1. Memtsoudis SG, Cozowicz C, Bekeris J, Bekere D, Liu J, Soffin EM, et al. Peripheral nerve block anesthesia/analgesia for patients undergoing primary hip and knee arthroplasty: recommendations from the International Consensus on Anesthesia-Related Outcomes after Surgery (ICAROS) group based on a systematic review and meta-analysis of current literature. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021; 46:971–85.
2. Anger M, Valovska T, Beloeil H, Lirk P, Joshi GP, Van de Velde M, et al. PROSPECT guideline for total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review and procedure-specific postoperative pain management recommendations. Anaesthesia. 2021; 76:1082–97.
3. Bugada D, Bellini V, Lorini LF, Mariano ER. Update on selective regional analgesia for hip surgery patients. Anesthesiol Clin. 2018; 36:403–15.
4. Birnbaum K, Prescher A, Hessler S, Heller KD. The sensory innervation of the hip joint--an anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 1997; 19:371–5.
5. Carella M, Beck F, Piette N, Denys S, Kurth W, Lecoq JP, et al. Effect of suprainguinal fascia iliaca compartment block on postoperative opioid consumption and functional recovery in posterolateral-approached total hip arthroplasty: a single-blind randomized controlled trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2022. Advance Access published on Jun 15, 2022. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2021-103427.
6. Desmet M, Vermeylen K, Van Herreweghe I, Carlier L, Soetens F, Lambrecht S, et al. A longitudinal supra-inguinal fascia iliaca compartment block reduces morphine consumption after total hip arthroplasty. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2017; 42:327–33.
7. Tulgar S, Senturk O. Ultrasound guided Erector Spinae Plane block at L-4 transverse process level provides effective postoperative analgesia for total hip arthroplasty. J Clin Anesth. 2018; 44:68.
8. Bugada D, Zarcone AG, Manini M, Lorini LF. Continuous Erector Spinae Block at lumbar level (L4) for prolonged postoperative analgesia after hip surgery. J Clin Anesth. 2019; 52:24–5.
9. Xu L, Leng JC, Elsharkawy H, Hunter OO, Harrison TK, Vokach-Brodsky L, et al. Replacement of fascia iliaca catheters with continuous erector spinae plane blocks within a clinical pathway facilitates early ambulation after total hip arthroplasty. Pain Med. 2020; 21:2423–9.
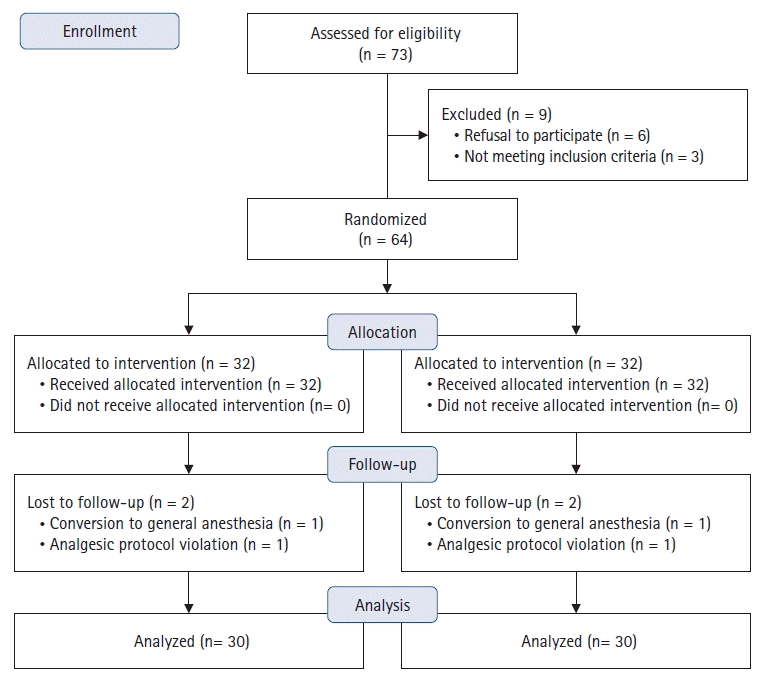
10. Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D; CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ. 2010; 340:c332.
11. Neal JM. Assessment of lower extremity nerve block: reprise of the Four P's acronym. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2002; 27:618–20.
12. Schug SA, Lavand'homme P, Barke A, Korwisi B, Rief W, Treede RD; IASP Taskforce for the Classification of Chronic Pain. The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: chronic postsurgical or posttraumatic pain. Pain. 2019; 160:45–52.
13. Tulgar S, Kose HC, Selvi O, Senturk O, Thomas DT, Ermis MN, et al. Comparison of ultrasound-guided lumbar erector spinae plane block and transmuscular quadratus lumborum block for postoperative analgesia in hip and proximal femur surgery: a prospective randomized feasibility study. Anesth Essays Res. 2018; 12:825–31.
