INTRODUCTION
I. EARLY NEURODEVELOPMENTAL ASSESSMENT PLAN
Fig. 1.
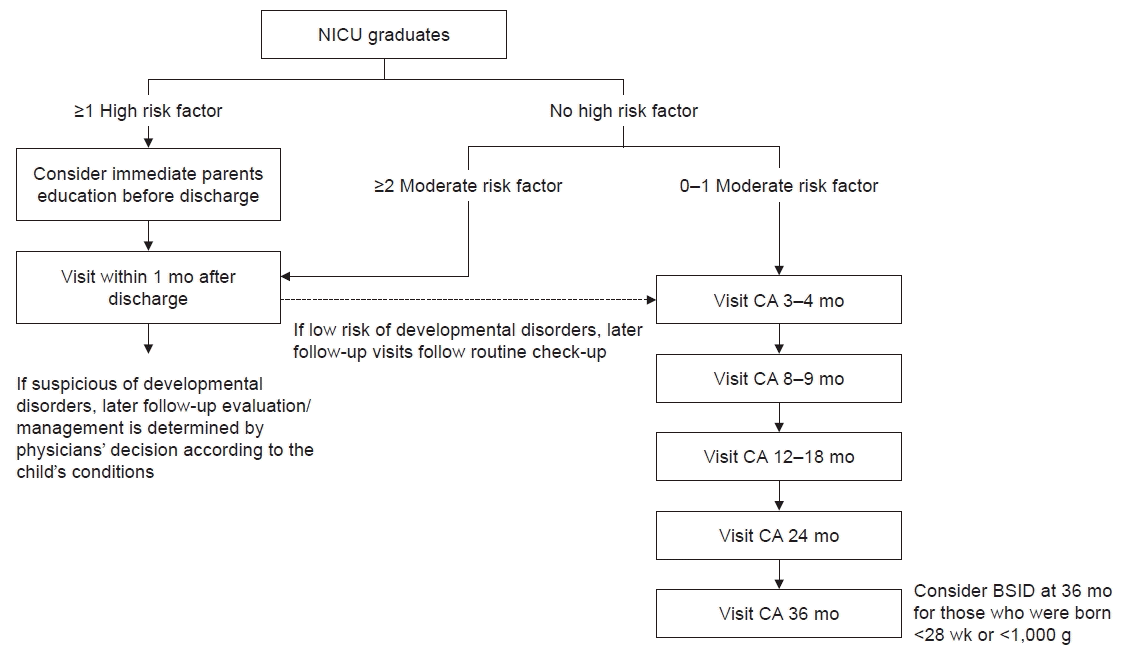
Table 1.
Table 2.
| Assessment tool | Age range | Test type | Components tested | Diagnostic Criteria | Time to administer (min) | Availability of Korean version & education | Equipment/cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developmental delay screening | |||||||
| DDST-II | 0–6 yr | Criterion | Personal-social, fine motor-adaptive, language, gross motor | <Item interpretation> | 10–30 | Korean ver.: available | Manual: ₩ 10,000 |
| Caution: items that can be completed by 75%–90% of children but are failed | Education: none | Total equipment: ₩ 130,000 | |||||
| Delay: items that can be completed by 90% of children but are failed | |||||||
| <Overall interpretation> | |||||||
| - Abnormal: in each area of development, more than 2 delays | |||||||
| -Caution: 1 delay and/or 2 or more caution | |||||||
| -Normal: no more than one caution | |||||||
| K-DST | 4–71 mo | Norm | <18 mo: gross motor, fine motor, cognition, language, social skills | Cutoff points at each domain, age | 5–10 | Korean ver.: available | Free (provided by Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) |
| (3,010 children, Korea, 2010) | ≥18 mo: same as above & self-help | -Recommendation for further evaluation: <-2 SD | Education: National Health Insurance Corporation | ||||
| Online education | |||||||
| -Need for follow-up: -1 SD to -2 SD | |||||||
| -Peer level: -1 SD to +1 SD | |||||||
| -High level: >+1 SD | |||||||
| K-ASQ | 4–60 mo | Criterion | Communication, fine motor, gross motor, problem solving, personal-social | -Further assessment needed: at least one score below cutoff | 10 | Korean ver.: available | |
| -Provide learning activities & monitor: at least one score adjacent to cutoff | Education: none | ||||||
| -Development is on track: all scores from each domain are above cutoff | |||||||
| Developmental delay diagnosis (discriminative) | |||||||
| BSID-IIIa) | 1–42 mo | Norm | Gross motor, fine motor, cognitive, communication, social/emotional, adaptive | Developmental delay: | 30–90 | Korean ver.: available | 1 set: ₩ 1,380,000 |
| (1,700 children from USA, 2000) | <25-percentile or below 2 SD | Education: DVD, webinars, and workshops | |||||
| Motor function evaluation | |||||||
| GMs | Preterm–5 mo | Criterion | Visual inspection of spontaneous movement | Preterm–6 wk: writhing movement | 5–20 | Korean ver.: none | Free |
| -Normal | Education: 4–5 day of authorized training course from GMs trust, providing certificates for each course (Basic, Advanced) | ||||||
| -Abnormal (poor repertoire, cramped synchronized or chaotic) | |||||||
| 9–20 wk: fidgety period | |||||||
| -Present | |||||||
| -Abnormal | |||||||
| -Absent | |||||||
| TIMP | 34 wk | Norm | Gross motor: 42 items of postural and selective control of movement | Raw score | 20–40 | Korean ver.: none | 25 test forms: $68 |
| (PMA)–4 mo | (990 infants, at risk of poor neurological outcome, USA, 2006) | - 13 Observed items for | Percentile rank (<5%, 5%–15%, 15%–25%, 25%–50%, 50%–75%, 75%–95%, >95 percentile) | Manual: $38 | |||
| (17 wk post-term) | spontaneous movement: | Age standard: | Workshops, or e-Learning Course: thetimp.com | Basic kit: $189 (including ball, cloth, rattle, etc.) | |||
| yes-no; 1-0 scores | -Average | ||||||
