Introduction
Materials and methods
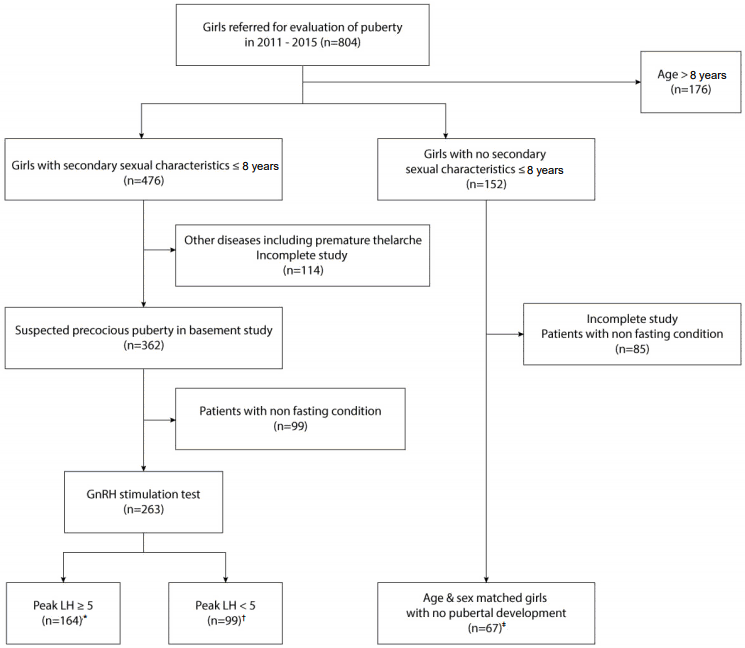
1. Study population and design
2. Clinical and laboratory data
3. Statistical analysis
Results
1. The comparison of the baseline clinical, biochemical characteristics and insulin resistance parameters of CPP, non-CPP, and control groups
Table 1.
| Characteristic | CPP (n=164) | Non-CPP (n=99) | Control (n=67) | P-value* | P-value† | P-value‡ | Overall P-value§ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA (yr) | 8.3±0.6 | 8.1±0.8 | 7.9±0.6 | 0.001 | 0.077 | 0.056 | 0.001 |
| BA (yr) | 9.7±0.9 | 9.2±1.0 | 8.2±0.9 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| BA–CA (yr) | 1.3±0.7 | 1.1±0.7 | 0.0±1.5 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.117 | 0.001 |
| Ht. SDS | 0.9±1.1 | 0.8±1.0 | 0.5±0.9 | 0.011 | 0.063 | 0.999 | 0.012 |
| Wt. SDS | 0.7±1.3 | 0.9±1.3 | 0.5±0.9 | 0.714 | 0.142 | 0.782 | 0.138 |
| BMI SDS | 0.3±1.1 | 0.9±1.3 | 0.4±0.9 | 0.999 | 0.633 | 0.237 | 0.195 |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | 80.2±36.7 | 76.5±34.7 | 83.3±31.5 | 0.999 | 0.671 | 0.999 | 0.460 |
| LH0 (IU/L) | 1.1±1.2 | 0.5±0.4 | 0.3±0.3 | 0.001 | 0.615 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Peak LH (IU/L) | 12.9±9.5 | 3.2±1.0 | - | - | - | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Peak LH/LH0 | 23.3±22.7 | 9.3±5.8 | - | - | - | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| E2 (pg/mL) | 12.0±12.5 | 9.5±9.0 | 5.0±0.3 | 0.001 | 0.016 | 0.162 | 0.001 |
| FEI (pmol/L) | 17.8±18.3 | 15.3±17.1 | 7.0±2.7 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.675 | 0.001 |
| IGF-1 (ug/L) | 271.6±91.4 | 238.9±70.9 | 220.6±64.3 | 0.001 | 0.463 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| AST (IU/L) | 27.3±8.9 | 28.6±10.3 | 27.1±5.1 | 0.999 | 0.883 | 0.713 | 0.433 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 14.8±5.7 | 17.5±12.1 | 14.8±6.7 | 0.999 | 0.112 | 0.037 | 0.028 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 168.5±28.7 | 164.7±27.2 | 169.4±23.0 | 0.999 | 0.831 | 0.842 | 0.457 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 116.0±68.6 | 109.5±61.6 | 111.4±58.1 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.718 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 94.6±27.1 | 93.5±26.6 | 95.9±21.8 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.850 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 51.2±10.1 | 50.4±9.9 | 51.8±8.5 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.637 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 94.7±11.1 | 96.1±11.9 | 91.8±8.1 | 0.204 | 0.035 | 0.864 | 0.040 |
| Insulin (μU/mL) | 23.5±22.9 | 22.5±26.5 | 12.0±6.8 | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.999 | 0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 5.69±5.85 | 5.68±7.37 | 2.78±1.72 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.999 | 0.002 |
| QUICKI | 0.32±0.04 | 0.33±0.05 | 0.34±0.04 | 0.003 | 0.194 | 0.390 | 0.004 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation.
