Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Conclusion
Notes
Fund
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (NRF-2020M3E5D2A01084578).
Ethics Statement
This study waived approval of the Institutional Review Board. This article does not contain any information that may identify the patient.
Author Contributions
Concept and design: MK, SCJ, and SCK. Analysis and interpretation: MK, SCJ, and SCK. Data collection: MK, SCJ, SCK, BJK, WKS, and BK. Writing the article: MK and SCJ. Critical revision of the article: MK, SCJ, BJK, WKS, and BK. Final approval of the article: MK, SCJ, BJK, WKS, and BK. Statistical analysis: MK and SCJ. Obtained funding: SCJ. Overall responsibility: SCJ.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1.
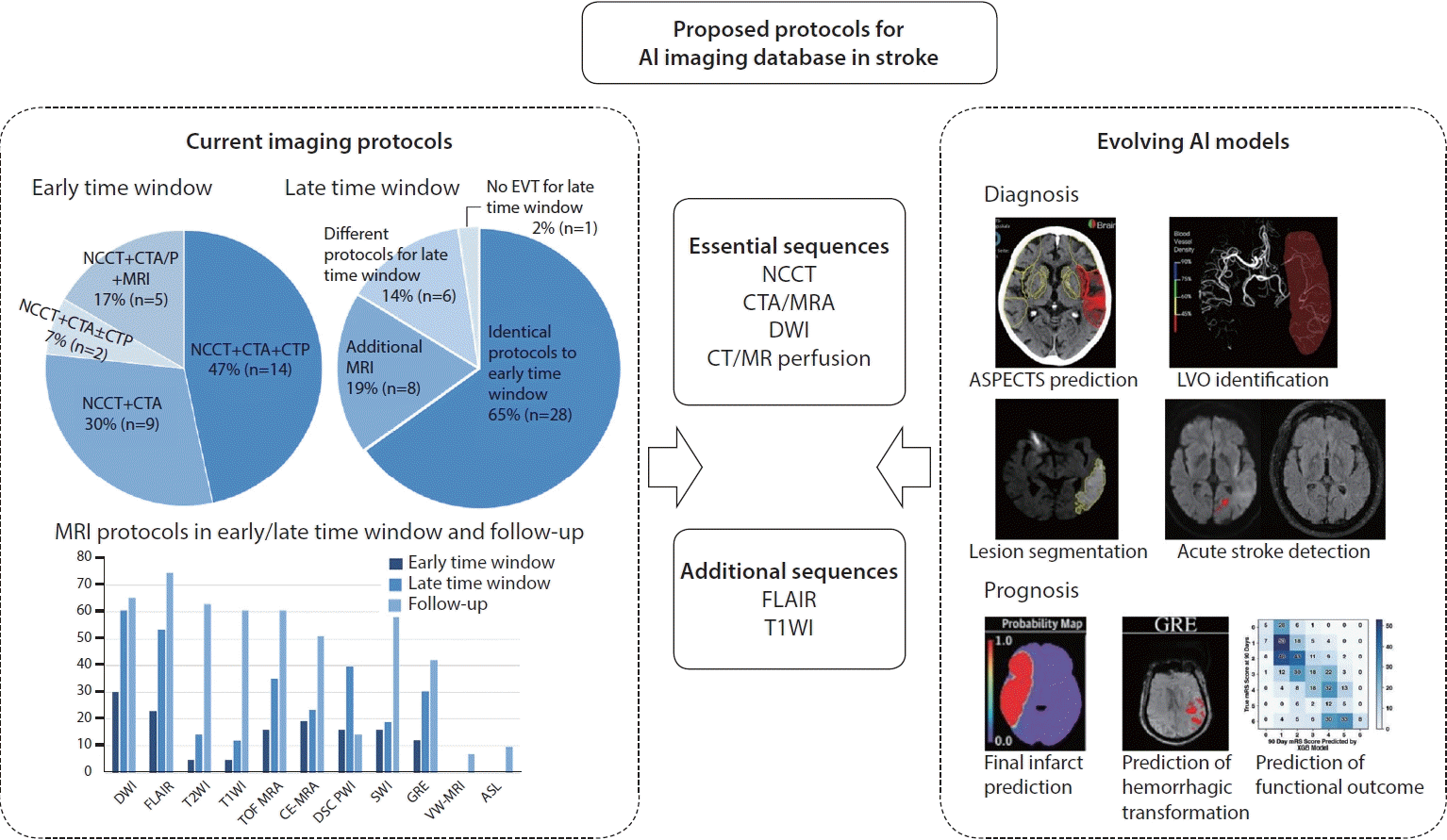
Table 1.