| - 29 Elicited items in supported sitting, supine, prone, side lying, supported standing: | -Below average: -1 SD to -2 SD | ||||||
| 0-3, 0-4, 0-5, 0-6 scores | -Far below average: <-2 SD | ||||||
| MAI | 0–12 mo | Criterion | Gross motor, fine motor, muscle tone, primitive reflex, automatic reactions, volitional movements | Cutoff of total scores (not validated) | 30–90 | Korean ver.: none | Standardized equipment is necessary (including 2 chairs, bell, rattle, red ball, etc.) |
| (m/c 4 mo) | Developmental delay or abnormal | Manual: free | |||||
| : suspect 8–13 | Training recommended 2-day seminar; currently not available | ||||||
| : high risk >13 | |||||||
| Total 65 items | : later neurological abnormality >10 | ||||||
| -Muscle tone: 1–6-points | : most probably normal <4 | ||||||
| -Others: 1–4 points | |||||||
| -High risk +1 points for each item | |||||||
| AIMS | 0–18 mo | Norm | Gross motor (no. of items) | Among all observed voluntary movements, the highest and lowest development stages are scored as window score | 20–25 | Korean ver.: none | 50sheets : $48.95 |
| (2,200 infants, Canada, 1990–1992) | Prone (21), supine (9), | Previous items created (below window score) are all checked as +1 | Observation for each posture (without cue): ≥5 min recommended | Guideline book: $80 | |||
| sitting (12), standing (16) | Age-adjusted subscale score (sum) | ||||||
| : total 58 items | Developmental delay or abnormal: | ||||||
| Items observed as voluntary movements are identified among above 4 posture-specific items | -At CA 4 mo: <10th percentile | ||||||
| -At CA 8 mo: <5th percentile | |||||||
| HINEb) | 2–24 mo | Criterion | Scorable 5 domains: | Each item 0–3 points | 10–15 | Korean ver.: none | Scoring sheets (on-line free) |
| -Cranial nerve function | Total score: 0–78 | Guideline book | |||||
| -Posture | : $100 | ||||||
| -Movements | : optimal | Workshops, teaching videos (online); currently not available anymore | https://bpna.org.uk/userfiles/HINE%20proforma_07_07_17.pdf | ||||
| -Muscle tone | -At 3 mo: >67 | ||||||
| -Reflexes and protective reactions | -At 6 mo: >70 | ||||||
| : risk of cerebral palsy | |||||||
| Non-scorable domains: | -At 3 mo: ≤56 | ||||||
| -Motor milestones | -At 12 mo: ≤65 | ||||||
| -Behavior | <40: severe CP risk (non-ambulatory): | ||||||
| -More predictive with general movement assessment together | |||||||
| - Evaluation of right-left discrepancy is possible | |||||||
| PDMS-II | 0–6 yr | Norm | A total of 6 subsets | Raw scores for each subtest | 45–60 (20–30 if only for motor-related subtest) | Korean ver.: available (for research-use only) | Kit: ~$550 |
| (using CA until 2 yr) | (2,003 infants, USA & Canada, 1997–1998) | A. Gross motor | Sum scores converted to standard score, %rank, age-equivalent | Test kit provides most of all equipment | |||
| -Reflex: 2 wk–11 mo | Standard score sum | Manual: $100 | Online scoring & report system: available | ||||
| -Stationary: body control | TMQ (total motor quotient) | ||||||
| -Locomotion: transfer | -GMQ (gross motor quotient) | ||||||
| (crawling, walking, | -FMQ (fine motor quotient) | ||||||
| running, hopping, jumping) | |||||||
| -Object manipulation: 12 mo~ | <-1 SD : below average, caution | ||||||
| : catch, throw | <-2 SD: suspicious of developmental delay | ||||||
| B. Fine motor | |||||||
| -Grasping: hand function | |||||||