14. Wainwright TW, Memtsoudis SG, Kehlet H. Fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty...how fast? Br J Anaesth. 2021; 126:348–9.
15. Memtsoudis SG, Danninger T, Rasul R, Poeran J, Gerner P, Stundner O, et al. Inpatient falls after total knee arthroplasty: the role of anesthesia type and peripheral nerve blocks. Anesthesiology. 2014; 120:551–63.
16. Bendtsen TF, Pedersen EM, Moriggl B, Hebbard P, Ivanusic J, Børglum J, et al. Suprainguinal fascia iliaca block: does it block the obturator nerve? Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021; 46:832.
17. Bendtsen TF, Pedersen EM, Moriggl B, Hebbard P, Ivanusic J, Børglum J, et al. Anatomical considerations for obturator nerve block with fascia iliaca compartment block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021; 46:806–12.
18. Weller RS. Does fascia iliaca block result in obturator block? Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009; 34:524.
19. Bonvicini D, Boscolo-Berto R, De Cassai A, Negrello M, Macchi V, Tiberio I, et al. Anatomical basis of erector spinae plane block: a dissection and histotopographic pilot study. J Anesth. 2021; 35:102–11.
20. Chin KJ, Lirk P, Hollmann MW, Schwarz SK. Mechanisms of action of fascial plane blocks: a narrative review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021; 46:618–28.
21. Tulgar S, Ahiskalioglu A, Aydin ME, Jadon A, Forero M, Gürkan Y. Lumbar erector spinae plane block: a miracle or self-persuasion? Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021; 46:638–9.
22. Elsharkawy H, Bajracharya GR, El-Boghdadly K, Drake RL, Mariano ER. Comparing two posterior quadratus lumborum block approaches with low thoracic erector spinae plane block: an anatomic study. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2019. Advance Access published on Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2018-100147.
23. Ivanusic J, Konishi Y, Barrington MJ. A cadaveric study investigating the mechanism of action of erector spinae blockade. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018; 43:567–71.
24. Costache I, Pawa A, Abdallah FW. Paravertebral by proxy - time to redefine the paravertebral block. Anaesthesia. 2018; 73:1185–8.
25. De Cassai A, Bonanno C, Padrini R, Geraldini F, Boscolo A, Navalesi P, et al. Pharmacokinetics of lidocaine after bilateral ESP block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021; 46:86–9.
26. Challapalli V, Tremont-Lukats IW, McNicol ED, Lau J, Carr DB. Systemic administration of local anesthetic agents to relieve neuropathic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 2019.
27. Haller Y, Gantenbein AR, Willimann P, Spahn DR, Maurer K. Systemic ropivacaine diminishes pain sensitization processes: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover study in healthy volunteers. Pain Ther. 2014; 3:45–58.
28. Panzenbeck P, von Keudell A, Joshi GP, Xu CX, Vlassakov K, Schreiber KL, et al. Procedure-specific acute pain trajectory after elective total hip arthroplasty: systematic review and data synthesis. Br J Anaesth. 2021; 127:110–32.
29. Kukreja P, MacBeth L, Sturdivant A, Morgan CJ, Ghanem E, Kalagara H, et al. Anterior quadratus lumborum block analgesia for total hip arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled study. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2019. Advance Access published on Oct 25, 2019. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2019-100804.
30. Polania Gutierrez JJ, Ben-David B, Rest C, Grajales MT, Khetarpal SK. Quadratus lumborum block type 3 versus lumbar plexus block in hip replacement surgery: a randomized, prospective, non-inferiority study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021; 46:111–7.
31. Aliste J, Layera S, Bravo D, Jara Á, Muñoz G, Barrientos C, et al. Randomized comparison between pericapsular nerve group (PENG) block and suprainguinal fascia iliaca block for total hip arthroplasty. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021; 46:874–8.
32. Pascarella G, Costa F, Del Buono R, Pulitanò R, Strumia A, Piliego C, et al. Impact of the pericapsular nerve group (PENG) block on postoperative analgesia and functional recovery following total hip arthroplasty: a randomised, observer-masked, controlled trial. Anaesthesia. 2021; 76:1492–8.
33. Nikolajsen L, Brandsborg B, Lucht U, Jensen TS, Kehlet H. Chronic pain following total hip arthroplasty: a nationwide questionnaire study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006; 50:495–500.
34. Grosu I, de Kock M. New concepts in acute pain management: strategies to prevent chronic postsurgical pain, opioid-induced hyperalgesia, and outcome measures. Anesthesiol Clin. 2011; 29:311–27.
35. Fletcher D, Stamer UM, Pogatzki-Zahn E, Zaslansky R, Tanase NV, Perruchoud C, et al. Chronic postsurgical pain in Europe: An observational study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2015; 32:725–34.
36. Zhang J, He Y, Wang S, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Gao Y, et al. The erector spinae plane block causes only cutaneous sensory loss on ipsilateral posterior thorax: a prospective observational volunteer study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020; 20:88.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download