1. Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg. 2013; 23:427–36.

2. Ortiz VE, Kwo J. Obesity: physiologic changes and implications for preoperative management. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015; 15:97.

3. Jones RL, Nzekwu MM. The effects of body mass index on lung volumes. Chest. 2006; 130:827–33.

4. Pelosi P, Croci M, Ravagnan I, Tredici S, Pedoto A, Lissoni A, et al. The effects of body mass on lung volumes, respiratory mechanics, and gas exchange during general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1998; 87:654–60.

5. Beuther DA, Sutherland ER. Overweight, obesity, and incident asthma: a meta-analysis of prospective epidemiologic studies. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175:661–6.
6. Dixon AE, Holguin F, Sood A, Salome CM, Pratley RE, Beuther DA, et al. An official American Thoracic Society Workshop report: obesity and asthma. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010; 7:325–35.

7. Guerra S, Sherrill DL, Bobadilla A, Martinez FD, Barbee RA. The relation of body mass index to asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. Chest. 2002; 122:1256–63.

8. Newell MA, Bard MR, Goettler CE, Toschlog EA, Schenarts PJ, Sagraves SG, et al. Body mass index and outcomes in critically injured blunt trauma patients: weighing the impact. J Am Coll Surg. 2007; 204:1056–61.

9. Rao SL, Kunselman AR, Schuler HG, DesHarnais S. Laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation in the head-elevated position in obese patients: a randomized, controlled, equivalence trial. Anesth Analg. 2008; 107:1912–8.

10. El-Solh A, Sikka P, Bozkanat E, Jaafar W, Davies J. Morbid obesity in the medical ICU. Chest. 2001; 120:1989–97.

11. Sakr Y, Madl C, Filipescu D, Moreno R, Groeneveld J, Artigas A, et al. Obesity is associated with increased morbidity but not mortality in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2008; 34:1999–2009.

12. Frat JP, Gissot V, Ragot S, Desachy A, Runge I, Lebert C, et al. Impact of obesity in mechanically ventilated patients: a prospective study. Intensive Care Med. 2008; 34:1991–8.

13. Bamgbade OA, Rutter TW, Nafiu OO, Dorje P. Postoperative complications in obese and nonobese patients. World J Surg. 2007; 31:556–60.

14. Martino JL, Stapleton RD, Wang M, Day AG, Cahill NE, Dixon AE, et al. Extreme obesity and outcomes in critically ill patients. Chest. 2011; 140:1198–206.

15. Britton J, Pavord I, Richards K, Wisniewski A, Knox A, Lewis S, et al. Dietary magnesium, lung function, wheezing, and airway hyperreactivity in a random adult population sample. Lancet. 1994; 344:357–62.

16. Gilliland FD, Berhane KT, Li YF, Kim DH, Margolis HG. Dietary magnesium, potassium, sodium, and children’s lung function. Am J Epidemiol. 2002; 155:125–31.

17. Reinhart RA. Magnesium metabolism. A review with special reference to the relationship between intracellular content and serum levels. Arch Intern Med. 1988; 148:2415–20.

18. Shaikh MN, Malapati BR, Gokani R, Patel B, Chatriwala M. Serum magnesium and vitamin D levels as indicators of asthma severity. Pulm Med. 2016; 2016:1643717.

19. Kshirsagar K, Patil VC. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Is serum magnesium level a risk factor for its acute exacerbation? Caspian J Intern Med. 2021; 12:223–7.
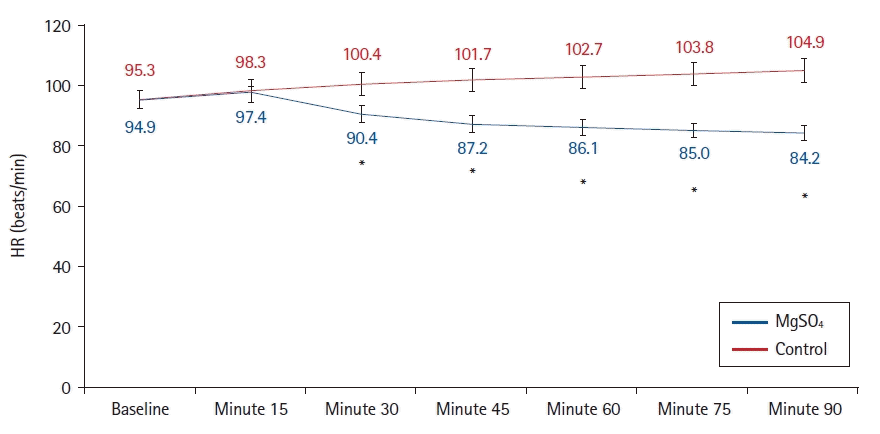
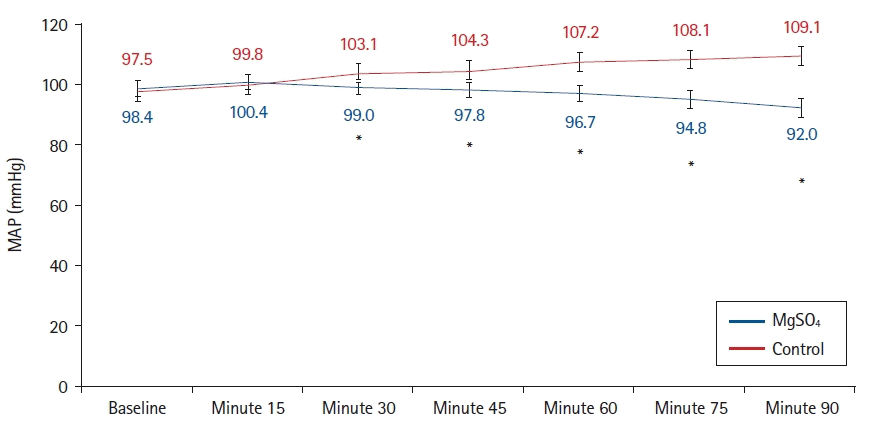
20. Ahmed A, Sayed AH, Elkholy J, Elshal S, Badwy A, Abdelhamid B, et al. Intraoperative MgSO4 infusion protects oxygenation and lung mechanics in COPD patients during general anesthesia. A randomized clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2020; 64:1460–8.