| : hold, pincer grasp, buttoning/unbuttoning, etc. | |||||||
| -Visual-motor integration: | |||||||
| complex eye-hand coordination | |||||||
| NSMDA | 1 mo–6 yr | Criterion | 6 Subscales (gross motor, fine motor, neurological, primitive reflexes, postural reactions, motor response to sensory input); abnormal, suspicious, normal | Functional score | 20–45 | Korean ver.: none | Specific toys required but easily accessible |
| 6–8: normal motor function | Comprehensive manual: £35 | ||||||
| 9–11: minimal motor problem | |||||||
| 12–14: mild motor problem | |||||||
| 15–19 moderate motor problem | |||||||
| 20–25 severe motor problem | |||||||
| >25 profound disability | |||||||
| Language function evaluation (Korean) | |||||||
| SELSI | 4–35 mo | Norm | 56 Questions for receptive and expressive language, respectively | Raw scores, equivalent age, percentile for semantics, phonology, syntax, and pragmatics | ₩ 123,300 (including all equipment and manual) | ||
| <-1 SD: caution | |||||||
| <-2 SD: advised for further evaluation about language delay | |||||||
| PRES | 2–6 yr (preschool) | Norm | 45 Questions for receptive and expressive language, respectively | Raw scores, equivalent age, percentile for semantics, phonology/syntax, and pragmatics | ₩ 300,000 (including all equipment and manual) | ||
| P-FA | Preschool, elementary & middle school | Norm | Fluency: word picture, repetition, sentence picture, reading, story picture, speaking picture (according to age level) | Raw scores, score distribution and percentile | ₩ 361,000 (including all equipment and manual) | ||
| Communication skills (not in preschool evaluation): any burden/difficulty in speaking or stuttering | |||||||
| K-M-B CDI | 8–17 mo (infant) | Norm | Parent-report form to evaluate communication skills | Level I (infant): words and gestures; short form – 89-word vocabulary checklist | ₩ 90,000 (including all equipment and manual) | ||
| 18–30 mo (toddler) | Level IIA/B (toddler): words and sentences; 100-word productive vocabulary checklist, questions about combining words | ||||||
| PPVT-R | 2 yr–8 yr 11 mo | Norm | Language comprehension, | The first question is determined by age, | ₩ 1,400,000 (including all equipment and manual) | ||
| receptive vocabulary skills | If 8 correct answers consecutively, this point is set as the baseline. (all questions before the point are scored as correct) | ||||||
| : Total 178 vocabulary | If 6 out of 8 consecutive questions are incorrect, the last incorrect questions is the upper limit; | ||||||
| Raw score with only correct answers to be calculated as percentile, equivalent age | |||||||
| REVT | 2 yr 6 mo–16 yr | Norm | Receptive/expressive vocabulary skills (initially developed for Korean vocabulary) | Scoring is same with PPVT-R | ₩ 380,000 (including all equipment and manual) | ||
| : 185 Questions (using pictures) for receptive and expressive domain, respectively | <-1 SD: below average, caution | ||||||
| <-2 SD: advised for further evaluation for vocabulary development | |||||||
| PCAT | 2–12 yr or preschool | Criterion (% accuracy) | Ability to modulate consonant pronunciation (using pictures) | For speech therapy for articulation, | |||
| : 30 Words including 43 phonemes | : consider <-1 SD, demand <-2 SD | ||||||
| Cognitive function evaluation | |||||||
