1. Lee SY, Lee HJ, Lim JY. Effects of leucine-rich protein supplements in older adults with sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2022; 102:104758.

2. Saad F. The relationship between testosterone deficiency and frailty in elderly men. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2010; 4:529–38.

3. Chen LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW, Chou MY, Iijima K, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020; 21:300–7.e2.

4. Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Sayer AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019; 393:2636–46. Erratum in: Lancet 2019;393:2590.

5. Chang KV, Hsu TH, Wu WT, Huang KC, Han DS. Is sarcopenia associated with depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Age Ageing. 2017; 46:738–46.

6. Pennings B, Boirie Y, Senden JM, Gijsen AP, Kuipers H, van Loon LJ. Whey protein stimulates postprandial muscle protein accretion more effectively than do casein and casein hydrolysate in older men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011; 93:997–1005.

7. Biolo G, Tipton KD, Klein S, Wolfe RR. An abundant supply of amino acids enhances the metabolic effect of exercise on muscle protein. Am J Physiol. 1997; 273(1 Pt 1):E122–9.

8. Bauer J, Biolo G, Cederholm T, Cesari M, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Morley JE, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: a position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013; 14:542–59.

9. Wright J, Baldwin C. Oral nutritional support with or without exercise in the management of malnutrition in nutritionally vulnerable older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2018; 37(6 Pt A):1879–91.

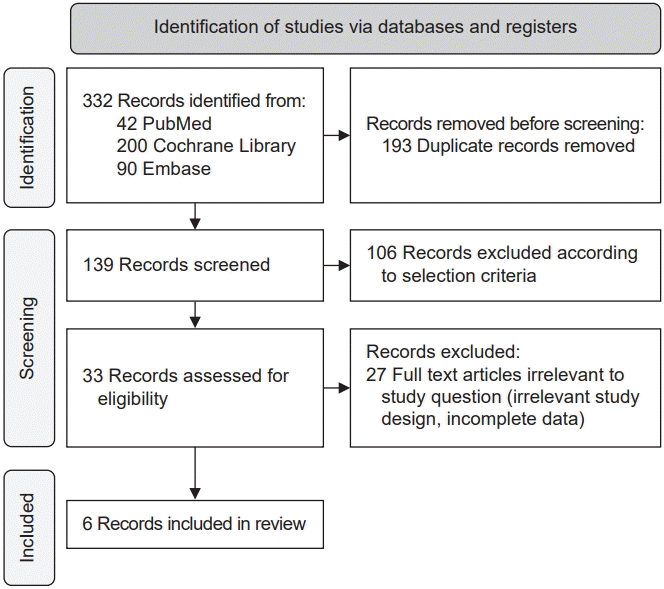
10. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151:264–9. W64.

