ, Cui YH, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124(3):478–84.E2.

6. Kim DK, Eun KM, Kim MK, Cho D, Han SA, Han SY, et al. Comparison between signature cytokines of nasal tissues in subtypes of chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019; 11(2):201–11.

7. Elhini A, Abdelwahab S, Ikeda K. Th1 and Th2 cell population in chronic ethmoidal rhinosinusitis: A chemokine receptor assay. Laryngoscope. 2005; 115(7):1272–7.

8. Suzuki H, Takahashi Y, Wataya H, Ikeda K, Nakabayashi S, Shimomura A, et al. Mechanism of neutrophil recruitment induced by IL-8 in chronic sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996; 98(3):659–70.

9. Kountakis SE, Arango P, Bradley D, Wade ZK, Borish L. Molecular and cellular staging for the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2004; 114(11):1895–905.

10. Vlaminck S, Vauterin T, Hellings PW, Jorissen M, Acke F, Van Cauwenberge P, et al. The importance of local eosinophilia in the surgical outcome of chronic rhinosinusitis: A 3-year prospective observational study. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2014; 28(3):260–4.

11. Van Zele T, Holtappels G, Gevaert P, Bachert C. Differences in initial immunoprofiles between recurrent and nonrecurrent chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2014; 28(3):192–8.

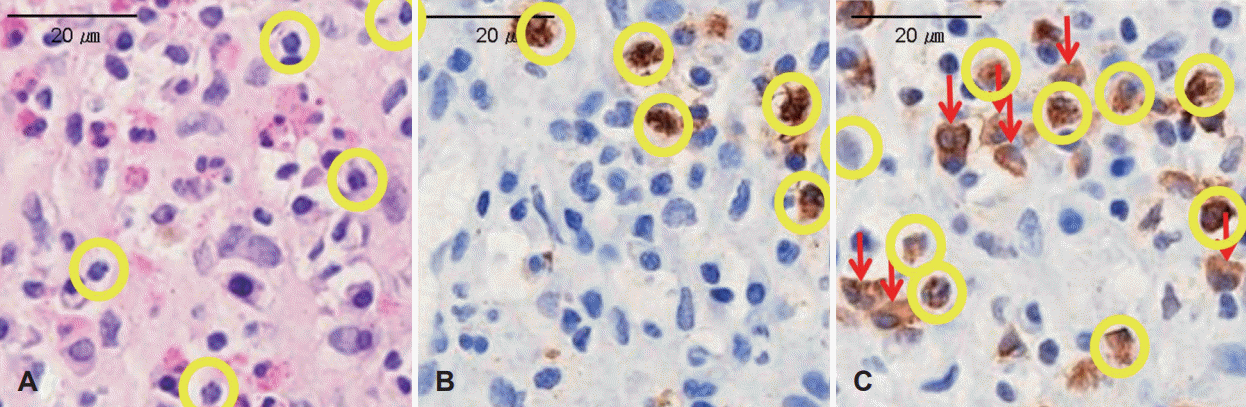
12. Wang J, MacKenzie JD, Ramachandran R, Chen DZ. Identifying neutrophils in H&E staining histology tissue images. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2014; 17(Pt 1):73–80.