CPP, central precocious puberty; CA, chronological age; BA, bone age; SDS, standard deviation scores; Ht., height; Wt., weight; BMI, body mass index; SHBG, sex hormone binding globulin; LH, luteinizing hormone; E2, estradiol; FEI, free estradiol index; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance; QUICKI, quantitative insulin sensitivity check index
2. Baseline clinical, biochemical characteristics and insulin resistance parameters according to BMI in CPP group
Table 2.
| Characteristic | BMI<50th %ile (n=87) | 50th %ile≤BMI<85th %ile (n=57) | BMI≥85th %ile (n=20) | P-value* | P for trend† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA (yr) | 8.3±0.6 | 8.4±0.6 | 8.2±0.7 | 0.482 | 0.960 |
| BA (yr) | 9.6±0.9 | 9.6±0.9 | 10.2±1.0 | 0.018 | 0.018 |
| BA–CA (yr) | 1.2±0.7 | 1.2±0.7 | 2.0±0.9 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | 98.6±34.2 | 66.0±27.2 | 40.7±17.0 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| LH0 (IU/L) | 1.1±1.3 | 1.1±1.3 | 1.1±0.8 | 0.952 | 0.842 |
| Peak LH (IU/L) | 12.7±9.7 | 13.3±9.2 | 12.5±9.9 | 0.924 | 0.953 |
| E2 (pg/mL) | 13.2±14.1 | 10.3±10.3 | 11.2±9.6 | 0.367 | 0.259 |
| FEI (pmol/L) | 15.0±16.7 | 18.1±18.7 | 29.5±20.1 | 0.007 | 0.004 |
| IGF-1 (ug/L) | 278.4±94.0 | 251.5±87.4 | 298.9±83.5 | 0.081 | 0.950 |
| AST (IU/L) | 26.4±5.7 | 29.6±12.5 | 24.3±6.8 | 0.032 | 0.887 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 12.8±3.4 | 16.1±6.0 | 19.8±8.0 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 165.6±25.7 | 174.0±33.2 | 165.2±26.2 | 0.198 | 0.457 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 108.3±72.8 | 122.4±66.3 | 130.9±53.4 | 0.284 | 0.117 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 92.8±27.3 | 98.3±26.6 | 92.4±27.6 | 0.457 | 0.630 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 52.0±10.5 | 51.2±9.6 | 46.9±8.7 | 0.139 | 0.081 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 94.3±11.6 | 94.4±11.2 | 96.9±8.1 | 0.647 | 0.461 |
| Insulin (μU/mL) | 17.2±13.9 | 23.2±22.8 | 51.9±32.8 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 4.15±3.87 | 5.60±5.79 | 12.60±8.14 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| QUICKI | 0.33±0.04 | 0.32±0.04 | 0.28±0.02 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation.
BMI, body mass index; CPP, central precocious puberty; CA, chronological age; BA, bone age; SHBG, sex hormone binding globulin; LH, luteinizing hormone; E2, estradiol; FEI, free estradiol index; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance; QUICKI, quantitative insulin sensitivity check index.
3. The correlation between clinical, biochemical characteristics and insulin resistance parameters in total girls
Table 3.
Insulin resistance is positively correlated with BA advancement, BMI SDS, FEI, IGF-1, and triglycerides and was negatively correlated with SHBG.
HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance; QUICKI, quantitative insulin sensitivity check index; BA, bone age; CA, chronological age; SDS, standard deviation scores; BMI, body mass index; SHBG, sex hormone binding globulin; LH, luteinizing hormone; FEI, free estradiol index; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDL, lowdensity lipoprotein.
4. The change of BA advancement associated with insulin resistance
Table 4.
When insulin resistance increased, the odds for BA advancement increased. Model 1 is a multiple logistic regression adjusted for chronological age. Adjusted OR for chronological age and BMI represented in model 2.
HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance; QUICKI, quantitative insulin sensitivity check index; SE β, standard error of β coefficient; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; model 1, adjusted for chronological age (CA); model 2, adjusted for CA and body mass index (BMI).




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download