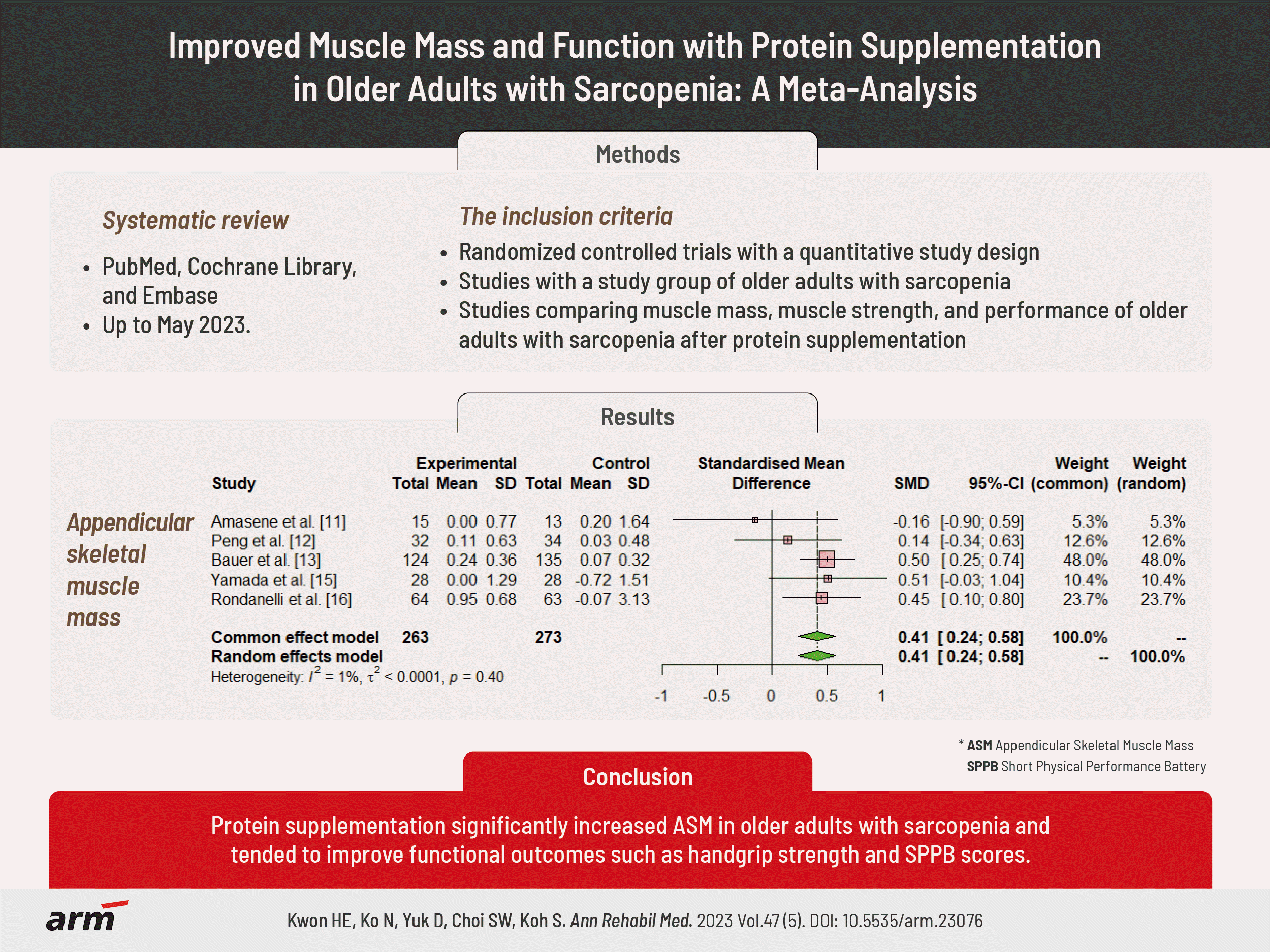
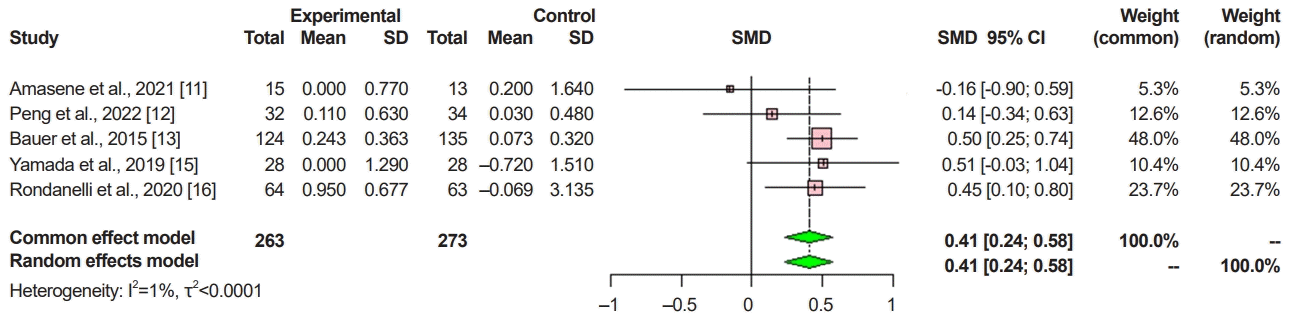
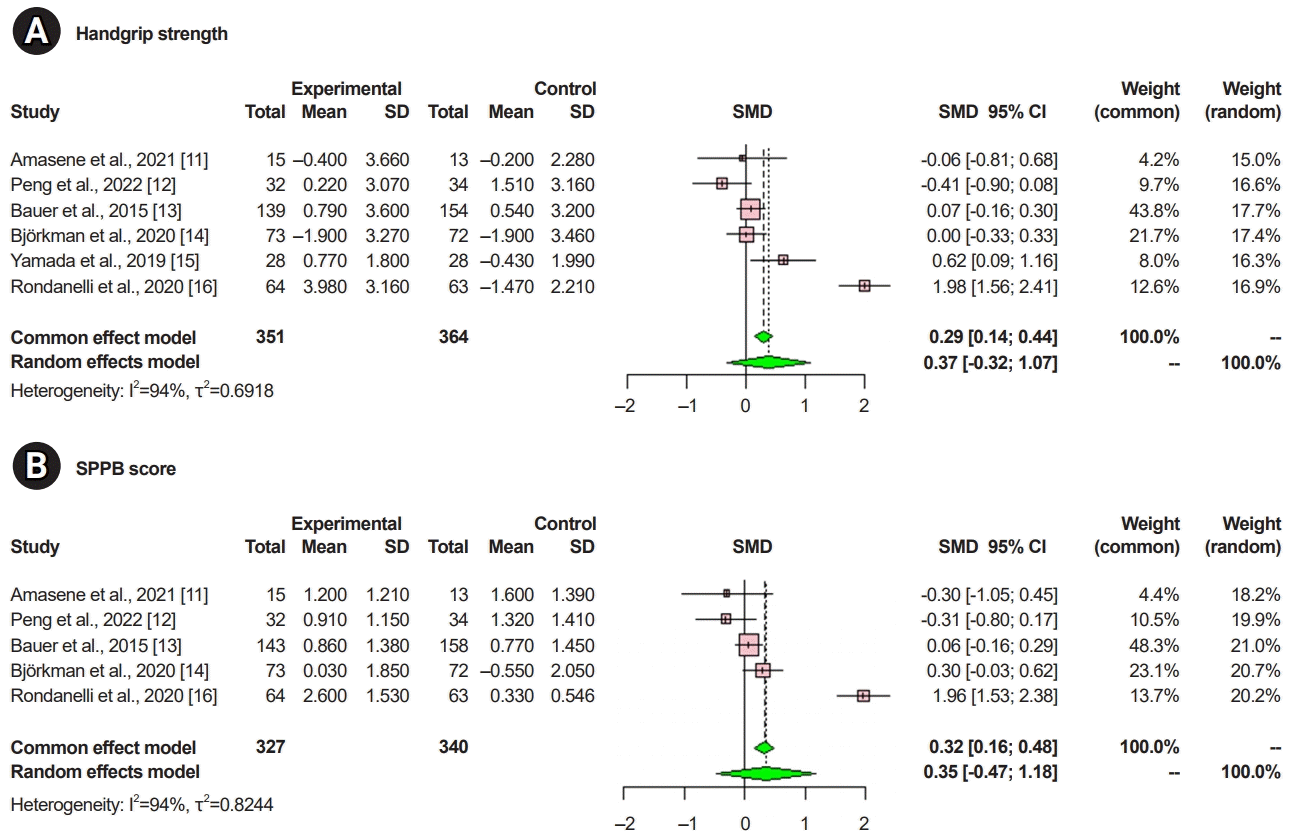
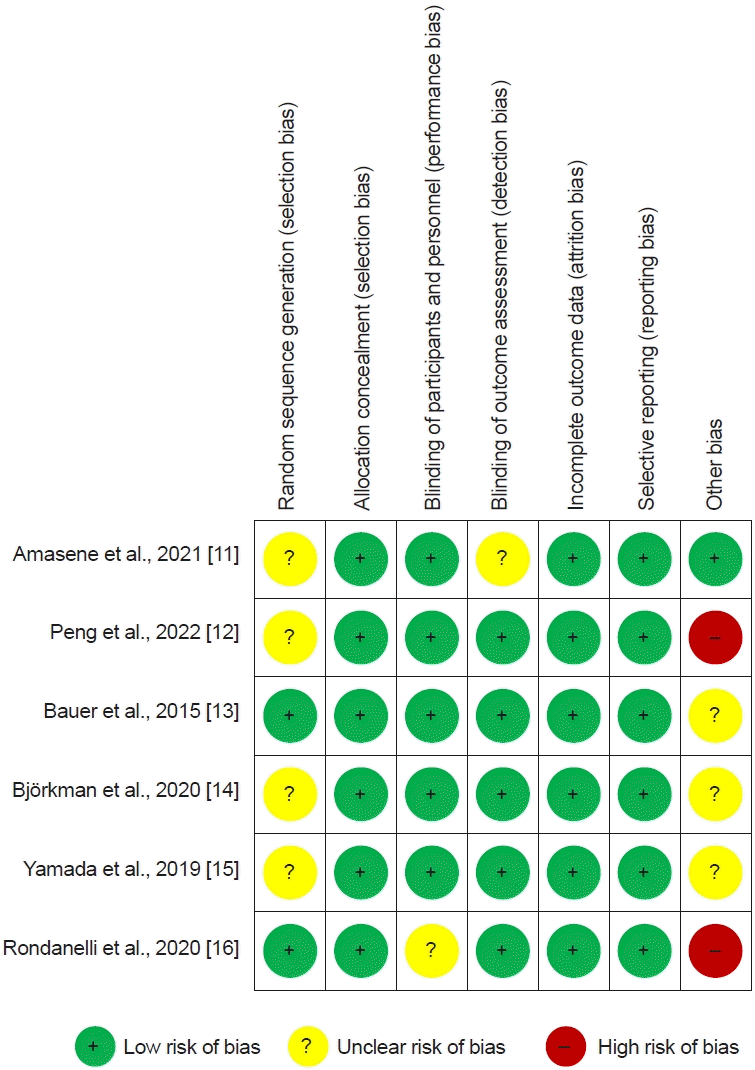
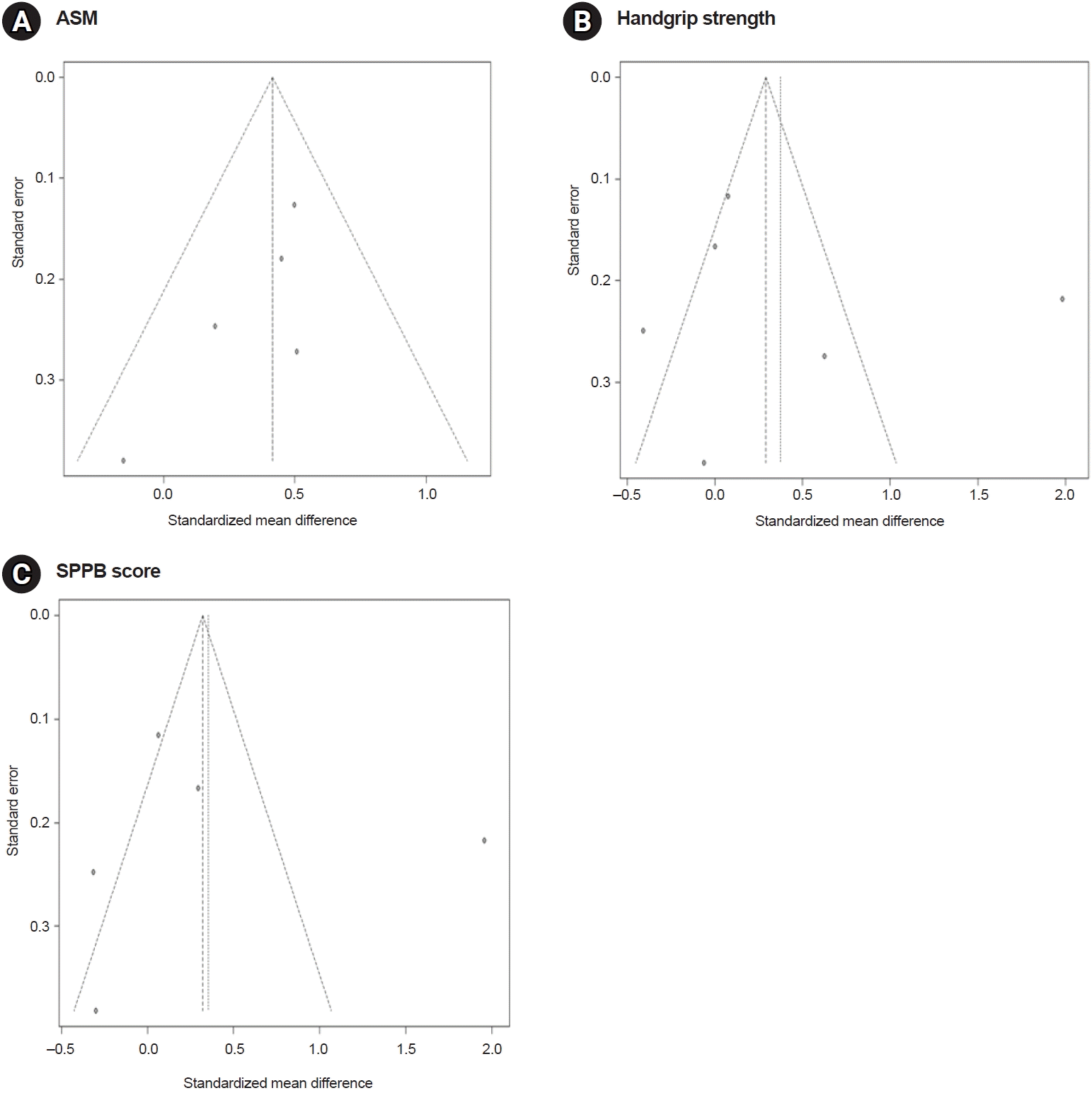
11. Amasene M, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Echeverria I, Sanz B, Alonso C, Tobalina I, et al. Effects of resistance training intervention along with leucine-enriched whey protein supplementation on sarcopenia and frailty in post-hospitalized older adults: preliminary findings of a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Med. 2021; 11:97.