| Applications | Required imaging sequences | N (center) | Algorithm performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | ||||
| Determination of ASPECTS (e-ASPECTS) [7] | NCCT (GT: DWI) | 34 (multi) | Sensitivity 46.5%, specificity 94.2% | |
| Determination of ASPECTS (e-ASPECTS) [9] | NCCT (GT: baseline/follow-up CT) | 132 (multi) | Sensitivity 44.0%, specificity 93.0% | |
| Determination of ASPECTS (e-ASPECTS) [10] | NCCT (GT: follow-up CT) | 119 (single) | Sensitivity 83.0%, specificity 57.0% | |
| Identification of stroke within 4.5 hours [11] | DSC perfusion, DWI/ADC, FLAIR | 105 (single) | Sensitivity 89.3%, specificity 81.8%, AUC 0.68 | |
| Identification of stroke within 4.5 hours [12] | DWI, FLAIR | 355 (single) | Sensitivity 72.7–75.8%, specificity 82.6% | |
| Identification of large vessel occlusion (Rapid) [13] | NCCT, CTA, CTP (GT: CTA) | 477 (single) | Sensitivity 0.92–0.94, specificity 0.76–0.81 | |
| Identification of large vessel occlusion [14] | CTA (GT: CTA) | 875 (multi) | Sensitivity 90.1%, specificity 82.5% | |
| Automatic lesion segmentation of acute infarct [15] | DWI (GT: DWI) | 741 (multi) | Dice coefficient 0.67 | |
| Automatic lesion segmentation of acute infarct [16] | DWI (GT: DWI) | 429 (single) | Dice coefficient 0.85–0.86 | |
| Automatic lesion segmentation of hemorrhage [17] | NCCT (GT: CT) | 58 (single) | Concordance correlation coefficient 0.95–0.99 | |
| Automatic lesion segmentation (subacute stage) [18] | FLAIR (GT: FLAIR) | 37 (single) | Dice coefficient 0.65 | |
| Automatic lesion segmentation (chronic stage) [19] | T1WI (GT: T1WI) | 60 (single) | Dice coefficient 0.696±0.16, r=0.961 | |
| Prognosis | ||||
| Prediction of final infarct (correlation, volume) [20] | NCCT, CTP | 479 (single) | Spearman correlation coefficient 0.43–0.52 | |
| Prediction of final infarct (correlation, volume) [21] | NCCT, CTA source image, CTP | 105 (single) | Spearman correlation coefficient 0.78–0.85 | |
| Prediction of final infarct (overlap) [22] | DWI, FLAIR, DSC perfusion | 195 (multi) | AUC 0.87–0.92 | |
| Prediction of final infarct (overlap) [23] | DWI, FLAIR, DSC perfusion | 222 (multi) | AUC 0.72–0.88 | |
| Prediction of final infarct (overlap) [24] | DWI, FLAIR, DSC perfusion | 182 (multi) | AUC 0.92 | |
| Prediction of hemorrhagic transformation [25] | DSC perfusion, DWI, GRE | 165 (single) | AUC 0.59–0.84 | |
| Prediction of hemorrhagic transformation [26] | NCCT (baseline and follow up) | 194 (single) | AUC 0.42–0.79 | |
| Prediction of hemorrhagic transformation [27] | NCCT | 116 (single) | AUC 0.74 | |
| Prediction of functional outcome (mRS) [8] | NCCT, CTA | 1,383 (multi) | AUC 0.77–0.91 | |
| Prediction of functional outcome (mRS) [28] | NCCT, CTA, CTP | 512 (single) | AUC 0.67–0.88 | |
| Prediction of functional outcome (mRS) [29] | NCCT | 204 (multi) | AUC 0.54–0.75 | |
| Prediction of functional outcome [30] | T1WI, DWI | 35 (single) | Prediction accuracy 66.1–91.3% | |
| Prediction of functional outcome [31] | T1WI | 50 (single) | Correlation 0.65–0.83 | |
AI, artificial intelligence; ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score; NCCT, noncontrast CT; GT, ground truth; DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging; DSC, dynamic susceptibility contrast; ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; AUC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; CTA, CT angiography; CTP, CT perfusion; T1WI, T1-weighted imaging; GRE, gradient echo.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download