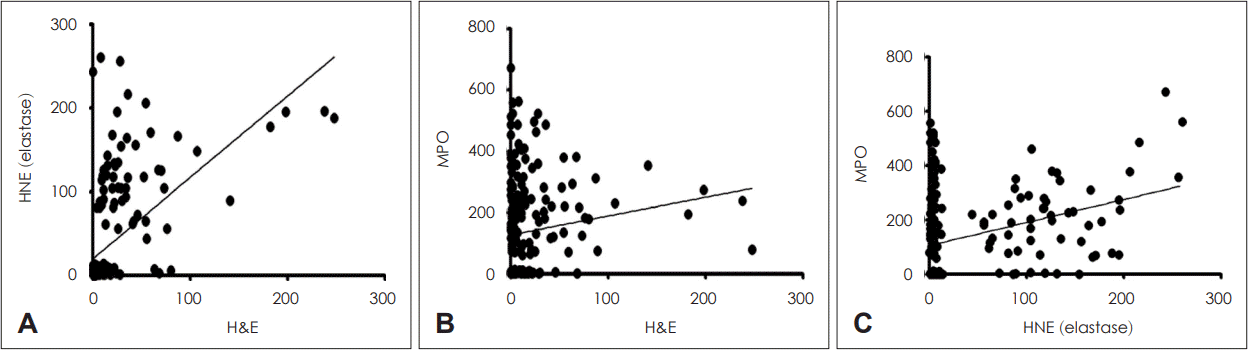
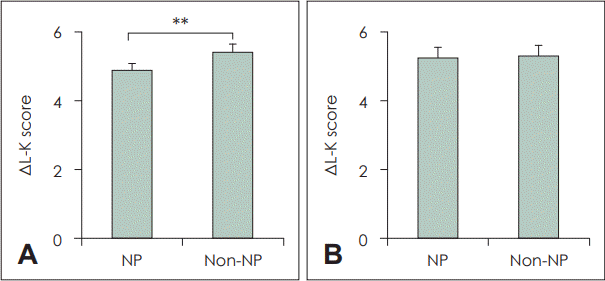
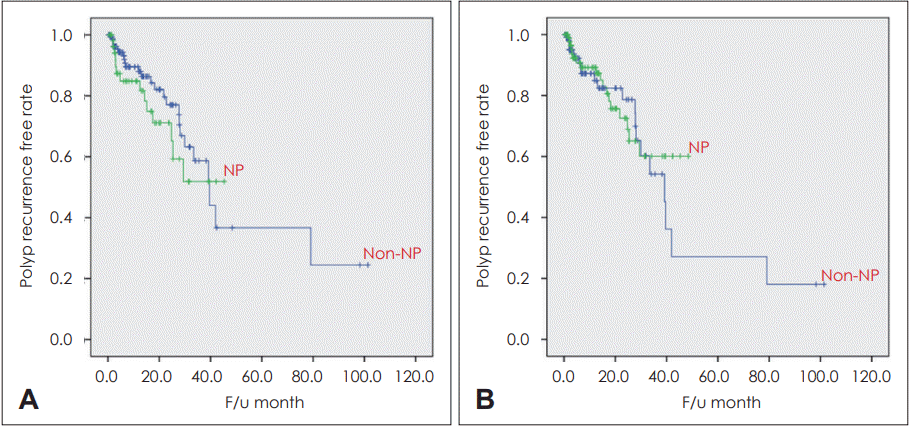
13. Kim DK, Kim JY, Han YE, Kim JK, Lim HS, Eun KM, et al. Elastase-positive neutrophils are associated with refractoriness of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in an Asian population. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2020; 12(1):42–55.

14. Kramps JA, van der Valk P, van der Sandt MM, Lindeman J, Meijer CJ. Elastase as a marker for neutrophilic myeloid cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984; 32(4):389–94.

15. Boettcher M, Esser M, Trah J, Klohs S, Mokhaberi N, Wenskus J, et al. Markers of neutrophil activation and extracellular traps formation are predictive of appendicitis in mice and humans: A pilot study. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):18240.

16. Ikeda K, Shiozawa A, Ono N, Kusunoki T, Hirotsu M, Homma H, et al. Subclassification of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp based on eosinophil and neutrophil. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123(11):E1–9.

17. Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Staging for rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; 117(3 Pt 2):S35–40.

18. Hellings PW, Borrelli D, Pietikainen S, Agache I, Akdis C, Bachert C, et al. European summit on the prevention and self-management of chronic respiratory diseases: Report of the European Union Parliament Summit (29 March 2017). Clin Transl Allergy. 2017; 7:49.

19. Jobran A, Sultan B, Alotaibi AE, Asiri AY, Alhayyani RM, Almanie NI. Nasal polyps and its histo-pathological evaluation. Egypt J Hosp Med. 2018; 70(11):2022–4.

20. Bachert C, Zhang L, Gevaert P. Current and future treatment options for adult chronic rhinosinusitis: Focus on nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 136(6):1431–40.

21. Wang X, Zhang N, Bo M, Holtappels G, Zheng M, Lou H, et al. Diversity of TH cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: A multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 138(5):1344–53.
22. Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N, et al. Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122(5):961–8.

23. Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, Bai J, Fan Y, Xia W, et al. Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129(6):1522–8.E5.

24. Wang H, Li ZY, Jiang WX, Liao B, Zhai GT, Wang N, et al. The activation and function of IL-36γ in neutrophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141(5):1646–58.

25. Ryu G, Kim DK, Dhong HJ, Eun KM, Lee KE, Kong IG, et al. Immunological characteristics in refractory chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps undergoing revision surgeries. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019; 11(5):664–76.

26. Kim DK, Kang SI, Kong IG, Cho YH, Song SK, Hyun SJ, et al. Two-track medical treatment strategy according to the clinical scoring system for chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018; 10(5):490–502.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download