12. Peng LN, Yu PC, Hsu CC, Tseng SH, Lee WJ, Lin MH, et al. Sarcojoint®, the branched-chain amino acid-based supplement, plus resistance exercise improved muscle mass in adults aged 50 years and older: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2022; 157:111644.
13. Bauer JM, Verlaan S, Bautmans I, Brandt K, Donini LM, Maggio M, et al. Effects of a vitamin D and leucine-enriched whey protein nutritional supplement on measures of sarcopenia in older adults, the PROVIDE study: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015; 16:740–7.

14. Björkman MP, Suominen MH, Kautiainen H, Jyväkorpi SK, Finne-Soveri HU, Strandberg TE, et al. Effect of protein supplementation on physical performance in older people with sarcopenia-a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020; 21:226–32.e1.

15. Yamada M, Kimura Y, Ishiyama D, Nishio N, Otobe Y, Tanaka T, et al. Synergistic effect of bodyweight resistance exercise and protein supplementation on skeletal muscle in sarcopenic or dynapenic older adults. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2019; 19:429–37.

16. Rondanelli M, Cereda E, Klersy C, Faliva MA, Peroni G, Nichetti M, et al. Improving rehabilitation in sarcopenia: a randomized-controlled trial utilizing a muscle-targeted food for special medical purposes. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020; 11:1535–47.

17. Rizzoli R, Reginster JY, Arnal JF, Bautmans I, Beaudart C, Bischoff-Ferrari H, et al. Quality of life in sarcopenia and frailty. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013; 93:101–20.

18. Malafarina V, Uriz-Otano F, Iniesta R, Gil-Guerrero L. Sarcopenia in the elderly: diagnosis, physiopathology and treatment. Maturitas. 2012; 71:109–14.

19. Chang MC, Choo YJ. Effects of whey protein, leucine, and vitamin d supplementation in patients with sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15:521.

20. Tieland M, van de Rest O, Dirks ML, van der Zwaluw N, Mensink M, van Loon LJ, et al. Protein supplementation improves physical performance in frail elderly people: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012; 13:720–6.

21. Kim KM, Jang HC, Lim S. Differences among skeletal muscle mass indices derived from height-, weight-, and body mass index-adjusted models in assessing sarcopenia. Korean J Intern Med. 2016; 31:643–50.

22. Cawthon PM, Peters KW, Shardell MD, McLean RR, Dam TT, Kenny AM, et al. Cutpoints for low appendicular lean mass that identify older adults with clinically significant weakness. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014; 69:567–75.

23. Liao CD, Chen HC, Huang SW, Liou TH. The role of muscle mass gain following protein supplementation plus exercise therapy in older adults with sarcopenia and frailty risks: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized trials. Nutrients. 2019; 11:1713.

24. Verstraeten LMG, de Haan NJ, Verbeet E, van Wijngaarden JP, Meskers CGM, Maier AB. Handgrip strength rather than chair stand test should be used to diagnose sarcopenia in geriatric rehabilitation inpatients: REStORing health of acutely unwell adulTs (RESORT). Age Ageing. 2022; 51:afac242.

25. Ling CH, Taekema D, de Craen AJ, Gussekloo J, Westendorp RG, Maier AB. Handgrip strength and mortality in the oldest old population: the Leiden 85-plus study. CMAJ. 2010; 182:429–35.

26. Yeung SSY, Reijnierse EM, Pham VK, Trappenburg MC, Lim WK, Meskers CGM, et al. Sarcopenia and its association with falls and fractures in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019; 10:485–500.

27. Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, Glynn RJ, Berkman LF, Blazer DG, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994; 49:M85–94.

28. Beaudart C, Zaaria M, Pasleau F, Reginster JY, Bruyère O. Health outcomes of sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0169548.

29. Dangin M, Guillet C, Garcia-Rodenas C, Gachon P, Bouteloup-Demange C, Reiffers-Magnani K, et al. The rate of protein digestion affects protein gain differently during aging in humans. J Physiol. 2003; 549(Pt 2):635–44.

30. Luiking YC, Deutz NE, Memelink RG, Verlaan S, Wolfe RR. Postprandial muscle protein synthesis is higher after a high whey protein, leucine-enriched supplement than after a dairy-like product in healthy older people: a randomized controlled trial. Nutr J. 2014; 13:9.

31. Chang KV, Wu WT, Huang KC, Han DS. Effectiveness of early versus delayed exercise and nutritional intervention on segmental body composition of sarcopenic elders - a randomized controlled trial. Clin Nutr. 2021; 40:1052–9.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download