21. De Baerdemaeker L, Margarson M. Best anaesthetic drug strategy for morbidly obese patients. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2016; 29:119–28.

22. Hardman JG, Aitkenhead AR. Estimating alveolar dead space from the arterial to end-tidal CO(2) gradient: a modeling analysis. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:1846–51.

23. Ramsay MA, Savege TM, Simpson BR, Goodwin R. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone. Br Med J. 1974; 2:656–9.

24. Littleton SW. Impact of obesity on respiratory function. Respirology. 2012; 17:43–9.

25. Poglio S, De Toni-Costes F, Arnaud E, Laharrague P, Espinosa E, Casteilla L, et al. Adipose tissue as a dedicated reservoir of functional mast cell progenitors. Stem Cells. 2010; 28:2065–72.

26. Andersson LE, Baath M, Thorne A, Aspelin P, Odeberg-Wernerman S. Effect of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum on development of atelectasis during anesthesia, examined by spiral computed tomography. Anesthesiology. 2005; 102:293–9.

27. Brodsky JB. Positioning the morbidly obese patient for anesthesia. Obes Surg. 2002; 12:751–8.

28. do Amaral AF, Rodrigues-Júnior AL, Terra Filho J, Vannucchi H, Martinez JA. Effects of acute magnesium loading on pulmonary function of stable COPD patients. Med Sci Monit. 2008; 14:CR524–9.
29. Haas NA, Kemke J, Schulze-Neick I, Lange PE. Effect of increasing doses of magnesium in experimental pulmonary hypertension after acute pulmonary embolism. Intensive Care Med. 2004; 30:2102–9.

30. Fawcett WJ, Haxby EJ, Male DA. Magnesium: physiology and pharmacology. Br J Anaesth. 1999; 83:302–20.

31. Spivey WH, Skobeloff EM, Levin RM. Effect of magnesium chloride on rabbit bronchial smooth muscle. Ann Emerg Med. 1990; 19:1107–12.

32. Cairns CB, Kraft M. Magnesium attenuates the neutrophil respiratory burst in adult asthmatic patients. Acad Emerg Med. 1996; 3:1093–7.

33. Skorodin MS, Freebeck PC, Yetter B, Nelson JE, Van de Graaff WB, Walsh JM. Magnesium sulfate potentiates several cardiovascular and metabolic actions of terbutaline. Chest. 1994; 105:701–5.

34. Bodenhamer J, Bergstrom R, Brown D, Gabow P, Marx JA, Lowenstein SR. Frequently nebulized beta-agonists for asthma: effects on serum electrolytes. Ann Emerg Med. 1992; 21:1337–42.
35. Hirota K, Sato T, Hashimoto Y, Yoshioka H, Ohtomo N, Ishihara H, et al. Relaxant effect of magnesium and zinc on histamine-induced bronchoconstriction in dogs. Crit Care Med. 1999; 27:1159–63.

36. Idama TO, Lindow SW. Magnesium sulphate: a review of clinical pharmacology applied to obstetrics. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998; 105:260–8.

37. Do SH. Magnesium: a versatile drug for anesthesiologists. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013; 65:4–8.

38. Chesley LC, Tepper I. Some effects of magnesium loading upon renal excretion of magnesium and certain other electrolytes. J Clin Invest. 1958; 37:1362–72.
39. Rower JE, Liu X, Yu T, Mundorff M, Sherwin CM, Johnson MD. Clinical pharmacokinetics of magnesium sulfate in the treatment of children with severe acute asthma. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2017; 73:325–31.

40. Singhi S, Grover S, Bansal A, Chopra K. Randomised comparison of intravenous magnesium sulphate, terbutaline and aminophylline for children with acute severe asthma. Acta Paediatr. 2014; 103:1301–6.

41. Morris I, Lyttle MD, O'Sullivan R, Sargant N, Doull IJ, Powell CV. Which intravenous bronchodilators are being administered to children presenting with acute severe wheeze in the UK and Ireland? Thorax. 2015; 70:88–91.

42. Ciarallo L, Brousseau D, Reinert S. Higher-dose intravenous magnesium therapy for children with moderate to severe acute asthma. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2000; 154:979–83.

43. Herroeder S, Schönherr ME, De Hert SG, Hollmann MW. Magnesium--essentials for anesthesiologists. Anesthesiology. 2011; 114:971–93.

44. Kutlesic MS, Kutlesic RM, Mostic-Ilic T. Magnesium in obstetric anesthesia and intensive care. J Anesth. 2017; 31:127–39.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download