| K-WPPSI-IV | 2yr6mo - 3yr11mo & | Norm | FSIQ | Raw scores from the subset | 30–60 | ||
| 4yr - 7yr7mo | Primary index scale (comprehensive cognitive functioning): composite scores of verbal comprehension index, visual spatial index, working memory index and fluid reasoning index, processing speed index for older age band | Age-corrected standard scores of scaled and composite scores (percentile) for FSIQ and each subset scores | |||||
| Ancillary index scale: verbal acquisition index, nonverbal index, general ability index and cognitive proficiency index for older age band | |||||||
| Sensory-perception function evaluation | |||||||
| VMI-6 | 2–90 yr | Norm (1,882 Korean, 2–90 yr) | Visual-motor integration, visual perception, motor coordination (spontaneous scribbling task, imitated scribbling task, imitation task) | Raw scores: success until 3 consecutive fails | 10–15 | Korean ver.: available | With manual |
| Equivalent age, standard score, percentile for screening visual motor coordination function | Education: none | : ₩ 110,000 | |||||
| Without manual | |||||||
| : ₩ 90,000 | |||||||
| Neonatal Visual Assessment | GA 35 wk–1 yr | Norm (110 healthy full-term neonate at 72 h, Italy) | 9 Items of spontaneous ocular motility, ocular movements with target, fixation, tracking (horizontal, vertical, arc), reaction to a colored contrast target, ability to discriminate stripes, attention at distance | Each item scored 0 if <90 percentile, scored 1 if abnormal | 5–10 | Korean ver.: none | Free |
| Education: none | |||||||
| Global score ≥2: abnormal | |||||||
| PreViAs | CA 0–24 mo | Norm (298 children from Spain) | Questionnaires of 30 items, 4 domains | Mean scores of each domain | Korean ver.: none | Free | |
| : visual attention; visual communication; visual-motor coordination; visual processing | Cutoff points for each visual domain and each age group by 2 mo | Education: none | |||||
| SP1 | Infant SP1 | Norm (1,037 children without disability, 32 children with autism and 61 with ADHD from USA) | Sensory processing (auditory, visual, vestibular, touch, multisensory, oral sensory), | Sensory seeking, emotionally reactive, low endurance/tone, oral sensory sensitivity, inattention/distractibility, poor registration, sensory sensitivity, sedentary, fine motor/perceptual | 20–30 | Korean ver.: available | Questionnaire: $193 |
| 0–6 mo | Modulation (sensory processing related to endurance/tone, body position/movement, movement affection activity level, sensory input affecting emotional responses, visual input affecting emotional responses and activity), | Typical performance | Comprehensive manual | ||||
| Toddler SP1 | Behavioral and emotional responses (emotional/social responses, behavioral outcomes of sensory processing, items indicating thresholds for responses) | <-1 SD: possible difference | : included in questionnaire | No special equipment | |||
| 7–36 mo | <-2 SD: definite difference | ||||||
| SP1 3–10 yr | |||||||
| Adolescent/adult SP1 ≥11 yr | |||||||
| SP2 | Infant SP2 | Norm (1,791 from USA) | Sensory sections: auditory, visual, touch, movement, body position, oral | Seeking score: degree to which a child obtains sensory input | 5–20 | Korean ver.: none | Questionnaire: $292 |
| 0–6 mo | Behavioral sections: conduct, social emotional, attentional | Avoiding score: degree to which a child is bothered by sensory input | Comprehensive manual | ||||
| Toddler SP2 | Caregiver questionnaire for 5 Likert score (1–5) | Sensitivity: degree to which a child detects sensory input (notification of sensory input) | : included in questionnaire | No special equipment | |||
| 7–35 mo | Registration: degree to which a child missss sensory input | ||||||
| Child SP2 | Raw scores, percentile range, standardized scores | ||||||
| 3–14 yr 11 mo | -1 SD to +1 SD: normal | ||||||
| Short SP2 | <-1 SD: less than others | ||||||
| 3–14 yr 11 mo | <-2 SD: much less than others | ||||||
| School companion SP2 | >+1 SD: more than others | ||||||
| 3–14 yr 11 mo | >+2 SD: much more than others | ||||||
| SPM-P | 2–5 yr | Norm (651 typically developing children from USA) | Social participation, vision, hearing, touch, total sensory system/taste and smell, body awareness, balance and motion, planning and ideas | Typical range (T-score: 40–59) | 15–20 | Korean ver.: none | Paper and online kit $160 |
| Some problems range (T-score: 60–69) | Education: none | ||||||
| Definite dysfunction range (T-score: 70–80) | |||||||
| TSFI | 4–18 mo | Norm (196 infants as typically developing, 27 infants with delayed, 27 difficult temperament infants, USA) | 24 Items of 5 domains: tactile deep pressure, visual tactile integration, vestibular functions, ocular motor control, reactivity to vestibular stimulation | Item scoring for each domain, | 20 | Korean ver.: none | Test kit (US $199) |
| Total test score: overall score of sensory processing and reactivity | Comprehensive manual | Test kit provides most equipment | |||||
| Cut-off points to diagnose sensory integrative dysfunction | : included in test kit | ||||||
DDST-II, Denver Development Screening Test-II; K-DST, Korean-Developmental Screening Test; SD, standard deviation; K-ASQ, Korean-Ages and Stages Questionnaires; BSID-III, Bayley Scales of Infant Development-III (a) version IV is also available in English from 2019; same five domains but scoring is changed from dichotomous to polytomous(2,1,0) with decreased number of items to make 30% less time needed to complete the assessment); GMs, general movements; TIMP, Test of Infant Motor Performance; PMA, postmenstrual age; MAI, Movement Assessment of Infants; AIMS, Alberta Infant Motor Scale; CA, corrected age; HINE, Hammersmith Infant Neurologic Examination (b) HNNE, Hammersmith Neonatal Neurological Examination also available); CP, cerebral palsy; PDMS-II, Peabody Developmental Motor Scales-II; NSMDA, Neuro-sensory Motor Developmental Assessment; SELSI, Sequenced Language Scale for Infants; PRES, Preschool Receptive-Expressive Language Scale; P-FA, Paradise-Fluency Assessment; K-M-B CDI, Korean-MacArthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventories; PPVT-R, Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test-Revised; REVT, Receptive Expressive Vocabulary Test; PCAT, picture consonant articulation test; K-WPPSI-IV, Korean-Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence-IV (version V is also available from 2019); FSIQ, full scale intelligence quotient; VMI-6, Developmental Test of Visual-Motor Integration-6; GA, gestational age; PreViAs, Preverbal Visual AssessmentSP1, Sensory Profile 1; SP2, Sensory Profile 2; SPM-P, Sensory Processing Measure-Preschool; TSFI, Test of Sensory Functions in Infants.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download